标签:最短路径 cti 题目 问题 struct ring path oid front
题目:
int maze[5][5] = {
0, 1, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 1, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
};
输入:
一个5 × 5的二维数组,表示一个迷宫。数据保证有唯一解。
输出:
左上角到右下角的最短路径,格式如样例所示。
样例:
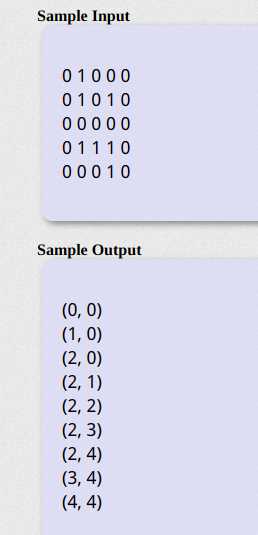
分析:BFS回溯,套路固定,定义结构体储存点和路径
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<sstream> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<cstdlib> 5 #include<string> 6 #include<cstring> 7 #include<algorithm> 8 #include<functional> 9 #include<iomanip> 10 #include<numeric> 11 #include<cmath> 12 #include<queue> 13 #include<vector> 14 #include<set> 15 #include<cctype> 16 #define PI acos(-1.0) 17 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 18 const int NINF = -INF - 1; 19 typedef long long ll; 20 using namespace std; 21 typedef pair<int, int> P; 22 int maze[5][5]; 23 int used[5][5]; 24 int dx[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1}; 25 struct node 26 { 27 int x, y; 28 int flag; 29 P path[30]; 30 }; 31 void bfs() 32 { 33 queue<node> q; 34 memset(used, 0, sizeof(used)); 35 node st; 36 st.x = 0, st.y = 0, st.flag = 0; 37 st.path[st.flag] = P(0, 0); 38 q.push(st); 39 used[st.x][st.y] = 1; 40 while (q.size()) 41 { 42 node temp = q.front(); 43 q.pop(); 44 if (temp.x == 4 && temp.y == 4) 45 { 46 for (int i = 0; i <= temp.flag; ++i) 47 cout << ‘(‘ << temp.path[i].first << ", " << temp.path[i].second << ‘)‘ << endl; 48 return; 49 } 50 for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) 51 { 52 node n = temp; 53 n.flag++; 54 n.x = temp.x + dx[i], n.y = temp.y + dy[i]; 55 if (n.x >= 0 && n.x < 5 && n.y >= 0 && n.y < 5 && !used[n.x][n.y] && maze[n.x][n.y] == 0) 56 { 57 used[n.x][n.y] = 1; 58 n.path[n.flag] = P(n.x, n.y); 59 q.push(n); 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 int main() 65 { 66 for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) 67 { 68 for (int j = 0; j < 5; ++j) 69 cin >> maze[i][j]; 70 } 71 bfs(); 72 return 0; 73 }
标签:最短路径 cti 题目 问题 struct ring path oid front
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/veasky/p/10989259.html