标签:顺序 oid 实验 打印 class 信息 tput printf 完整
Part1:
实验2:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 10
typedef struct student {
int num;
char name[20];
int score;
}STU;
int main() {
STU st, stmax, stmin;
int i;
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("file1.dat", "r");
if( !fp ) {
printf("fail to open file1.dat\n");
exit(0);
}
stmax.score = 0;
stmin.score = 100;
while(!feof(fp)) {
fscanf(fp, "%d %s %d", &st.num, st.name, &st.score);
if(st.score > stmax.score)
stmax = st;
else if(st.score < stmin.score)
stmin = st;
}
fclose(fp);
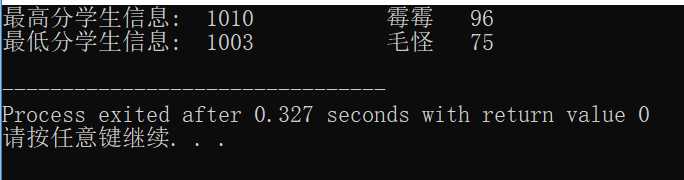
printf("最高分学生信息: %5d%15s%5d\n", stmax.num, stmax.name, stmax.score);
printf("最低分学生信息: %5d%15s%5d\n", stmin.num, stmin.name, stmin.score);
return 0;
}
实验3:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 10
typedef struct student {
int num;
char name[20];
int score;
}STU;
void sort(STU *pst, int n);
int main() {
FILE *fin, *fout;
STU st[N];
int i;
fin = fopen("file1.dat", "r");
if( !fin ) {
printf("fail to open file1.dat\n");
exit(0);
}
for(i=0; i<N; i++)
fscanf(fin, "%d %s %d", &st[i].num, st[i].name, &st[i].score);
fclose(fin);
sort(st, N);
fout = fopen("file3.dat", "w");
if( !fout ) {
printf("fail to open file1.dat\n");
exit(0);
}
for(i=0; i<N; i++) {
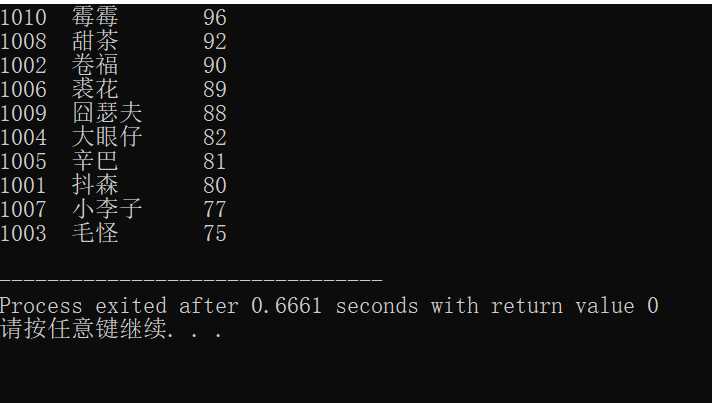
printf("%-6d%-10s%3d\n", st[i].num, st[i].name, st[i].score);
fprintf(fout, "%-6d%-10s%3d\n", st[i].num, st[i].name, st[i].score);
}
fclose(fout);
return 0;
}
void sort(STU *pst, int n) {
STU *pi, *pj, t;
for(pi = pst; pi < pst+n-1; pi++)
for(pj = pi+1; pj < pst+n; pj++)
if(pi->score < pj->score) {
t = *pi;
*pi = *pj;
*pj = t;
}
}
实验4:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 10
typedef struct student {
int num;
char name[20];
int score;
}STU;
void sort(STU *pst, int n);
int main() {
FILE *fin, *fout;
STU st[N];
int i;
fin = fopen("file1.dat", "r");
if( !fin ) {
printf("fail to open file1.dat\n");
exit(0);
}
for(i=0; i<N; i++)
fscanf(fin, "%d %s %d", &st[i].num, st[i].name, &st[i].score);
fclose(fin);
sort(st, N);
fout = fopen("file4.dat", "wb");
if( !fout ) {
printf("fail to open file1.dat\n");
exit(0);
}
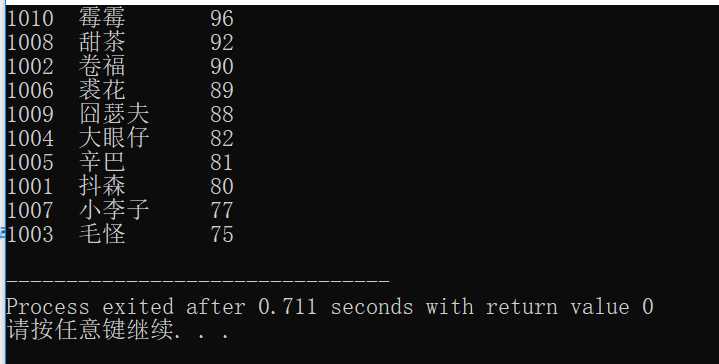
for(i=0; i<N; i++)
printf("%-6d%-10s%3d\n", st[i].num, st[i].name, st[i].score);
fwrite(st, sizeof(STU), N, fout);
fclose(fout);
return 0;
}
void sort(STU *pst, int n) {
STU *pi, *pj, t;
for(pi = pst; pi < pst+n-1; pi++)
for(pj = pi+1; pj < pst+n; pj++)
if(pi->score < pj->score) {
t = *pi;
*pi = *pj;
*pj = t;
}
}
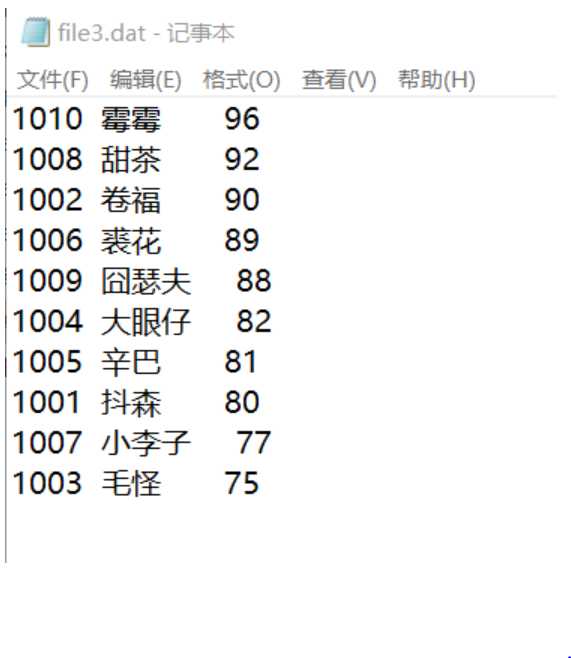

文本文件是直接可读可看的 是一种顺序文件,而二进制文件是一种人看不懂,供计算机读看的,需要进行转化才可以。
Part2:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
const int N = 10;
typedef struct student {
long int id;
char name[20];
float objective;
float subjective;
float sum;
char level[10];
}STU;
void input(STU s[], int n);
void output(STU s[], int n);
void process(STU s[], int n);
int main() {
STU stu[N];
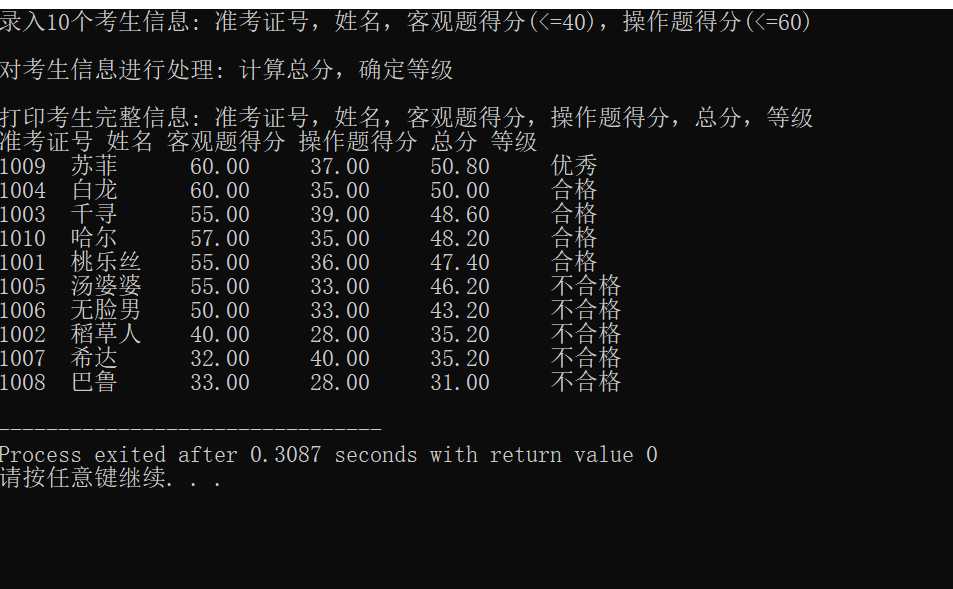
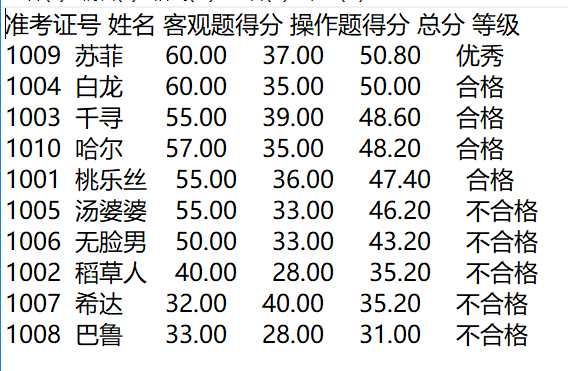
printf("录入%d个考生信息: 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分(<=40),操作题得分(<=60)\n", N);
input(stu, N);
printf("\n对考生信息进行处理: 计算总分,确定等级\n");
process(stu, N);
printf("\n打印考生完整信息: 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分,总分,等级\n");
output(stu, N);
return 0;
}
void input(STU s[], int n) {
FILE *fin;
int i;
fin = fopen("examinee.txt","r") ;
if( !fin ) {
printf("fail to open file\n");
exit(0);
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
fscanf(fin,"%ld %s %f %f", &s[i].id,s[i].name,&s[i].objective,&s[i].subjective);
if( fscanf(fin,"%ld %s %f %f", &s[i].id,s[i].name,&s[i].objective,&s[i].subjective)==0)
{
printf("读取错误!请重试!");
}
fclose(fin);
}
标签:顺序 oid 实验 打印 class 信息 tput printf 完整
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yesung/p/11080072.html