标签:style 搜索 com alt 遍历 lin ret -- 节点
题目简介:这道题就是求割点的板子题。我们使用tarjan算法。
算法分析:使用数组dfn与low来分别表示一个点在tarjan算法的搜索中被搜索到的时间以及它能够达到的拥有最小dfn的点的dfn值。
一个点是割点有两种情况。1.(当它不是tarjan开始节点,意味着还有dfn更小的点)它的子孙最小只能访问到它,那么当它不在的时候就访问不到其他dfn更小的点了,原图被切断。
2.当它是tarjan开始节点,且有两个及以上只能与它相连的点(因为如果第一次遍历都遍历完了都还是没有遍历到它,就证明这个图是一个以这个点为根可以看做一根树的无向图,断了则会分裂成两个互不相交的树)以与它相连(若只有一个则只断了一个最边缘,断了也没关系的点)
算法流程: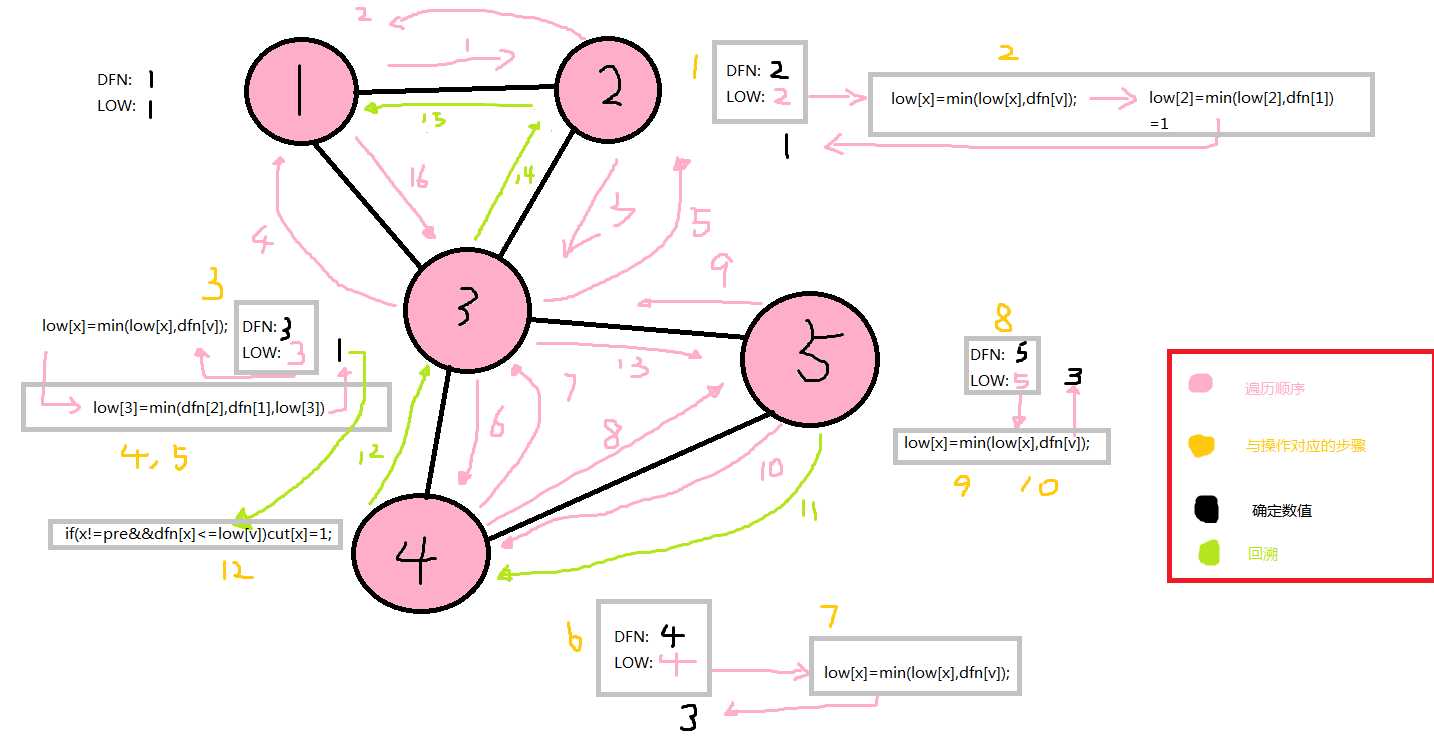
代码
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int read(){ int res=0,f=1; char ch=getchar(); while(ch<‘0‘||ch>‘9‘){ if(ch==‘-‘)f=-1; ch=getchar(); } while(ch>=‘0‘&&ch<=‘9‘){ res=res*10+(ch-‘0‘); ch=getchar(); } return res*f; } int head[500001],nextt[5000005],to[5000005],dfn[5000005],low[5000005]; int n,m,tot,dt,cut[5000001],ans,anss[5000001]; inline void add(int u,int v){ tot++; to[tot]=v; nextt[tot]=head[u]; head[u]=tot; } void tarjan(int x,int pre){ dt++;dfn[x]=dt;low[x]=dt; int c=0; for(int i=head[x];i;i=nextt[i]){ int v=to[i]; if(!dfn[v]){ tarjan(v,x); low[x]=min(low[x],low[v]); if(x!=pre&&dfn[x]<=low[v])cut[x]=1; if(x==pre)c++; } else low[x]=min(low[x],dfn[v]); } if(c>=2&&x==pre)cut[x]=1; } int main(){ n=read();m=read(); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ int u,v; u=read();v=read(); add(u,v);add(v,u); } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)if(!dfn[i])tarjan(i,i); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(cut[i])ans++; } cout<<ans<<endl; for(int i=1;i<n,ans;i++){ if(cut[i]){ ans--; printf("%d ",i); } } return 0; }
标签:style 搜索 com alt 遍历 lin ret -- 节点
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/clockwhite/p/11217249.html