标签:通过 pre 对象 sed icc 元素 概念 mic 是什么
实验目的
1. 理解类的继承和派生机制
2. 掌握派生类的定义和使用
3. 理解和掌握派生类成员的标识和访问中同名覆盖原则、二元作用域分辨符和虚基类的用法
4. 掌握派生类构造函数和析构函数的定义及调用次序
5. 理解运算符重载的目的,掌握运算符重载函数的编写方法
实验准备
1. 类的继承和派生
引入继承和派生机制的目的
基本概念:继承、派生、基类、直接基类、间接基类 、派生类
语法 派生类定义的语法格式(单重继承和多重继承)
派生类构造函数及其初始化列表书写形式 派生类成员的标识与访问 同名覆盖指的是什么?
二元作用域分辨符在什么情况下使用? 什么是虚基类?引入虚基类的目的是什么?如何使用?
类的继承和派生 vs. 类的组合
2. 运算符重载
运算符重载的目的
运算符重载的规则和限制
运算符重载函数的语法格式
运算符重载时,重载为成员函数,还是非成员函数(友元、普通函数),需要综合考量哪些因素?
实验结论
1.ElectricCar类
//重载<<时多打了",",已改正

#ifndef BATTERY_H #define BATTERY_H class Battery { public: Battery(int nb = 70); int showbatterysize(); void change(int n); private: int batterysize; }; #endif

#include"battery.h" #include<iostream> using namespace std; //构造函数 Battery::Battery(int nb/*=70*/) :batterysize(nb) {} //返回电池容量 int Battery::showbatterysize() { return batterysize; } void Battery::change(int n) { batterysize = n; }

#ifndef CAR_H #define CAR_H #include<string> #include<iostream> using namespace std; class Car { private: string maker; string model; int year; long odometer; public: Car(string n1 = "unknown", string n2 = "unknown", int n3 = 2000,long n4=0); void flashodo(long a); friend ostream & operator<<(ostream &out, const Car &c); }; #endif

#include"car.h" #include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; Car::Car(string n1/*="unknown"*/, string n2/*="unknown"*/, int n3/*=2000*/, long n4/*=0*/) :maker(n1), model(n2), year(n3), odometer(n4) {} void Car::flashodo(long no) { if (no < odometer) cout << "WARNING!" << endl; else odometer = no; } ostream & operator<<(ostream &out, const Car &c) { out << "(" << "maker:" << "," << c.maker << "," << endl << "," << "model:" << "," << c.model << "," << endl << "," << "year:" << "," << c.year << "," << endl << "," << "odometer:" << "," << c.odometer << ")"; return out; }

#ifndef ELECTRICCAR_H #define ELECTRICCAR_H #include<string> #include<iostream> using namespace std; #include"car.h" #include"battery.h" class ElectricCar :public Car { public: ElectricCar(string n1 = "unknown", string n2 = "unknown", int n3 = 2000, long n4 = 0, int nb = 70); friend ostream & operator<<(ostream &out, const ElectricCar &c); private: Battery battery; }; #endif

#include<string> #include<string> #include<iostream> #include"car.h" #include"battery.h" #include"electricCar.h" using namespace std; ElectricCar::ElectricCar(string n1/*="unknown"*/, string n2/*="unknown"*/, int n3/*=2000*/, long n4/*=0*/, int nb/*=70*/) :Car(n1, n2, n3, n4) { battery.change(nb); } ostream & operator<<(ostream &out, const ElectricCar &c) { Battery a = c.battery; out << "("<< (Car)c <<"," << endl << "," << "batterysize:" << "," << a.showbatterysize() << ")"; return out; }

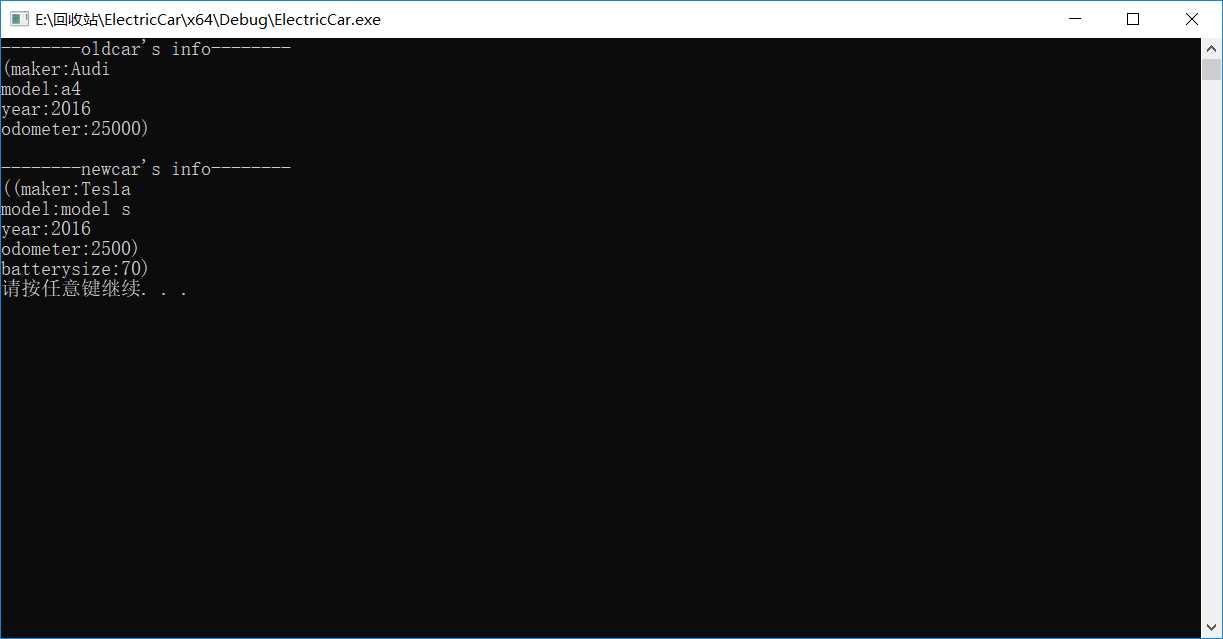
#include<string> #include<iostream> #include<cstdlib> using namespace std; #include "car.h" #include "electricCar.h" int main() { // 测试Car类 Car oldcar("Audi", "a4", 2016); cout << "--------oldcar‘s info--------" << endl; oldcar.flashodo(25000); cout << oldcar << endl; // 测试ElectricCar类 ElectricCar newcar("Tesla", "model s", 2016); newcar.flashodo(2500); cout << "\n--------newcar‘s info--------\n"; cout << newcar << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
运行截图:
2.arrayint类

#ifndef ARRAY_INT_H #define ARRAY_INT_H class ArrayInt{ public: ArrayInt(int n, int value=0); ~ArrayInt(); int &operator[](int a); void print(); private: int *p; int size; }; #endif

#include "arrayInt.h" #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> using std::cout; using std::endl; ArrayInt::ArrayInt(int n, int value): size(n) { p = new int[size]; if (p == nullptr) { cout << "fail to mallocate memory" << endl; exit(0); } for(int i=0; i<size; i++) p[i] = value; } ArrayInt::~ArrayInt() { delete[] p; } void ArrayInt::print() { for(int i=0; i<size; i++) cout << p[i] << " "; cout << endl; } int &ArrayInt::operator[](int a) { return p[a]; }

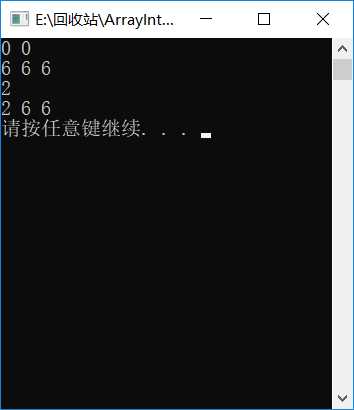
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include "arrayInt.h" int main() { // 定义动态整型数组对象a,包含2个元素,初始值为0 ArrayInt a(2); a.print(); // 定义动态整型数组对象b,包含3个元素,初始值为6 ArrayInt b(3, 6); b.print(); // 通过对象名和下标方式访问并修改对象元素 b[0] = 2; cout << b[0] << endl; b.print(); system("pause"); return 0; }
运行截图:
实验结论
1.在写EletricCar类时,出现了无法重载Car类的bug,后来重写了一遍Car类就解决了问题,不知道有大佬可以解释一下吗?
评论:
1.
2.
3.
标签:通过 pre 对象 sed icc 元素 概念 mic 是什么
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wyf-blogs/p/10891275.html