标签:知识 handle 欺骗 策略 style roc RoCE 百度百科 ble
http://www.aboutyun.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=16563&highlight=neutron%2B%2B%CF%B5%C1%D0
问题导读:
1.OVS bridge有几种模式?
2.Neutron 中的流表是怎样实现的?![]()
1. 基础知识
1.1 OpenFlow 结构、流表和数据包处理
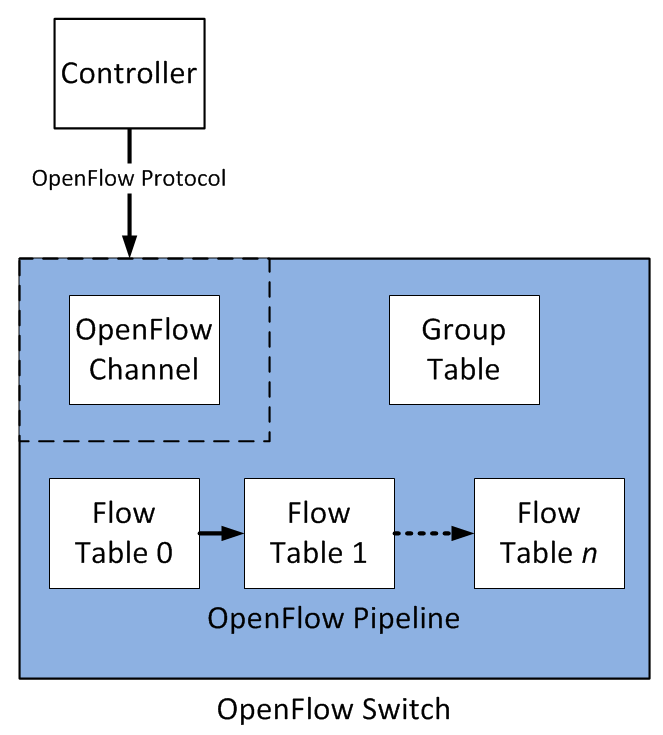
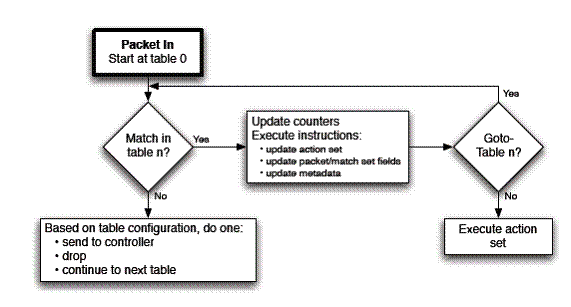
1.2 ARP Proxy
举个例子:主机A,IP地址是192.168.0.11/24;主机B,IP地址是192.168.1.22/24。主机A和主机B通过路由器R相连接,并且路由器R启用了Proxy ARP,并配置有路由。网络拓扑如下:
eth0 eth0 eth1 eth0
A------------------------Router R----------------------B
192.168.0.11/24 192.168.0.0/24 eth0 192.168.1.22/24
192.168.1.0/24 eth1
在主机A上执行:ping 192.168.1.22,主机 A 不知道主机 B 的 MAC 地址是多少,首先要发送 ARP 查询报文,路由器 R 接收到主机 A 发出的 ARP 查询报文,并代替主机 B 作出应答,应答 ARP 报文中填入的就是路由器 R 的MAC地址。这样,主机A就会认为路由器R的地址是192.168.1.22。以后所有发往192.168.1.22的报文都发到路由器R,路由器R再根据已配置好的路由表将报文转发给主机B。
这样做的好处就是,主机A上不需要设置任何默认网关或路由策略,不管路由器R的IP地址怎么变化,主机A都能通过路由器B到达主机B,也就是实现了所谓的透明代理。相反,若主机A上设置有默认网关或路由策略时,当主机A向192.168.1.22发送报文,首先要查找路由表,而主机A所在的网段是192.168.0.0/24,主机B所在网段是192.168.1.0/24,主机A只能通过默认网关将报文发送出去,这样代理ARP也就失去了作用。
优点:
2. 不使用 ARP Responder 和 DVR 时 br-tun 中的流表(flow tables)
2.1 流表分析
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
1(patch-int): addr:a6:d4:dd:37:00:522(vxlan-0a000127): addr:36:ec:de:b4:b9:6b {in_key=flow, local_ip="10.0.1.31", out_key=flow, remote_ip="10.0.1.39"} 计算节点23(vxlan-0a000115): addr:4a:c8:21:3c:3f:f1 {in_key=flow, local_ip="10.0.1.31", out_key=flow, remote_ip="10.0.1.21"} 网络节点4(gre-0a000115): addr:4a:8b:0f:9d:59:52 {in_key=flow, local_ip="10.0.1.31", out_key=flow, remote_ip="10.0.1.21"} 网络节点5(gre-0a000127): addr:aa:58:6d:0a:f7:6a {in_key=flow, local_ip="10.0.1.31", out_key=flow, remote_ip="10.0.1.39"} 计算节点2 |
| 表号 | 用途 | 例子 |
| 0 |
table=0, priority=1,in_port=3 actions=resubmit(,4) //从网络节点来的,转 4,结果被丢弃
table=0, priority=1,in_port=4 actions=resubmit(,3) //从网络节点来的,转 3
table=0, priority=1,in_port=5 actions=resubmit(,3) //从计算节点来的,转 3 table=0, priority=1,in_port=2 actions=resubmit(,4) //从计算节点来的,转 4,结果被丢弃
table=0, priority=1,in_port=1 actions=resubmit(,2) //从虚机来的,转 2
table=0, priority=0 actions=drop //其余的丢弃 |
|
| DVR_PROCESS = 1 | handle packets coming from patch_int unicasts go to table UCAST_TO_TUN where remote addresses are learnt | 用于 DVR |
| PATCH_LV_TO_TUN = 2 |
table=2, priority=0,dl_dst=00:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00
actions=resubmit(,20) //单播包,转 20
table=2, priority=0,dl_dst=01:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00 actions=resubmit(,22)
//组播(包括广播)包,转 22
|
|
| GRE_TUN_TO_LV = 3 |
table=3, priority=1,tun_id=0x4 actions=mod_vlan_vid:1,resubmit(,10) //将 tun_id 为 4 的,
修改 vlan id 为1,转 10 处理
table=3, priority=0 actions=drop //其余的丢弃 |
|
| VXLAN_TUN_TO_LV = 4 | table=4, priority=0 actions=drop //丢弃 | |
| DVR_NOT_LEARN = 9 | 用于 DVR | |
| LEARN_FROM_TUN = 10 | 学习table |
table=10,priority=1 actions=learn(table=20,hard_timeout=300,priority=1,NXM_OF_VLAN_TCI[0..11],
NXM_OF_ETH_DST[]
=NXM_OF_ETH_SRC[],load:0->NXM_OF_VLAN_TCI[],load:NXM_NX_TUN_ID[]->NXM_NX_TUN_ID[],output:NXM_OF_IN_PORT[]),output:1
|
| UCAST_TO_TUN = 20 | 外出的单播会被 table 20 处理,table 2 |
//学习到的规则
table=20, priority=2,dl_vlan=1,dl_dst=fa:16:3e:7e:ab:cc actions=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:0x3e9,output:5 //如果vlan 为1,而且目的MAC地址等于 fa:16:3e:7e:ab:cc,设置 tunnel id,从端口 5 发出
table=20,priority=0 actions=resubmit(,22) //直接转 22
|
| ARP_RESPONDER = 21 | ARP table | 当使用 arp_responder 和 l2population 时候用到 |
| FLOOD_TO_TUN = 22 | Flood table |
table=22,dl_vlan=1 actions=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:0x4,output:5,output:4
//对于 dl_vlan 为1的,设置 tunnel id 为 4,从端口4 和 5 转出
table=22,priority=0 actions=drop |
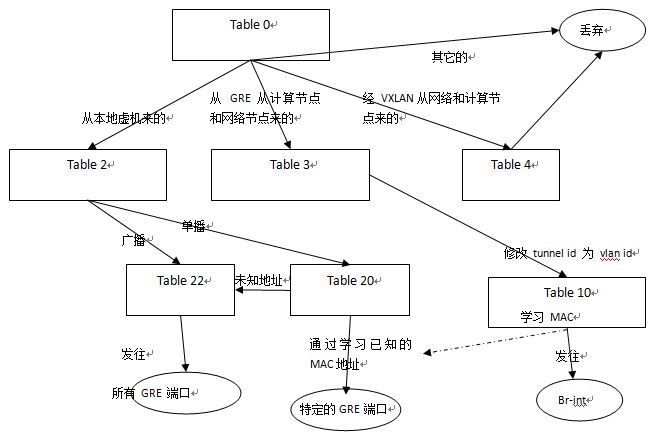
2.2 MAC 地址学习
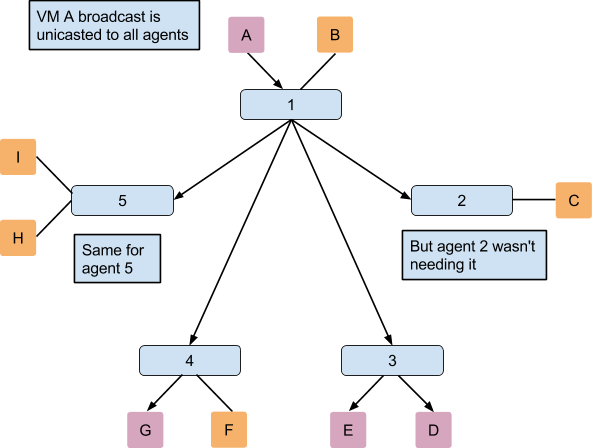
相关内容:
Neutron系列 : Neutron OVS OpenFlow 流表 和 L2 Population(7)
标签:知识 handle 欺骗 策略 style roc RoCE 百度百科 ble
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/liuhongru/p/11121134.html