标签:关于 包装 ops raw next 部分 abs size mda
剑指offer
两道关于 数据结构——栈 的题目
1. 包含min函数的栈
简要分析一下这道题,这道题做了3遍才过,踩了一些小坑

看看示例:
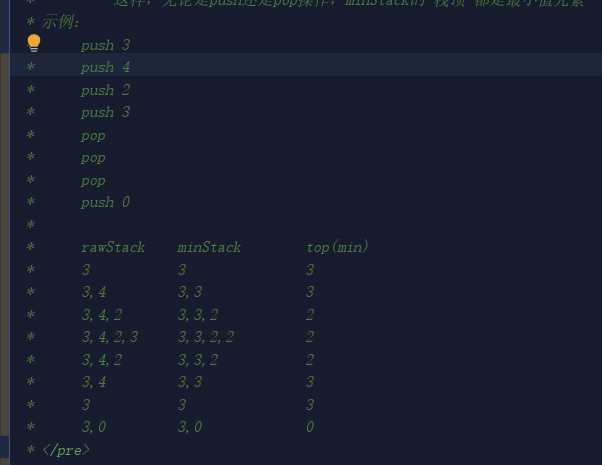
得到了规律,那么关键部分的代码实现,就在于 两个栈(rawStack 和 minStack) 和 push() 方法
Stack<Integer> rawStack = new Stack<>(); Stack<Integer> minStack = new Stack<>(); public void push1(int node) { rawStack.push(node); int min = rawStack.peek(); for (Integer integer : rawStack) { if (min > integer) { min = integer; } } minStack.push(min); }
其他部分就比较简单
public void pop() { rawStack.pop(); minStack.pop(); } public int top() { return minStack.peek(); } public int min() { return top(); }
2. 栈的压入、弹出序列
同样,事先分析题目

如上分析:
感觉这题还是在于 抽象思维 转化为 代码,还有注意特殊情况,这题也是测了3遍过的,实现代码比较简单。
public static boolean IsPopOrder(int[] pushA, int[] popA) { // 将 数组 转为 List(Java 8 新特性,Stream流的方式,将 基本类型数组 转为 对应包装类对象list) List<Integer> pushSeq = Arrays.stream(pushA).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList()); List<Integer> popSeq = Arrays.stream(popA).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList()); while (!popSeq.isEmpty()) { // 仅剩1个的情况 if (popSeq.size() == 1) { return popSeq.get(0).equals(pushSeq.get(0)); } // 获取对应的下一个元素所在下标 int index = pushSeq.indexOf(popSeq.get(0)); popSeq.remove(0); int nextIndex = pushSeq.indexOf(popSeq.get(0)); if (Math.abs(nextIndex - index) == 1 || nextIndex == pushSeq.size() - 1) pushSeq.remove(index); else return false; } return true; }
两题的具体源码可以在 https://github.com/ihaokun/algorithm 里的offer包中看看
标签:关于 包装 ops raw next 部分 abs size mda
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ihaokun/p/11370785.html