标签:生成 contains dha print exception tin ace set 效率
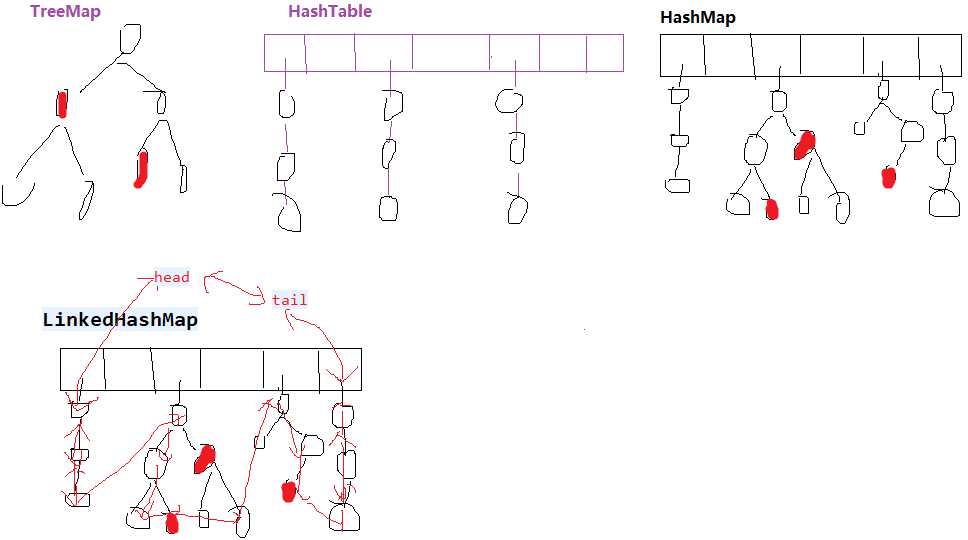
LinkedHashMap底层存储结构与HashMap一样,不同的是LinkedHashMap增加了一个双向链表的头节点,插入的数据除了插入HashMap,还会插入链表中,因而可以保存插入节点的顺序
LinkedHashMap的节点在HashMap节点的基础上增加了前后节点的引用
LinkedHashMap相比HashMap在查找值和删除值时效率要高
LinkedHashMap还可以设置按插入顺序排序或是按访问顺序排序,默认是按插入顺序排序
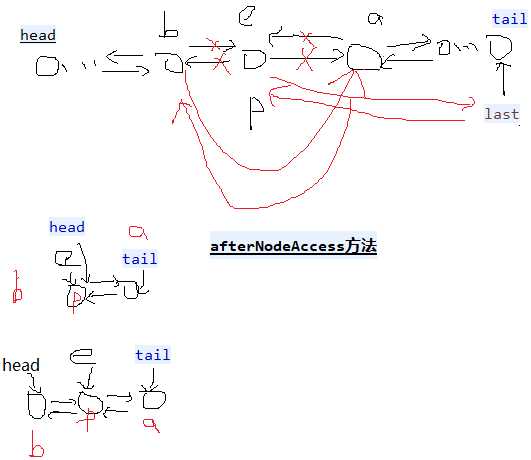
LinkedHashMap没有put方法,而是覆写了afterNodeAccess方法和afterNodeInsertion方法。当插入的数据已经存在时,会调用afterNodeAccess方法看是否需要将数据插入到链表末尾;当插入的数据是新数据时,会通过afterNodeInsertion方法来根据设置删除近期使用最少的节点
LinkedHashMap可以用来实现LRU算法。首先需要用可以设置accessOrder的构造函数设置accessOrder为true,也就是按照节点访问顺序排序;
而LinkedHashMap还拥有HashMap一样的结构,原因在于其继承自HashMap,因此HashMap中用于存储元素的table也被继承过来,于是乎元素的存储也具备和HashMap一样的规则,所有元素存储在table中,table下的每个索引在原HashMap的结构下也是一个单向链表,同时每个元素中额外增加的before和after引用将table中的元素互连起来。
public class testLinkedHashMap1 { @SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" }) public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedHashMap1<Integer,String> hh = new LinkedHashMap1<Integer,String>(); //链表添加 hh.put(0, "0");//放到LinkedHashMap1的table[0]中,此时是链表(节点有next没有after,before) hh.put(16, "16"); // hh.remove(4);//链表删除 // hh.put(4, "4"); hh.put(32, "32"); hh.put(48, "48");//0位置转成红黑树 hh.put(54, "54"); hh.put(60, "60"); hh.put(76, "76"); hh.put(1, "1");//1位置链表添加 hh.put(2, "2"); hh.put(3, "3"); hh.get(1); Set s = hh.keySet();//[0, 16, 32, 48, 54, 60, 76, 1, 2, 3] Iterator i = s.iterator(); if(i.hasNext()) System.out.println(i.next()); // i.remove(); if(i.hasNext()) System.out.println(i.next()); } }
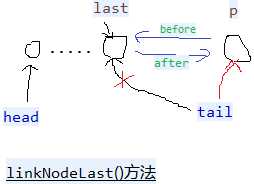
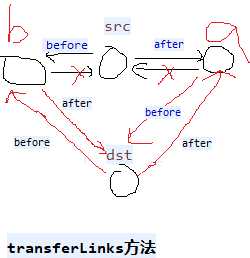
//extends HashMap1,table也被继承过来,数组+链表+红黑树。 public class LinkedHashMap1<K, V> extends HashMap1<K, V> implements Map1<K, V> { private static final long serialVersionUID = 3801124242820219131L; transient LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> head;// 双向链表的头节点和尾节点 transient LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> tail; final boolean accessOrder;// true,使用节点之后就把节点放到最末尾。false就不放。用于删除第一个最不常用的元素。 private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> p) {// 链表末尾添加,有before,after LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> last = tail;//保留原来的tail tail = p;//修改tail if (last == null)// tail=null head = p;// tail = head = p else { p.before = last; last.after = p; } } // dst替换src private void transferLinks(LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> src, LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> dst) { LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> b = dst.before = src.before; LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> a = dst.after = src.after; if (b == null)// 替换的src是第一个节点 head = dst; else b.after = dst; if (a == null)// 替换的src是最后一个节点 tail = dst; else a.before = dst; } public void reinitialize() { super.reinitialize();// table = null; entrySet = null; keySet = null; values = null; head = tail = null; } //生成一个节点(链表中的节点,不是红黑树中的节点,有hash, key, value, next没有before,after) public Node<K, V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> e) {// LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> p = new LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V>(hash, key, value, e); linkNodeLast(p);// 生成新的节点并插入到尾部 return p; } public Node<K, V> replacementNode(Node<K, V> p, Node<K, V> next) { LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> q = (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V>) p; LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> t = new LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V>(q.hash, q.key, q.value, next); transferLinks(q, t);// t替换q return t; } public TreeNode<K, V> newTreeNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) { TreeNode<K, V> p = new TreeNode<K, V>(hash, key, value, next); linkNodeLast(p);// 末尾添加p return p; } public TreeNode<K, V> replacementTreeNode(Node<K, V> p, Node<K, V> next) { LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> q = (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V>) p; TreeNode<K, V> t = new TreeNode<K, V>(q.hash, q.key, q.value, next); transferLinks(q, t);// t替换q return t; } public void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K, V> e) { // 删除节点e LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> p = (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V>) e, b = p.before, a = p.after; p.before = p.after = null; if (b == null) head = a; else b.after = a; if (a == null) tail = b; else a.before = b; } public void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // 添加新的节点时候,有可能删除最老的元素 LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> first; if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) { K key = first.key;// 删除第一个元素,每次使用元素之后,就会把元素放到最末尾,第一个元素就是最少使用的元素。 removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);// hashMap方法, } } public void afterNodeAccess(Node<K, V> e) { // 节点e被修改后,e不是尾节点(e是尾节点就不动),把e节点移到最后。 LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> last; if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) { LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> p = (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V>) e, b = p.before, a = p.after; p.after = null;// 多个属性指向同一地址值,只是修改其中一个的地址值,其余不变。 if (b == null) head = a;// else b.after = a; if (a != null) a.before = b; else last = b;// if (last == null) head = p; else { p.before = last; last.after = p; } tail = p; ++modCount; } } public void internalWriteEntries(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException { for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) { s.writeObject(e.key); s.writeObject(e.value); } } public LinkedHashMap1(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);// hashMap方法,构造hashMap的table,一个数组+链表+红黑树 accessOrder = false;// true,使用节点之后就把节点放到最末尾。false就不放。 } public LinkedHashMap1(int initialCapacity) { super(initialCapacity);// hashMap方法,构造hashMap的table,一个数组+链表+红黑树 accessOrder = false; } public LinkedHashMap1() { super();// hashMap方法,构造hashMap的table,一个数组+链表+红黑树 accessOrder = false; } public LinkedHashMap1(Map1<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { super();// hashMap方法,构造hashMap的table,一个数组+链表+红黑树 accessOrder = false; putMapEntries(m, false); } public LinkedHashMap1(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder) { super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);// hashMap方法,构造hashMap的table,一个数组+链表+红黑树 this.accessOrder = accessOrder; } public boolean containsValue(Object value) { for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) { V v = e.value; if (v == value || (value != null && value.equals(v))) return true; } return false; } public V get(Object key) { Node<K, V> e; if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)// hashMap方法 return null; if (accessOrder) afterNodeAccess(e);// 把e节点移到最后。 return e.value; } public V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) { Node<K, V> e; if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)// hashMap方法 return defaultValue; if (accessOrder)// 把e节点移到最后。 afterNodeAccess(e); return e.value; } public void clear() { super.clear(); head = tail = null; } // 添加一个元素时候是否删除最老的。 map是缓存有用。比如到达100之后,添加一个元素就删除最老的元素。要重写。 protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map1.Entry<K, V> eldest) { return false; } public Set<K> keySet() { Set<K> ks = keySet; if (ks == null) { ks = new LinkedKeySet(); keySet = ks; } return ks; } final class LinkedKeySet extends AbstractSet<K> { public final int size() { return size; } public final void clear() { LinkedHashMap1.this.clear(); } public final Iterator<K> iterator() { return new LinkedKeyIterator(); } public final boolean contains(Object o) { return containsKey(o); } public final boolean remove(Object key) { return removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true) != null;// hashMap方法 } public final Spliterator<K> spliterator() { return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.DISTINCT); } public final void forEach(Consumer<? super K> action) { if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int mc = modCount; for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) action.accept(e.key); if (modCount != mc) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } public Collection<V> values() { Collection<V> vs = values; if (vs == null) { vs = new LinkedValues(); values = vs; } return vs; } final class LinkedValues extends AbstractCollection<V> { public final int size() { return size; } public final void clear() { LinkedHashMap1.this.clear(); } public final Iterator<V> iterator() { return new LinkedValueIterator(); } public final boolean contains(Object o) { return containsValue(o); } public final Spliterator<V> spliterator() { return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.ORDERED); } public final void forEach(Consumer<? super V> action) { if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int mc = modCount; for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) action.accept(e.value); if (modCount != mc) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } public Set<Map1.Entry<K, V>> entrySet() { Set<Map1.Entry<K, V>> es; return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new LinkedEntrySet()) : es; } final class LinkedEntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map1.Entry<K, V>> { public final int size() { return size; } public final void clear() { LinkedHashMap1.this.clear(); } public final Iterator<Map1.Entry<K, V>> iterator() { return new LinkedEntryIterator(); } public final boolean contains(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map1.Entry)) return false; Map1.Entry<?, ?> e = (Map1.Entry<?, ?>) o; Object key = e.getKey(); Node<K, V> candidate = getNode(hash(key), key);// hashMap方法 return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e); } public final boolean remove(Object o) { if (o instanceof Map1.Entry) { Map1.Entry<?, ?> e = (Map1.Entry<?, ?>) o; Object key = e.getKey(); Object value = e.getValue(); return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null;// hashMap方法 } return false; } public final Spliterator<Map1.Entry<K, V>> spliterator() { return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.DISTINCT); } public final void forEach(Consumer<? super Map1.Entry<K, V>> action) { if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int mc = modCount; for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) action.accept(e); if (modCount != mc) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } public void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) { if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int mc = modCount; for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) action.accept(e.key, e.value); if (modCount != mc) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } public void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) { if (function == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int mc = modCount; for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) e.value = function.apply(e.key, e.value); if (modCount != mc) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } public static class Entry<K, V> extends HashMap1.Node<K, V> { public Entry<K, V> before, after;// hash, key, value, next public Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) { super(hash, key, value, next);// before和after引用节点以支持双向链表 } } abstract class LinkedHashIterator {//头结点head开始一路after到末尾 LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> next; LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> current; int expectedModCount; LinkedHashIterator() { next = head;// 初始化时下一个是head expectedModCount = modCount; current = null; } public final boolean hasNext() { return next != null; } final LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> nextNode() { LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = next; if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); if (e == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); current = e; next = e.after;// before和after遍历链表 return e; } public final void remove() { Node<K, V> p = current; if (p == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); current = null; K key = p.key; removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false);// hashMap方法 expectedModCount = modCount; } } final class LinkedKeyIterator extends LinkedHashIterator implements Iterator<K> { public final K next() { return nextNode().getKey(); } } final class LinkedValueIterator extends LinkedHashIterator implements Iterator<V> { public final V next() { return nextNode().value; } } final class LinkedEntryIterator extends LinkedHashIterator implements Iterator<Map1.Entry<K, V>> { public final Map1.Entry<K, V> next() { return nextNode(); } } }
标签:生成 contains dha print exception tin ace set 效率
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yaowen/p/11232637.html