标签:返回 根据 创建 ssi put add array gdi alt
当执行一个 TensorFlow 函数的时候,并不会马上执行运算,而是把运算存储到一个称为“图”(graph)的数据结构里面。
图存储的各种运算,只有在会话(session)里执行图,才会真正地执行。
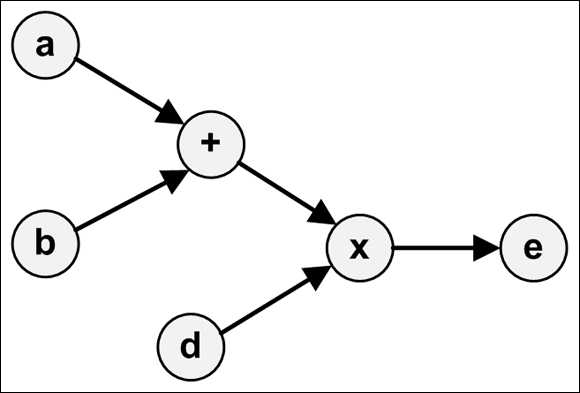
对于
1 c = tf.add(a, b) 2 e = tf.multiply(c, d)
它们所形成的图就是:
TensorFlow 用 Graph 这个容器数据结构来表示图。图的方法可以分为两类:
有这么一些访问图数据的方法:
示例代码:
1 # 访问图中的数据 2 x1 = tf.constant(2, name=‘x1‘) 3 x2 = tf.constant(3, name=‘x2‘) 4 my_sum = x1 + x2 5 print(tf.get_default_graph().get_operations()) 6 print(tf.get_default_graph().get_tensor_by_name(‘x1:0‘))
[<tf.Operation ‘x1‘ type=Const>, <tf.Operation ‘x2‘ type=Const>, <tf.Operation ‘add‘ type=Add>] Tensor("x1:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
其中 ‘x1:0‘ 表示的是 ‘name:index‘,0 表示的是这个张量的索引。
GraphDef 是序列化之后的 Graph。
GraphDef 以一种特殊的格式(protocol buffer 或 protobuf)存储图中的数据。protobuf 可以是二进制格式或者文本格式(长得像 JSON)。
在 GraphDef 中,所有的张量和运算都用节点来表示。每个节点都有 name/op/attr 这些字段。它的样子就像:
node {
name: { ... }
op: { ... }
attr { ... }
attr { ... }
...
versions { ... }
}
再通过一段代码来熟悉,as_graph_def 可以访问 TensorFlow 应用中的图:
1 a = tf.constant(666) 2 b = tf.constant(777) 3 sum1 = a + b 4 print(tf.get_default_graph().as_graph_def())
node { name: "Const" op: "Const" attr { key: "dtype" value { type: DT_INT32 } } attr { key: "value" value { tensor { dtype: DT_INT32 tensor_shape { } int_val: 666 } } } } node { name: "Const_1" op: "Const" attr { key: "dtype" value { type: DT_INT32 } } attr { key: "value" value { tensor { dtype: DT_INT32 tensor_shape { } int_val: 777 } } } } node { name: "add" op: "Add" input: "Const" input: "Const_1" attr { key: "T" value { type: DT_INT32 } } } versions { producer: 38 }
tf.train 中的 write_graph 可以把图输出到文件。
函数签名如下:
write_graph(graph/graph_def, logdir, name, as_text=True)
代码示例:
print(tf.train.write_graph(tf.get_default_graph(), os.getcwd(), ‘graph.dat‘, as_text=True))
此时会输出:
/your/path/graph.dat
即新生成了这个文件。
在 TensorFlow 里,都是先构建好 Graph,然后再在会话(session)中执行。
会话必须显式地创建,通过 tf.Session,它有 3 个参数:
一般我们使用默认参数,那就是:
1 with tf.Session() as sess: 2 pass
session 最重要的方法就是 run(),它接收 4 个方法:
如果 fetches 是一个张量,run 会返回一个和张量等值的 ndarray。
1 t = tf.constant([6, 66, 666]) 2 with tf.Session() as sess: 3 res = sess.run(t) 4 print(res)
[ 6 66 666]
如果 fetches 是一个运算,run 会返回一个运算之后的 ndarray 值。
1 t1 = tf.constant(6) 2 t2 = tf.constant(66) 3 my_multiply = t1 * t2 4 5 with tf.Session() as sess: 6 res = sess.run(my_multiply) 7 print(res)
396
如果 fetches 是元素的集合,run 也会返回一个相应的集合。
1 t1 = tf.constant(6) 2 t2 = tf.constant(66) 3 4 with tf.Session() as sess: 5 res1, res2 = sess.run([t1, t2]) 6 print(res1) 7 print(res2)
6 66
TensorFlow 的日志是通过 tf.logging 实现的。示例代码:
1 import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf 2 3 tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.INFO) 4 t = tf.constant(6) 5 6 with tf.Session() as sess: 7 res = sess.run(t) 8 tf.logging.info(‘Output: %f‘, res)
I0713 18:06:02.146098 140734845322688 <ipython-input-22-3ef84fc83efc>:8] Output: 6.000000
标签:返回 根据 创建 ssi put add array gdi alt
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/noluye/p/11150657.html