标签:const 相加 void 根据 copyright opera use span amp
/*前边两个为一种做法*/
/*后边有另外的做法(差分方程以及利用矩阵去做)*/
//***************************************************//***************************************************//***************************************************
第一种做法
这是2018王道数据结构考研复习指导的第一章思维拓展的题目。
关于斐波那契数列的简介:
斐波那契数列,又称黄金分割数列,指的是这样一个数列:0、1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、34、……在数学上,斐波纳契数列以如下被以递归的方法定义:F(0)=0,F(1)=1,F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2)(n≥2,n∈N*)在现代物理、准晶体结构、化学等领域,斐波纳契数列都有直接的应用,为此,美国数学会从1963起出版了以《斐波纳契数列季刊》为名的一份数学杂志,用于专门刊载这方面的研究成果。
具体题目:
求解斐波那契数列的F(n)有两种常用算法:递归算法和非递归算法。试分析两种算法的时间复杂度。
1.递归算法
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 long Fibonacci(int n) { 5 if (n == 0) 6 return 0; 7 else if (n == 1) 8 return 1; 9 else 10 return Fibonacci(n - 1) + Fibonacci(n-2); 11 } 12 13 int main() { 14 cout << "Enter an integer number:" << endl; 15 int N; 16 cin >> N; 17 cout << Fibonacci(N) << endl; 18 system("pause"); 19 return 0; 20 }
时间复杂度分析:
求解F(n),必须先计算F(n-1)和F(n-2),计算F(n-1)和F(n-2),又必须先计算F(n-3)和F(n-4)。。。。。。以此类推,直至必须先计算F(1)和F(0),然后逆推得到F(n-1)和F(n-2)的结果,从而得到F(n)要计算很多重复的值,在时间上造成了很大的浪费,算法的时间复杂度随着N的增大呈现指数增长,时间的复杂度为O(2^n),即2的n次方
2.非递归算法
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 long Fibonacci(int n) { 5 if (n <= 2) 6 return 1; 7 else { 8 long num1 = 1; 9 long num2 = 1; 10 for (int i = 2;i < n - 1;i++) { 11 num2 = num1 + num2; 12 num1 = num2 - num1; 13 } 14 return num1 + num2; 15 } 16 } 17 18 int main() { 19 cout << "Enter an integer number:" << endl; 20 int N; 21 cin >> N; 22 cout << Fibonacci(N) << endl; 23 system("pause"); 24 return 0; 25 }
时间复杂度分析:
从n(>2)开始计算,用F(n-1)和F(n-2)两个数相加求出结果,这样就避免了大量的重复计算,它的效率比递归算法快得多,算法的时间复杂度与n成正比,即算法的时间复杂度为O(n).
/**************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************/
第二种做法。
应用网址:
https://blog.csdn.net/beautyofmath/article/details/48184331
斐波那契数列: f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2); n>=2
f(0)=0; f(1)=1;
即有名的兔子繁衍问题。
斐波那契数列共有三种解法,因而写这篇文章总结一下。
1. 递归求解
递归求解比较简单,是大家常见的一种解法。
1 int fibonacci(int n) 2 { 3 cout<<"calculating "<<n<<endl; 4 if (n<=0) { 5 return 0; 6 } 7 if (n==1) { 8 return 1; 9 } 10 return fb(n-1)+fb(n-2); 11 }
关于这种解法,不再赘述,下面主要说下时间复杂度分析。
设f(n)为参数为n时的时间复杂度,很明显:f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)
这就转化为了数学上的二阶常系数差分方程,并且为其次方程。
即转化为了求f(n)的值,f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)且f(0)=0; f(1)=1;
特征方程为:x^2-x-1=0
得 x=(1±√5)/2
因而f(n)的通解为:
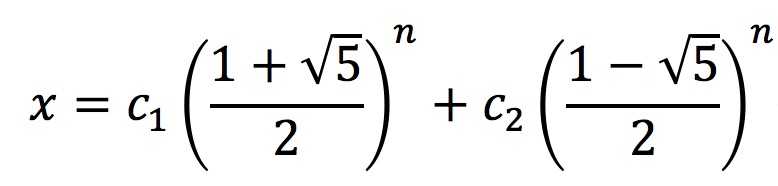
由f(0)=0; f(1)=1可解得c_1,c_2
最终可得,时间复杂度为:
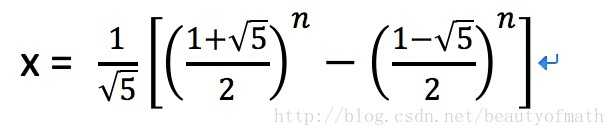
第一种解法比较简单,但是多个元素重复计算,因而时间复杂度较高,为了避免重复计算,可进行循环计算减少时间复杂度
1 int Fibonacci(int n) { 2 if (n<=0) { 3 return 0; 4 } 5 if (n==1) { 6 return 1; 7 } 8 int min=0; 9 int max=1; 10 int i=2; 11 int result=0; 12 while (i<=n) { 13 result=min+max; 14 min=max; 15 max=result; 16 ++i; 17 }
return result;
}
第二种算法时间复杂度为O(n)
3. 还有一种时间复杂度更低的算法。
根据上面的递归公式,我们可以得到
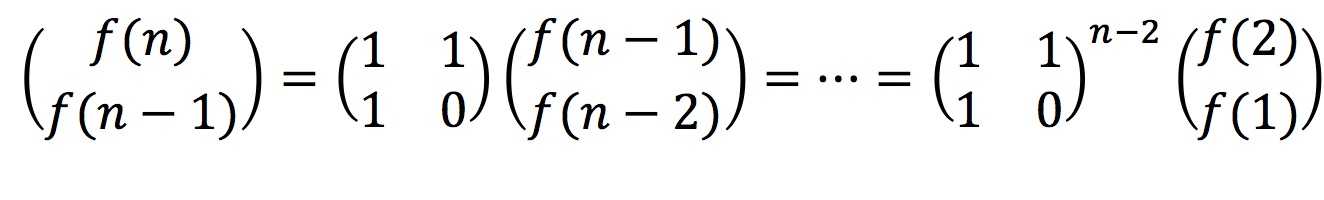
因而计算f(n)就简化为了计算矩阵的(n-2)次方,而计算矩阵的(n-2)次方,我们又可以进行分解,即计算矩阵(n-2)/2次方的平方,逐步分解下去,由于折半计算矩阵次方,因而时间复杂度为O(log n)
具体代码实现如下:
1 // 2 // main.cpp 3 // fibonaccimatrix 4 // 5 // Created by shunagao on 15/8/31. 6 // Copyright © 2015年 shunagao. All rights reserved. 7 // 8 9 #include <iostream> 10 using namespace std; 11 12 class Matrix 13 { 14 public: 15 int n; 16 int **m; 17 Matrix(int num) 18 { 19 m=new int*[num]; 20 for (int i=0; i<num; i++) { 21 m[i]=new int[num]; 22 } 23 n=num; 24 clear(); 25 } 26 void clear() 27 { 28 for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) { 29 for (int j=0; j<n; ++j) { 30 m[i][j]=0; 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 void unit() 35 { 36 clear(); 37 for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) { 38 m[i][i]=1; 39 } 40 } 41 Matrix operator=(const Matrix mtx) 42 { 43 Matrix(mtx.n); 44 for (int i=0; i<mtx.n; ++i) { 45 for (int j=0; j<mtx.n; ++j) { 46 m[i][j]=mtx.m[i][j]; 47 } 48 } 49 return *this; 50 } 51 Matrix operator*(const Matrix &mtx) 52 { 53 Matrix result(mtx.n); 54 result.clear(); 55 for (int i=0; i<mtx.n; ++i) { 56 for (int j=0; j<mtx.n; ++j) { 57 for (int k=0; k<mtx.n; ++k) { 58 result.m[i][j]+=m[i][k]*mtx.m[k][j]; 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 return result; 63 } 64 }; 65 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { 66 unsigned int num=2; 67 Matrix first(num); 68 first.m[0][0]=1; 69 first.m[0][1]=1; 70 first.m[1][0]=1; 71 first.m[1][1]=0; 72 int t; 73 cin>>t; 74 Matrix result(num); 75 result.unit(); 76 int n=t-2; 77 while (n) { 78 if (n%2) { 79 result=result*first; 80 } 81 first=first*first; 82 n=n/2; 83 } 84 cout<<(result.m[0][0]+result.m[0][1])<<endl; 85 return 0; 86 }
标签:const 相加 void 根据 copyright opera use span amp
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zlshtml/p/11267310.html