标签:当前日期 fst namespace 直接 alt 利用 pre 方法 字符
part 2
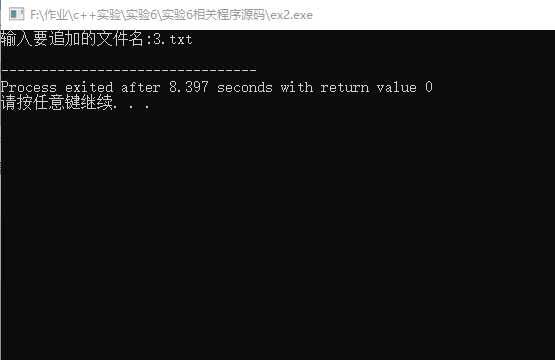
*以追加模式打开文件

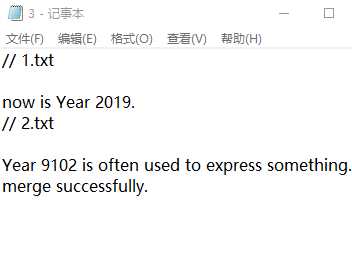
// 合并两个文件内容到一个新文件中。 // 文件名均从键盘输入 #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <string> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; int main() { string filename1, filename2, newfilename; cout << "输入要合并的两个文件名: " ; cin >> filename1 >> filename2; cout << "输入合并后新文件名: " ; cin >> newfilename; ofstream fout; // 输出文件流对象 ifstream fin; // 输入文件流对象 fin.open(filename1); // 将输入文件流对象fin与文件filename1建立关联 if(!fin.is_open()) { // 如果打开文件失败,则输出错误提示信息并退出 cerr << "fail to open file " << filename1 << endl; system("pause"); exit(0); } fout.open(newfilename); // 将输出文件流对象fout与文件newfilename建立关联 if(!fin.is_open()) { // 如果创建/打开文件失败,输出错误提示信息并退出 cerr << "fail to open file " << newfilename << endl; system("pause"); exit(0); } char ch; // 从文件输入流对象fin中获取字符,并将其插入到文件输出流对象fout中 while(fin.get(ch)) fout << ch; fin.close(); // 关闭文件输入流对象fin与文件filename1的关联 fout << endl; // 向文件输出流对象fout中插入换行 fin.open(filename2); // 将输入文件流对象fin与文件filename2建立关联 if(!fin.is_open()) { // 如果打开文件失败,则输出错误提示信息并退出 cerr << "fail to open file " << filename2 << endl; system("pause"); exit(0); } // 从文件输入流对象fin中获取字符,并将其插入到文件输出流对象fout中 while(fin.get(ch)) fout << ch; fin.close(); // 关闭文件输入流对象fin与文件filename2的关联 fout.close(); // 关闭文件输出流对象fout与文件newfilename的关联 system("pause"); return 0; } // 说明: // 这个简单示例中,合并两个文件的具体方法,是逐个读取文件中的字符直到文件末尾,并写入到新文件中 // 还可以一次读取一行 // 或者,直接利用标准模板库的成员函数,一次性将整个文件内容读取至缓冲区 // 等过了期末考,时间宽松一些的时候可以学习体验更多标准模板库的内容,对后续专业课的学习(如数据结构、算法、操作系统等)也会有帮助

#include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<string> #include<cstdlib> using namespace std; int main(){ string filename; cout<<"输入要追加的文件名:"; cin>>filename; ofstream fout; fout.open(filename,ios_base::app); fout<<endl; fout<<"merge successfully."; fout.close(); return 0; }
part 3
1
选做:不会出现重复的(达成)

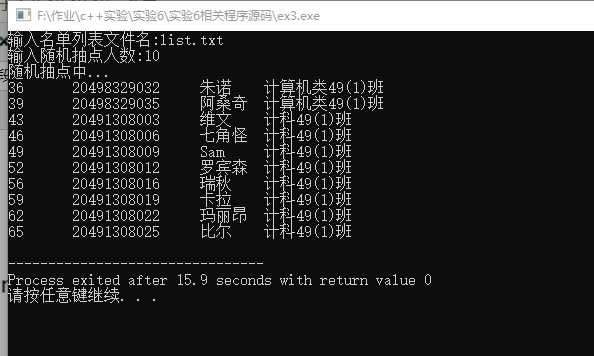
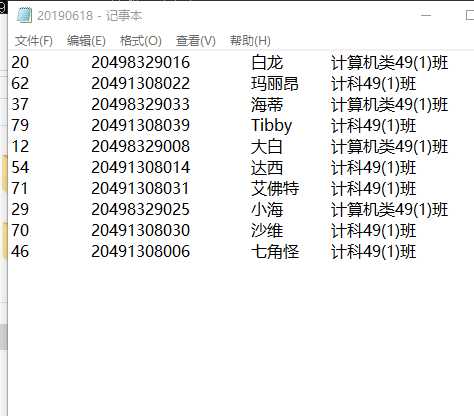
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include<fstream> #include<ctime> #include<cstdlib> #include "utils.h" using namespace std; int main() { cout<<"输入名单列表文件名:"; string filename1,filename2; cin>>filename1; filename2=getCurrentDate(); cout<<"输入随机抽点人数:"; int n; cin>>n; cout<<"随机抽点中..."<<endl; ofstream fout; fout.open(filename2); ifstream fin; fin.open(filename1); string k[83]; string s; for(int i=0;i<83;i++) getline(fin,k[i]); fin.close(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { ifstream fin; fin.open(filename1); int a; do{ srand(time(NULL)); int w=rand(); a=rand()%83+1; }while(k[a]=="0"); fout<<k[a]; cout<<k[a]<<endl; fout<<endl; k[a]="0"; fin.close(); } fout.close(); return 0; }

//这个头文件里包含了可用工具函数的声明 #include <string> using std::string; // 函数声明 // 返回当前系统时间,格式诸如20190611 string getCurrentDate();

#include "utils.h" #include <ctime> using std::string; const int SIZE = 20; // 函数功能描述:返回当前系统日期 // 参数描述:无参数 // 返回值描述:以string类型返回系统当前日期,格式诸如20190611 string getCurrentDate() { time_t now = time(0); // 获取当前系统日历时间 struct tm *local_time = localtime(&now); // 把系统日历时间转换为当地时间 char date[SIZE]; strftime(date, SIZE, "%Y%m%d", local_time); return (string(date)); }
part 3
2

#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <fstream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; int main(){ string filename; ifstream fin; ofstream fout; int num=0,num1=0,line=0; cout<<"输入要统计的英文文本文件名:"; cin>>filename; fin.open(filename); if(!fin.is_open()){ cout<<"fail to open"<<endl; exit(0); } string a; string b[10000]; int i,j; while (getline(fin,a)){ b[line]=a; line++; j=a.length(); for(i=0;i<j;i++){ if(a[i]==‘ ‘) num1++; } num1++; } for(i=0;i<line;i++){ j=b[i].length(); num+=j; } fin.close(); cout<<"字符数:"<<num<<endl; cout<<"单词数:"<<num1<<endl; cout<<"行数:"<<line<<endl; return 0; }
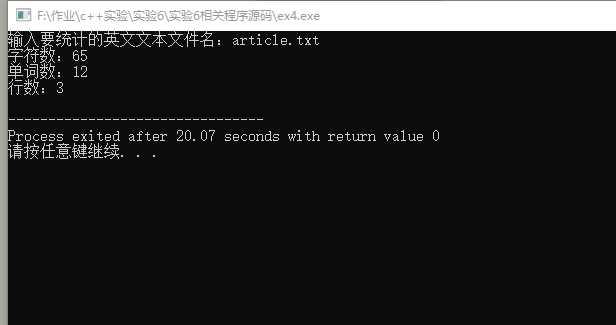
实验总结
1、定义string数组:string x[n];或string x[]=new string[n];
2、getline(fin,x[i])可以,string s;x[i]=getline(fin,s);不行,会有ambiguou的错误;
3、srand(time(NULL));a=rand()%xxx;随机出的数是递增的,两句中加一句int b=rand();可以每个数都随机到,虽然我不晓得为啥子
标签:当前日期 fst namespace 直接 alt 利用 pre 方法 字符
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/99563220-fhy/p/11044559.html