标签:lte average split current 存储 延时 顺序 mat 综合
使用stream的前提是对lambda表达式和函数式接口有一定的了解,同时对方法引用和普通传参的区别有一定的认识。
stream的三大特性:1、不存储数据2、不改变源数据3、延时执行。
stream优点:1、简化代码2、使用并行流可以利用多核特性,提升效率。
stream上的所有操作分为两类:中间操作和结束操作,中间操作只是一种标记,只有结束操作才会触发实际计算。
常用api如下
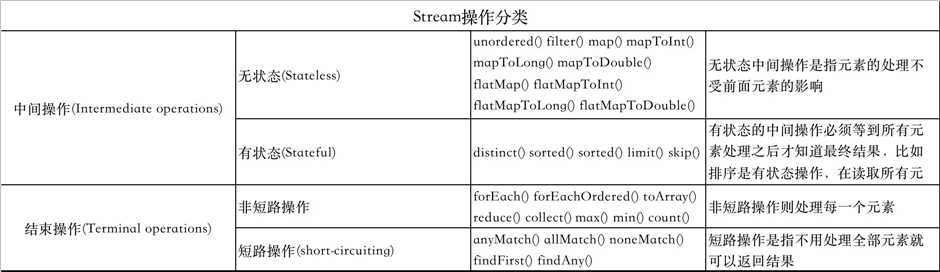
中间操作
filter:过滤流,过滤流中的元素,返回一个符合条件的Stream
map:转换流,将一种类型的流转换为另外一种流。(mapToInt、mapToLong、mapToDouble 返回int、long、double基本类型对应的Stream)
flatMap:简单的说,就是一个或多个流合并成一个新流。(flatMapToInt、flatMapToLong、flatMapToDouble 返回对应的IntStream、LongStream、DoubleStream流。)
distinct:返回去重的Stream。
sorted:返回一个排序的Stream。
peek:主要用来查看流中元素的数据状态。
limit:返回前n个元素数据组成的Stream。属于短路操作
skip:返回第n个元素后面数据组成的Stream。
结束操作
forEach: 循环操作Stream中数据。
toArray: 返回流中元素对应的数组对象。
reduce: 聚合操作,用来做统计。
collect: 聚合操作,封装目标数据。
min、max、count: 聚合操作,最小值,最大值,总数量。
anyMatch: 短路操作,有一个符合条件返回true。
allMatch: 所有数据都符合条件返回true。
noneMatch: 所有数据都不符合条件返回true。
findFirst: 短路操作,获取第一个元素。
findAny: 短路操作,获取任一元素。
forEachOrdered: 暗元素顺序执行循环操作。
流的创建demo
package com.example.test.stream; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; import java.util.stream.IntStream; import java.util.stream.Stream; public class StreamCreate { public static void main(String[] args) { unLimitStream2(); } public static void testArrayStream(){ int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5}; IntStream intStream = Arrays.stream(arr); Student[] students = new Student[]{Student.builder().name("zhangsan").age(12).score(12).build(),Student.builder().name("zhangsan").age(12).score(12).build()}; Stream<Student> studentStream = Arrays.stream(students); Stream<Integer> integerStream =Stream.of(1,2,5,4,6); Stream<int[]> intArrayStrean = Stream.of(arr,arr); intArrayStrean.forEach(System.out::println); } public static void testCollectionStream(){ List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("sdf","sdfdsf","ertert","sdfdsf"); //创建普通流 Stream<String> stringStream = strings.stream(); //创建并行流 Stream<String> parallelStream = strings.parallelStream(); } public static void emptyStream(){ Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.empty(); } public static void unLimitStream(){ Stream.generate((() -> "number" + new Random().nextInt())).limit(20).forEach(System.out::println); } public static void unLimitStream2(){ Stream.iterate(0,x ->x+1).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); Stream.iterate(0,x ->x).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); } }
流的操作demo
package com.example.test.stream; import java.util.*; import java.util.stream.Collectors; import java.util.stream.Stream; public class OpepateStream { private static String[] arr = new String[]{"b","ab","abc","abcd","abcde"}; public static void main(String[] args) { testFlatMap(); } public static void testMap(){ String[] str = {"sdf","sdfdsFFF","dfsGdsf"}; Stream.of(str).map(t ->t.toUpperCase()).forEach(System.out::println); } public static void filter(){ String[] str = {"sdf","sdfdsFFF","dfsGdsf"}; Stream.of(str).filter(t -> ! t.equals("sdf")).forEach(System.out::println); } public static void testFlatMap(){ List<String> list = Arrays.asList("beijing changcheng", "beijing gugong", "beijing tiantan", "gugong tiananmen"); list.stream().map(item -> Arrays.stream(item.split(" "))).forEach(System.out::println); list.stream().flatMap(item -> Arrays.stream(item.split(" "))).forEach(System.out::println); List<Integer> a=new ArrayList<>(); a.add(1); a.add(2); List<Integer> b=new ArrayList<>(); b.add(3); b.add(4); List<Integer> figures=Stream.of(a,b).flatMap(u->u.stream()).collect(Collectors.toList()); figures.forEach(f->System.out.println(f)); } public static void sort(){ String[] arr1 = {"abc","a","bc","abcd"}; Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.comparing(String::length).reversed()).forEach(System.out::println); } public static void sort2(){ String[] arr1 = {"abc","a","bc","abcd"}; Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.comparing(String::length).reversed()).forEach(System.out::println); } public static void sort3(){ String[] arr1 = {"abc","a","bc","abcd"}; Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.comparing(OpepateStream::com1).thenComparing(String::length)).forEach(System.out::println); } public static char com1(String x){ return x.charAt(0); } public static void testMaxAndMin(){ Optional<String> option = Stream.of(arr).max(Comparator.comparing(String::length)); option.ifPresent(System.out::println); Stream.of(arr).min(Comparator.comparing(String::length)).ifPresent(System.out::println); } public static void findFirst(){ String str = Stream.of(arr).parallel().filter(t -> t.length()>3).findFirst().orElse("noting"); System.out.println(str); } public static void testFindAny(){ Optional<String> optional = Stream.of(arr).parallel().filter(x->x.length()>3).findAny(); optional.ifPresent(System.out::println); } public static void reduceTest(){ Optional<Integer> optional = Stream.of(1,2,3).reduce((x,y) -> x+y); optional.ifPresent(System.out::println); } public static Optional<Double> inverse(Double x) { return x == 0 ? Optional.empty() : Optional.of(1 / x); } public static Optional<Double> squareRoot(Double x) { return x < 0 ? Optional.empty() : Optional.of(Math.sqrt(x)); } public static void testStream2() { double x = 4d; Optional<Double> result1 = inverse(x).flatMap(OpepateStream::squareRoot); result1.ifPresent(System.out::println); Optional<Double> result2 = Optional.of(4.0).flatMap(OpepateStream::inverse).flatMap(OpepateStream::squareRoot); result2.ifPresent(System.out::println); } public static void testToMap(){ List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){ { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build()); } } }; studentList.add(Student.builder().name("student08").age(12).score(1000).build()); studentList.add(Student.builder().name("student08").age(12).score(234).build()); studentList.add(Student.builder().name("student08").age(12).score(123).build()); studentList.add(Student.builder().name("student08").age(12).score(3000).build()); Map<String,Integer> map = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Student::getName,Student::getScore,(a,b) -> b)); map.forEach((x,y) -> System.out.println(x + "->" + y)); } public static void toAssign(){ List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){ { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build()); } } }; HashSet<Student> s = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new)); s.forEach(System.out::println); } public static void aggregation(){ List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){ { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build()); } } }; IntSummaryStatistics summaryStatistics = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(Student::getScore)); System.out.println("getAverage->"+summaryStatistics.getAverage()); System.out.println("getMax->"+summaryStatistics.getMax()); System.out.println("getMin->"+summaryStatistics.getMin()); System.out.println("getCount->"+summaryStatistics.getCount()); System.out.println("getSum->"+summaryStatistics.getSum()); } public static void group(){ List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){ { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build()); } } }; Map<Boolean,Integer> map = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy((x -> x.getScore()>50) ,Collectors.summingInt(Student::getScore))); map.forEach((x,y) -> { System.out.println(x); System.out.println(y); }); Map<String,Set<Integer>> map4 = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getName,Collectors.mapping(Student::getScore,Collectors.toSet()))); map4.forEach((x,y)-> System.out.println(x+"->"+y)); } public static void group1(){ List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){ { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build()); } } }; Map<Boolean,Integer> map = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy((x -> x.getScore()>50) ,Collectors.summingInt(Student::getScore))); map.forEach((x,y) -> { System.out.println(x); System.out.println(y); }); Map<String,List<Student>> map4 = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getName)); map4.forEach((x,y)-> System.out.println(x+"->"+y)); } }
并行流
package com.example.test.stream; import java.util.stream.Stream; public class ParalellTest { public void peek1(int x) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":->peek1->" + x); } public void peek2(int x) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":->peek2->" + x); } public void peek3(int x) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":->final result->" + x); } public static void main(String[] args) { ParalellTest paralellTest = new ParalellTest(); Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.iterate(1,x -> x+1).limit(10); stream.peek(paralellTest::peek1).filter(x -> x>5) .peek(paralellTest::peek2).filter(x -> x<9) .peek(paralellTest::peek3).forEach(System.out::println); System.out.println("-------------------------------------"); Stream<Integer> stream2 = Stream.iterate(1,x -> x+1).limit(10).parallel(); stream2.peek(paralellTest::peek1).filter(x -> x>5) .peek(paralellTest::peek2).filter(x -> x<9) .peek(paralellTest::peek3).forEach(System.out::println); } }
综合应用
package com.example.test.stream; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; import java.util.stream.Collectors; import java.util.stream.Stream; public class StreamTest { public static void main(String[] args) { test2(); } public static void test1(){ Random random = new Random(); List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){ { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build()); } } }; List<String> names = studentList.stream().filter(t -> t.getScore()>50) .sorted(Comparator.comparingDouble(Student::getScore).reversed()) .map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(names); } public static void test2(){ List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){ { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build()); } } }; Stream<Student> stream = studentList.stream().filter(StreamTest::filter) .sorted(Comparator.comparingDouble(Student::getScore).reversed()); System.out.println("--------------"); System.out.println(stream.map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.toList())); } private static boolean filter(Student student){ System.out.println("123123123"); return student.getScore() >50; } }
标签:lte average split current 存储 延时 顺序 mat 综合
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/hhhshct/p/11275516.html