标签:closeable assert sed 手写 ace ali resource 操作 source
JDK1.7之后,引入了try-with-resource,使得关闭资源操作无需层层嵌套在finally中,代码简洁不少,本质是一个语法糖,能够使用try-with-resource关闭资源的类,必须实现AutoCloseable接口。
1.7版本之前,传统的关闭资源操作如下:
public static void main(String[] args){
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("file.txt");
fileInputStream.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
assert fileInputStream != null;
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
可以看到,为了确保资源关闭正常,需要finall中再嵌入finally,try中打开资源越多,finall嵌套越深,可能会导致关闭资源的代码比业务代码还要多。
但是使用了try-with-resource语法后,上面的例子可改写为:
try(FileInputStream fileInputStream1 = new FileInputStream("file.txt")){
fileInputStream1.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
如何判读资源是否真的被关闭了呢,我们手写个Demo:
实现AutoCloseable的资源类
class MyResource implements AutoCloseable{
public void open(){
System.out.println("resource is open!");
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
System.out.println("resource is close!");
}
}
调用方:
public static void main(String[] args){
try(MyResource myResource = new MyResource()){
myResource.open();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
输出如下,可以看到close方法被自动调用了,
resource is open!
resource is close!
底层原理是什么呢,看一下编译后的class文件:
try {
MyResource myResource = new MyResource();
Throwable var2 = null;
try {
myResource.open();
} catch (Throwable var12) {
var2 = var12;
throw var12;
} finally {
if (myResource != null) {
if (var2 != null) {
try {
myResource.close();
} catch (Throwable var11) {
var2.addSuppressed(var11);
}
} else {
myResource.close();
}
}
}
} catch (Exception var14) {
var14.printStackTrace();
}
}
很明显,编译器生成了finally代码块,并在其中调用了close 方法,同1.7之前的关闭资源操作的实现原理是相同的,但是可以看到,这里多调用了一个addSuppressed方法,这么做其实是为了处理异常屏蔽,什么是异常屏蔽,首先,我们先修改一下刚刚的Demo,使资源类在open和close方法中抛出异常,并且使用1.7之前的关闭资源的方法,资源类以及调用方代码修改如下:
public void open() throws IOException {
System.out.println("resource is open!");
throw new IOException("open() exception!");
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
System.out.println("resource is close!");
throw new IOException("close() exception!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MyResource myResource = null;
try{
myResource = new MyResource();
myResource.open();
}finally {
try {
myResource.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
控制台打印如下:
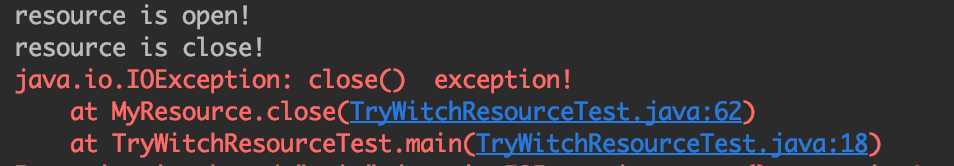
open方法抛出的异常被自动忽略了,而异常信息丢失将导致程序调试困难,所以try-with-resource语法中加入了addSuppressed处理异常屏蔽,现在修改Demo为使用try-with-resource关闭资源,调用方代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try(MyResource myResource = new MyResource()){
myResource.open();
}
控制台打印如下
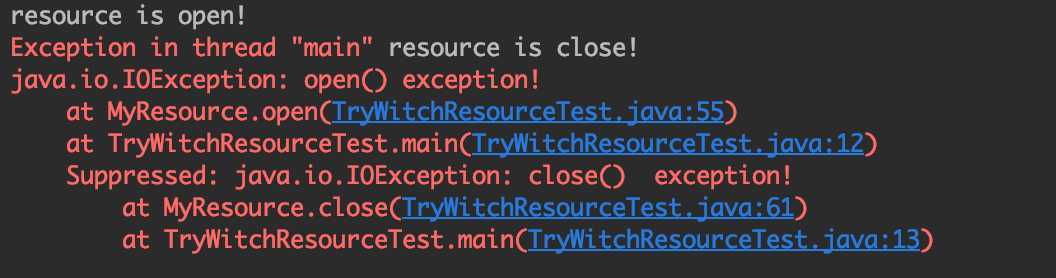
异常信息中多了提示:close方法中抛出的异常被open方法中抛出的异常抑制了。
其他问题:使用try-catch-resource,并不能完全保证资源被关闭,在javaBIO中,使用了大量的装饰器模式,调用装饰类的close方法时实际是在调用其中包裹的流的close方法,但是在调用包裹的流的close方法时,装饰类还做了一些其他的操作,如果这些操作出现异常,将导致包裹流的close方法被跳过,资源没有被正确关闭,正确的方式是在try中单独声明底层资源类以及装饰类,这样就可以保证,每个类的close方法都被调用。
标签:closeable assert sed 手写 ace ali resource 操作 source
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/youtang/p/11441959.html