标签:ref 概率dp 转移 inf next ems 机器人 double 技术
题目链接:https://nanti.jisuanke.com/t/41301
题目大意:
给定一个没有循环的有向图,它从节点1开始,到节点n结束。
有一个机器人从1开始,每天都会以相同的概率前往相邻节点之一或静止不动。每天机器人的耐久性消耗量等于经过的天数。
请计算机器人到达节点n时的预期耐久性消耗量。
保证只有一个节点(节点1)的in-degree等于00,并且只有一个节点(节点n)的out-degree等于0.并且图中没有多个边缘。
解题思路:
设dp【i】为从i到达终点n的期望时间那么很容易得到: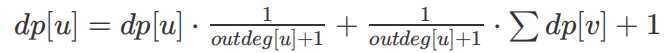
接下来设ans【i】为从i到达终点的耐久值消耗量,那么状态转移方程为 ans【u】=ans【u】*1(outdeg【u】+1)+1/(outdey【u】+1)*∑ans【v】+dp【u】。由于此图为有向无环图,所以跑边拓扑边转移即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxn=1e5+5; struct st{ int to,next; }stm[maxn*2]; int cnt; int head[maxn]; void add(int u,int v){ stm[cnt].to=v; stm[cnt].next=head[u]; head[u]=cnt++; } int cd[maxn]; int cd1[maxn]; double dp[maxn]; double ans[maxn]; queue<int> que; int main(){ int t; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--){ int n,m; int u,v; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); memset(cd,0,sizeof(cd)); memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp)); memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans)); memset(cd1,0,sizeof(cd1)); cnt=0; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ scanf("%d%d",&u,&v); add(v,u); cd[u]++; cd1[u]++; } while(!que.empty())que.pop(); que.push(n); while(!que.empty()){ int now=que.front(); que.pop(); for(int i=head[now];~i;i=stm[i].next){ int to=stm[i].to; dp[to]+=1.0/(cd[to]+1)*dp[now]; ans[to]+=1.0/(cd[to]+1)*ans[now]; //1.0*(cd[to]+1)/cd[to]; cd1[to]--; if(cd1[to]==0){ dp[to]=(dp[to]+1)*1.0*(cd[to]+1)/cd[to]; ans[to]=(ans[to]+dp[to])*1.0*(cd[to]+1)/cd[to]; que.push(to); } } } printf("%.2lf\n",ans[1]); } return 0; }
The Preliminary Contest for ICPC Asia Nanjing 2019 D. Robots(概率dp)
标签:ref 概率dp 转移 inf next ems 机器人 double 技术
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Zhi-71/p/11444076.html