标签:pil 复杂 func block targe 算法 tle 表示 second
题意:给一棵树每个点有权值,树的权值定义为所有节点的异或和,依次询问树里有多少子树的权值是k, (0 <= k < m)
先考虑朴素算法,用dp[i][j]表示i这个点异或为j的子树有多少,每加入一颗t的子树v就通过枚举t的树权值和v的树权值,用Om²的复杂度更新dp,那么总的时间复杂度就是nm²

#include <map> #include <set> #include <ctime> #include <cmath> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <bitset> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <sstream> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <functional> using namespace std; #define For(i, x, y) for(int i=x;i<=y;i++) #define _For(i, x, y) for(int i=x;i>=y;i--) #define Mem(f, x) memset(f,x,sizeof(f)) #define Sca(x) scanf("%d", &x) #define Sca2(x,y) scanf("%d%d",&x,&y) #define Sca3(x,y,z) scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z) #define Scl(x) scanf("%lld",&x) #define Pri(x) printf("%d\n", x) #define Prl(x) printf("%lld\n",x) #define CLR(u) for(int i=0;i<=N;i++)u[i].clear(); #define LL long long #define ULL unsigned long long #define mp make_pair #define PII pair<int,int> #define PIL pair<int,long long> #define PLL pair<long long,long long> #define pb push_back #define fi first #define se second typedef vector<int> VI; int read(){int x = 0,f = 1;char c = getchar();while (c<‘0‘ || c>‘9‘){if (c == ‘-‘) f = -1;c = getchar();} while (c >= ‘0‘&&c <= ‘9‘){x = x * 10 + c - ‘0‘;c = getchar();}return x*f;} const double eps = 1e-9; const int maxn = 1010; const int maxm = 1200; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1e9 + 7; int N,M,K; struct Edge{ int to,next; }edge[maxn << 2]; int head[maxn],tot; void init(){ for(int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++) head[i] = -1; tot = 0; } void add(int u,int v){ edge[tot].to = v; edge[tot].next = head[u]; head[u] = tot++; } int val[maxn]; int dp[maxn][maxm],dp2[maxn][maxm],ans[maxm]; void dfs(int t,int la){ dp[t][val[t]] = 1; for(int i = head[t]; ~i ; i = edge[i].next){ int v = edge[i].to; if(v == la) continue; dfs(v,t); for(int j = 0 ; j < M ; j ++){ for(int k = 0 ; k < M ; k ++){ dp2[t][j ^ k] += dp[t][j] * dp[v][k]; } } for(int j = 0 ; j < M ; j ++){ dp[t][j] += dp2[t][j]; dp2[t][j] = 0; } } for(int i = 0 ; i < M ; i ++) ans[i] += dp[t][i]; } int main(){ int T; Sca(T); while(T--){ Sca2(N,M); init(); for(int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++){ for(int j = 0 ; j <= M ; j ++) dp[i][j] = dp2[i][j] = 0; } for(int i = 0 ; i < M; i ++) ans[i] = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= N ; i ++) Sca(val[i]); for(int i = 1; i <= N - 1; i ++){ int u,v; Sca2(u,v); add(u,v); add(v,u); } dfs(1,-1); for(int i = 0 ; i < M; i ++){ printf("%d ",ans[i]); } puts(""); } return 0; }
然后我们考虑去优化这层m²,发现这事实上是一个形如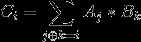 的逻辑运算卷积,可以上FWT优化为nmlogm,就可以了
的逻辑运算卷积,可以上FWT优化为nmlogm,就可以了
这题的正解应该是树分治,回头补图论的时候来把树分治代码补上,FWT像是卡常卡过去的,交GCC能过交C++就TLE
#include <map> #include <set> #include <ctime> #include <cmath> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <bitset> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <sstream> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <functional> using namespace std; #define For(i, x, y) for(int i=x;i<=y;i++) #define _For(i, x, y) for(int i=x;i>=y;i--) #define Mem(f, x) memset(f,x,sizeof(f)) #define Sca(x) scanf("%d", &x) #define Sca2(x,y) scanf("%d%d",&x,&y) #define Sca3(x,y,z) scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z) #define Scl(x) scanf("%lld",&x) #define Pri(x) printf("%d\n", x) #define Prl(x) printf("%lld\n",x) #define CLR(u) for(int i=0;i<=N;i++)u[i].clear(); #define LL long long #define ULL unsigned long long #define mp make_pair #define PII pair<int,int> #define PIL pair<int,long long> #define PLL pair<long long,long long> #define pb push_back #define fi first #define se second typedef vector<int> VI; int read(){int x = 0,f = 1;char c = getchar();while (c<‘0‘ || c>‘9‘){if (c == ‘-‘) f = -1;c = getchar();} while (c >= ‘0‘&&c <= ‘9‘){x = x * 10 + c - ‘0‘;c = getchar();}return x*f;} const double eps = 1e-9; const int maxn = 1010; const int maxm = 1200; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const LL mod = 1e9 + 7; LL inv2 = mod + 1 >> 1; int N,M,K; struct Edge{ int to,next; }edge[maxn << 2]; int head[maxn],tot; void init(){ for(int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++) head[i] = -1; tot = 0; } void add(int u,int v){ edge[tot].to = v; edge[tot].next = head[u]; head[u] = tot++; } int val[maxn]; LL dp[maxn][maxm],tmp[maxm],ans[maxm]; inline LL add(LL a,LL b){ return ((a + b) % mod + mod) % mod; } inline LL mul(LL a,LL b){ return (a % mod * b % mod + mod) % mod; } void FWT(int limit,LL *a,int op){ for(int i = 1; i < limit; i <<= 1){ for(int p = i << 1,j = 0; j < limit ; j += p){ for(int k = 0 ; k < i; k ++){ LL x = a[j + k],y = a[i + j + k]; a[j + k] = add(x,y); a[i + j + k] = add(x,-y); if(op == -1) a[j + k] = mul(a[j + k],inv2),a[i + j + k] = mul(a[i + j + k],inv2); } } } } void dfs(int t,int la){ dp[t][val[t]] = 1; for(int i = head[t]; ~i ; i = edge[i].next){ int v = edge[i].to; if(v == la) continue; dfs(v,t); for(int j = 0 ; j < M; j ++) tmp[j] = dp[t][j]; FWT(M,tmp,1); FWT(M,dp[v],1); for(int j = 0 ; j < M ; j ++) tmp[j] = mul(tmp[j],dp[v][j]); FWT(M,tmp,-1); for(int j = 0 ; j < M ; j ++) dp[t][j] = add(tmp[j],dp[t][j]); } for(int i = 0 ; i < M ; i ++) ans[i] = add(ans[i],dp[t][i]); } int main(){ int T; Sca(T); while(T--){ Sca2(N,M); init(); for(int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++){ for(int j = 0 ; j <= M ; j ++) dp[i][j] = 0; } for(int i = 0; i < M; i ++) ans[i] = tmp[i] = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= N ; i ++) val[i] = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= N - 1; i ++){ int u,v; u = read(); v = read(); add(u,v); add(v,u); } dfs(1,-1); for(int i = 0 ; i < M; i ++) printf("%d%c",ans[i],i == M - 1?‘\n‘:‘ ‘); } return 0; }
标签:pil 复杂 func block targe 算法 tle 表示 second
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Hugh-Locke/p/11210691.html