标签:main spl 快速 复杂 == 接下来 recent second cli
复杂度 O(log n)
模板:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int mod=1e5+7; int ksm(int a,int b){ int ans=1; while(b){ if(b&1) ans=ans*a%mod; a=a*a%mod; a>>=1; } return ans; } int main(){ return 0; }

示例如斐波那契数列:

其中要知道,一条对角线为1,其他为0的矩阵乘以其他矩阵其他矩阵不发生改变,即可以把他当成相乘时的1。
其中还有其他较为复杂的类型:

这需要用到二项式定理: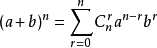
复杂度O(log n)
模板
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int mod=2147493647; int f=7; struct node{ int arr[10][10]; }; node mul(node x,node y){ node ans; memset(ans.arr,0,sizeof(ans.arr)); for(int i=1;i<=f;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=f;j++){ for(int k=1;k<=f;k++){ ans.arr[i][j]=(ans.arr[i][j]+x.arr[i][k]*y.arr[k][j]%mod)%mod; } } } return ans; } node ksm(node a,int b){ node ans; memset(ans.arr,0,sizeof(ans.arr)); for(int i=1;i<=f;i++){ ans.arr[i][i]=1; } while(b){ if(b&1) ans=mul(ans,a); a=mul(a,a); b>>=1; } return ans; } int main(){ return 0; }
例题:
Farmer John likes to play mathematics games with his N cows. Recently, they are attracted by recursive sequences. In each turn, the cows would stand in a line, while John writes two positive numbers a and b on a blackboard. And then, the cows would say their identity number one by one. The first cow says the first number a and the second says the second number b. After that, the i-th cow says the sum of twice the (i-2)-th number, the (i-1)-th number, and i4i4. Now, you need to write a program to calculate the number of the N-th cow in order to check if John’s cows can make it right.
Input
The first line of input contains an integer t, the number of test cases. t test cases follow.
Each case contains only one line with three numbers N, a and b where N,a,b < 231231 as described above.
Output
For each test case, output the number of the N-th cow. This number might be very large, so you need to output it modulo 2147493647.
Sample Input
2
3 1 2
4 1 10
Sample Output
85
369
题目大意:
一个人有n只牛,他会给两个数a b,第一只牛说a,第二只说b,接下来的i只都会说(i-2)只说的数的二倍,(i-1)只说的一倍,再加上i^4。通项公式为f(n)=f(n-2)*2+f(n-1)+n^4.
题解:
n^4无法直接写,因为会使常数矩阵与n有关。所以要用到二项式公式。
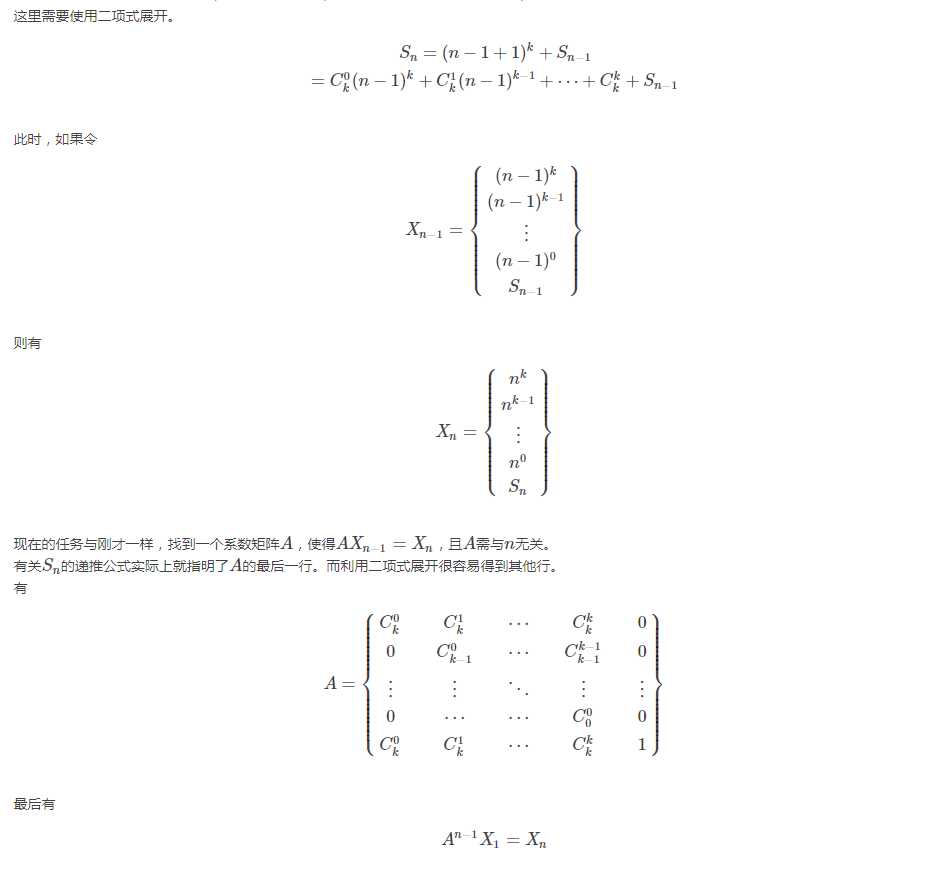
代码:

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; ll c[7]={1,4,6,4,1,2,1}; ll f=7; const ll mod=2147493647; struct aa{ ll arr[10][10]; }; aa mul(aa x,aa y){ aa ans; memset(ans.arr,0,sizeof(ans.arr)); for(ll i=1;i<=f;i++){ for(ll j=1;j<=f;j++){ for(ll k=1;k<=f;k++){ ans.arr[i][j]=(ans.arr[i][j]+x.arr[i][k]*y.arr[k][j]%mod)%mod; } } } return ans; } aa ksm(aa a,ll b){ aa ans; memset(ans.arr,0,sizeof(ans.arr)); for(ll i=1;i<=f;i++){ ans.arr[i][i]=1; } while(b){ if(b&1) ans=mul(ans,a); a=mul(a,a); b>>=1; } return ans; } int main(){ aa x,y,ans; ll t,n,a,b; cin>>t; while(t--){ memset(ans.arr,0,sizeof(ans.arr)); memset(x.arr,0,sizeof(x.arr)); memset(y.arr,0,sizeof(y.arr)); cin>>n; cin>>a>>b; x.arr[1][1]=1;x.arr[1][2]=2;x.arr[1][3]=1;x.arr[1][4]=4;x.arr[1][5]=6;x.arr[1][6]=4;x.arr[1][7]=1; x.arr[2][1]=1;x.arr[2][2]=0;x.arr[2][3]=0;x.arr[2][4]=0;x.arr[2][5]=0;x.arr[2][6]=0;x.arr[2][7]=0; x.arr[3][1]=0;x.arr[3][2]=0;x.arr[3][3]=1;x.arr[3][4]=4;x.arr[3][5]=6;x.arr[3][6]=4;x.arr[3][7]=1; x.arr[4][1]=0;x.arr[4][2]=0;x.arr[4][3]=0;x.arr[4][4]=1;x.arr[4][5]=3;x.arr[4][6]=3;x.arr[4][7]=1; x.arr[5][1]=0;x.arr[5][2]=0;x.arr[5][3]=0;x.arr[5][4]=0;x.arr[5][5]=1;x.arr[5][6]=2;x.arr[5][7]=1; x.arr[6][1]=0;x.arr[6][2]=0;x.arr[6][3]=0;x.arr[6][4]=0;x.arr[6][5]=0;x.arr[6][6]=1;x.arr[6][7]=1; x.arr[7][1]=0;x.arr[7][2]=0;x.arr[7][3]=0;x.arr[7][4]=0;x.arr[7][5]=0;x.arr[7][6]=0;x.arr[7][7]=1; y.arr[1][1]=b; y.arr[2][1]=a; y.arr[3][1]=16; y.arr[4][1]=8; y.arr[5][1]=4; y.arr[6][1]=2; y.arr[7][1]=1; if(n==1){ cout<<a<<endl; } else if(n==2){ cout<<b<<endl; } else{ ans=ksm(x,n-2); ans=mul(ans,y); cout<<ans.arr[1][1]<<endl; } } return 0; }
神奇的矩阵快速幂
标签:main spl 快速 复杂 == 接下来 recent second cli
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/meanttobe/p/11283841.html