标签:link list reference 比较 solution ++ enc for node
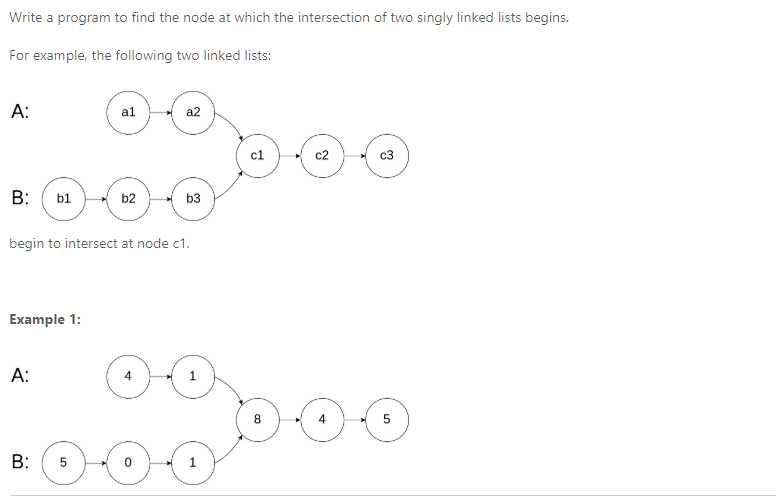
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Reference of the node with value = 8
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.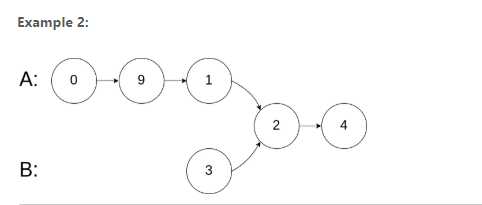
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output: Reference of the node with value = 2
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.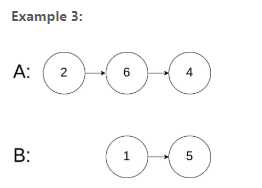
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
Output: null
Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
int lenA = getLen(headA), lenB = getLen(headB);
if(lenA>lenB){
for(int i=0; i<lenA-lenB; i++){
headA = headA->next;
}
}
else{
for(int i=0; i<lenB-lenA; i++){
headB = headB->next;
}
}
while(headA&&headB&&headA!=headB){
headA = headA->next;
headB = headB->next;
}
return (headA==headB) ? headA : NULL;
}
private:
int getLen(ListNode *list){
int cnt = 0;
ListNode *tmp = list;
while(tmp){
tmp = tmp->next;
++cnt;
}
return cnt;
}
};先计算出两个链表的长度,然后进行比较,将较长的链表缩短(即将头节点指针向后移),使得两个链表长度一致,然后让指针同时同步长迭代,当发现地址相同时则知道当前节点开始共用。
LeetCode——160 Intersection of Two Linked Lists
标签:link list reference 比较 solution ++ enc for node
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yejianying/p/leetcode_160.html