标签:fas reference 内存 The ons extra sha 继承 交换
struct objc_object {
private:
isa_t isa;
public:
// ISA() assumes this is NOT a tagged pointer object
Class ISA();
// getIsa() allows this to be a tagged pointer object
Class getIsa();
// initIsa() should be used to init the isa of new objects only.
// If this object already has an isa, use changeIsa() for correctness.
// initInstanceIsa(): objects with no custom RR/AWZ
// initClassIsa(): class objects
// initProtocolIsa(): protocol objects
// initIsa(): other objects
void initIsa(Class cls /*nonpointer=false*/);
void initClassIsa(Class cls /*nonpointer=maybe*/);
void initProtocolIsa(Class cls /*nonpointer=maybe*/);
void initInstanceIsa(Class cls, bool hasCxxDtor);
// changeIsa() should be used to change the isa of existing objects.
// If this is a new object, use initIsa() for performance.
Class changeIsa(Class newCls);
bool hasNonpointerIsa();
bool isTaggedPointer();
bool isBasicTaggedPointer();
bool isExtTaggedPointer();
bool isClass();
// object may have associated objects?
bool hasAssociatedObjects();
void setHasAssociatedObjects();
// object may be weakly referenced?
bool isWeaklyReferenced();
void setWeaklyReferenced_nolock();
// object may have -.cxx_destruct implementation?
bool hasCxxDtor();
// Optimized calls to retain/release methods
id retain();
void release();
id autorelease();
// Implementations of retain/release methods
id rootRetain();
bool rootRelease();
id rootAutorelease();
bool rootTryRetain();
bool rootReleaseShouldDealloc();
uintptr_t rootRetainCount();
// Implementation of dealloc methods
bool rootIsDeallocating();
void clearDeallocating();
void rootDealloc();
private:
void initIsa(Class newCls, bool nonpointer, bool hasCxxDtor);
// Slow paths for inline control
id rootAutorelease2();
bool overrelease_error();
#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
// Unified retain count manipulation for nonpointer isa
id rootRetain(bool tryRetain, bool handleOverflow);
bool rootRelease(bool performDealloc, bool handleUnderflow);
id rootRetain_overflow(bool tryRetain);
bool rootRelease_underflow(bool performDealloc);
void clearDeallocating_slow();
// Side table retain count overflow for nonpointer isa
void sidetable_lock();
void sidetable_unlock();
void sidetable_moveExtraRC_nolock(size_t extra_rc, bool isDeallocating, bool weaklyReferenced);
bool sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock(size_t delta_rc);
size_t sidetable_subExtraRC_nolock(size_t delta_rc);
size_t sidetable_getExtraRC_nolock();
#endif
// Side-table-only retain count
bool sidetable_isDeallocating();
void sidetable_clearDeallocating();
bool sidetable_isWeaklyReferenced();
void sidetable_setWeaklyReferenced_nolock();
id sidetable_retain();
id sidetable_retain_slow(SideTable& table);
uintptr_t sidetable_release(bool performDealloc = true);
uintptr_t sidetable_release_slow(SideTable& table, bool performDealloc = true);
bool sidetable_tryRetain();
uintptr_t sidetable_retainCount();
#if DEBUG
bool sidetable_present();
#endif
};
struct objc_class : objc_object {
// Class ISA;
Class superclass;
cache_t cache; // formerly cache pointer and vtable
class_data_bits_t bits; // class_rw_t * plus custom rr/alloc flags
class_rw_t *data() {
return bits.data();
}
void setData(class_rw_t *newData) {
bits.setData(newData);
}
void setInfo(uint32_t set) {
assert(isFuture() || isRealized());
data()->setFlags(set);
}
void clearInfo(uint32_t clear) {
assert(isFuture() || isRealized());
data()->clearFlags(clear);
}
// set and clear must not overlap
void changeInfo(uint32_t set, uint32_t clear) {
assert(isFuture() || isRealized());
assert((set & clear) == 0);
data()->changeFlags(set, clear);
}
bool hasCustomRR() {
return ! bits.hasDefaultRR();
}
void setHasDefaultRR() {
assert(isInitializing());
bits.setHasDefaultRR();
}
void setHasCustomRR(bool inherited = false);
void printCustomRR(bool inherited);
bool hasCustomAWZ() {
return ! bits.hasDefaultAWZ();
}
void setHasDefaultAWZ() {
assert(isInitializing());
bits.setHasDefaultAWZ();
}
void setHasCustomAWZ(bool inherited = false);
void printCustomAWZ(bool inherited);
bool instancesRequireRawIsa() {
return bits.instancesRequireRawIsa();
}
void setInstancesRequireRawIsa(bool inherited = false);
void printInstancesRequireRawIsa(bool inherited);
bool canAllocNonpointer() {
assert(!isFuture());
return !instancesRequireRawIsa();
}
bool canAllocFast() {
assert(!isFuture());
return bits.canAllocFast();
}
bool hasCxxCtor() {
// addSubclass() propagates this flag from the superclass.
assert(isRealized());
return bits.hasCxxCtor();
}
void setHasCxxCtor() {
bits.setHasCxxCtor();
}
bool hasCxxDtor() {
// addSubclass() propagates this flag from the superclass.
assert(isRealized());
return bits.hasCxxDtor();
}
void setHasCxxDtor() {
bits.setHasCxxDtor();
}
bool isSwiftStable() {
return bits.isSwiftStable();
}
bool isSwiftLegacy() {
return bits.isSwiftLegacy();
}
bool isAnySwift() {
return bits.isAnySwift();
}
// Return YES if the class's ivars are managed by ARC,
// or the class is MRC but has ARC-style weak ivars.
bool hasAutomaticIvars() {
return data()->ro->flags & (RO_IS_ARC | RO_HAS_WEAK_WITHOUT_ARC);
}
// Return YES if the class's ivars are managed by ARC.
bool isARC() {
return data()->ro->flags & RO_IS_ARC;
}
#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
// Tracked in non-pointer isas; not tracked otherwise
#else
bool instancesHaveAssociatedObjects() {
// this may be an unrealized future class in the CF-bridged case
assert(isFuture() || isRealized());
return data()->flags & RW_INSTANCES_HAVE_ASSOCIATED_OBJECTS;
}
void setInstancesHaveAssociatedObjects() {
// this may be an unrealized future class in the CF-bridged case
assert(isFuture() || isRealized());
setInfo(RW_INSTANCES_HAVE_ASSOCIATED_OBJECTS);
}
#endif
bool shouldGrowCache() {
return true;
}
void setShouldGrowCache(bool) {
// fixme good or bad for memory use?
}
bool isInitializing() {
return getMeta()->data()->flags & RW_INITIALIZING;
}
void setInitializing() {
assert(!isMetaClass());
ISA()->setInfo(RW_INITIALIZING);
}
bool isInitialized() {
return getMeta()->data()->flags & RW_INITIALIZED;
}
void setInitialized();
bool isLoadable() {
assert(isRealized());
return true; // any class registered for +load is definitely loadable
}
IMP getLoadMethod();
// Locking: To prevent concurrent realization, hold runtimeLock.
bool isRealized() {
return data()->flags & RW_REALIZED;
}
// Returns true if this is an unrealized future class.
// Locking: To prevent concurrent realization, hold runtimeLock.
bool isFuture() {
return data()->flags & RW_FUTURE;
}
bool isMetaClass() {
assert(this);
assert(isRealized());
return data()->ro->flags & RO_META;
}
// NOT identical to this->ISA when this is a metaclass
Class getMeta() {
if (isMetaClass()) return (Class)this;
else return this->ISA();
}
bool isRootClass() {
return superclass == nil;
}
bool isRootMetaclass() {
return ISA() == (Class)this;
}
const char *mangledName() {
// fixme can't assert locks here
assert(this);
if (isRealized() || isFuture()) {
return data()->ro->name;
} else {
return ((const class_ro_t *)data())->name;
}
}
const char *demangledName(bool realize = false);
const char *nameForLogging();
// May be unaligned depending on class's ivars.
uint32_t unalignedInstanceStart() {
assert(isRealized());
return data()->ro->instanceStart;
}
// Class's instance start rounded up to a pointer-size boundary.
// This is used for ARC layout bitmaps.
uint32_t alignedInstanceStart() {
return word_align(unalignedInstanceStart());
}
// May be unaligned depending on class's ivars.
uint32_t unalignedInstanceSize() {
assert(isRealized());
return data()->ro->instanceSize;
}
// Class's ivar size rounded up to a pointer-size boundary.
uint32_t alignedInstanceSize() {
return word_align(unalignedInstanceSize());
}
size_t instanceSize(size_t extraBytes) {
size_t size = alignedInstanceSize() + extraBytes;
// CF requires all objects be at least 16 bytes.
if (size < 16) size = 16;
return size;
}
void setInstanceSize(uint32_t newSize) {
assert(isRealized());
if (newSize != data()->ro->instanceSize) {
assert(data()->flags & RW_COPIED_RO);
*const_cast<uint32_t *>(&data()->ro->instanceSize) = newSize;
}
bits.setFastInstanceSize(newSize);
}
void chooseClassArrayIndex();
void setClassArrayIndex(unsigned Idx) {
bits.setClassArrayIndex(Idx);
}
unsigned classArrayIndex() {
return bits.classArrayIndex();
}
};union isa_t {
isa_t() { } // union 的构造函数
isa_t(uintptr_t value) : bits(value) { }
Class cls;
uintptr_t bits;
#if defined(ISA_BITFIELD)
struct {
ISA_BITFIELD; // defined in isa.h
};
#endif
};struct cache_t {
struct bucket_t *_buckets;
mask_t _mask;
mask_t _occupied;
public:
struct bucket_t *buckets();
mask_t mask();
mask_t occupied();
void incrementOccupied();
void setBucketsAndMask(struct bucket_t *newBuckets, mask_t newMask);
void initializeToEmpty();
mask_t capacity();
bool isConstantEmptyCache();
bool canBeFreed();
static size_t bytesForCapacity(uint32_t cap);
static struct bucket_t * endMarker(struct bucket_t *b, uint32_t cap);
void expand();
void reallocate(mask_t oldCapacity, mask_t newCapacity);
struct bucket_t * find(cache_key_t key, id receiver);
static void bad_cache(id receiver, SEL sel, Class isa) __attribute__((noreturn));
};struct class_data_bits_t {
// Values are the FAST_ flags above.
uintptr_t bits;
private:
bool getBit(uintptr_t bit)
{
return bits & bit;
}
#if FAST_ALLOC
static uintptr_t updateFastAlloc(uintptr_t oldBits, uintptr_t change)
{
if (change & FAST_ALLOC_MASK) {
if (((oldBits & FAST_ALLOC_MASK) == FAST_ALLOC_VALUE) &&
((oldBits >> FAST_SHIFTED_SIZE_SHIFT) != 0))
{
oldBits |= FAST_ALLOC;
} else {
oldBits &= ~FAST_ALLOC;
}
}
return oldBits;
}
#else
static uintptr_t updateFastAlloc(uintptr_t oldBits, uintptr_t change) {
return oldBits;
}
#endif
void setBits(uintptr_t set)
{
uintptr_t oldBits;
uintptr_t newBits;
do {
oldBits = LoadExclusive(&bits);
newBits = updateFastAlloc(oldBits | set, set);
} while (!StoreReleaseExclusive(&bits, oldBits, newBits));
}
void clearBits(uintptr_t clear)
{
uintptr_t oldBits;
uintptr_t newBits;
do {
oldBits = LoadExclusive(&bits);
newBits = updateFastAlloc(oldBits & ~clear, clear);
} while (!StoreReleaseExclusive(&bits, oldBits, newBits));
}
public:
class_rw_t* data() {
return (class_rw_t *)(bits & FAST_DATA_MASK);
}
void setData(class_rw_t *newData)
{
assert(!data() || (newData->flags & (RW_REALIZING | RW_FUTURE)));
// Set during realization or construction only. No locking needed.
// Use a store-release fence because there may be concurrent
// readers of data and data's contents.
uintptr_t newBits = (bits & ~FAST_DATA_MASK) | (uintptr_t)newData;
atomic_thread_fence(memory_order_release);
bits = newBits;
}
#if FAST_HAS_DEFAULT_RR
bool hasDefaultRR() {
return getBit(FAST_HAS_DEFAULT_RR);
}
void setHasDefaultRR() {
setBits(FAST_HAS_DEFAULT_RR);
}
void setHasCustomRR() {
clearBits(FAST_HAS_DEFAULT_RR);
}
#else
bool hasDefaultRR() {
return data()->flags & RW_HAS_DEFAULT_RR;
}
void setHasDefaultRR() {
data()->setFlags(RW_HAS_DEFAULT_RR);
}
void setHasCustomRR() {
data()->clearFlags(RW_HAS_DEFAULT_RR);
}
#endif
#if FAST_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ
bool hasDefaultAWZ() {
return getBit(FAST_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ);
}
void setHasDefaultAWZ() {
setBits(FAST_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ);
}
void setHasCustomAWZ() {
clearBits(FAST_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ);
}
#else
bool hasDefaultAWZ() {
return data()->flags & RW_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ;
}
void setHasDefaultAWZ() {
data()->setFlags(RW_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ);
}
void setHasCustomAWZ() {
data()->clearFlags(RW_HAS_DEFAULT_AWZ);
}
#endif
#if FAST_HAS_CXX_CTOR
bool hasCxxCtor() {
return getBit(FAST_HAS_CXX_CTOR);
}
void setHasCxxCtor() {
setBits(FAST_HAS_CXX_CTOR);
}
#else
bool hasCxxCtor() {
return data()->flags & RW_HAS_CXX_CTOR;
}
void setHasCxxCtor() {
data()->setFlags(RW_HAS_CXX_CTOR);
}
#endif
#if FAST_HAS_CXX_DTOR
bool hasCxxDtor() {
return getBit(FAST_HAS_CXX_DTOR);
}
void setHasCxxDtor() {
setBits(FAST_HAS_CXX_DTOR);
}
#else
bool hasCxxDtor() {
return data()->flags & RW_HAS_CXX_DTOR;
}
void setHasCxxDtor() {
data()->setFlags(RW_HAS_CXX_DTOR);
}
#endif
#if FAST_REQUIRES_RAW_ISA
bool instancesRequireRawIsa() {
return getBit(FAST_REQUIRES_RAW_ISA);
}
void setInstancesRequireRawIsa() {
setBits(FAST_REQUIRES_RAW_ISA);
}
#elif SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
bool instancesRequireRawIsa() {
return data()->flags & RW_REQUIRES_RAW_ISA;
}
void setInstancesRequireRawIsa() {
data()->setFlags(RW_REQUIRES_RAW_ISA);
}
#else
bool instancesRequireRawIsa() {
return true;
}
void setInstancesRequireRawIsa() {
// nothing
}
#endif
#if FAST_ALLOC
size_t fastInstanceSize()
{
assert(bits & FAST_ALLOC);
return (bits >> FAST_SHIFTED_SIZE_SHIFT) * 16;
}
void setFastInstanceSize(size_t newSize)
{
// Set during realization or construction only. No locking needed.
assert(data()->flags & RW_REALIZING);
// Round up to 16-byte boundary, then divide to get 16-byte units
newSize = ((newSize + 15) & ~15) / 16;
uintptr_t newBits = newSize << FAST_SHIFTED_SIZE_SHIFT;
if ((newBits >> FAST_SHIFTED_SIZE_SHIFT) == newSize) {
int shift = WORD_BITS - FAST_SHIFTED_SIZE_SHIFT;
uintptr_t oldBits = (bits << shift) >> shift;
if ((oldBits & FAST_ALLOC_MASK) == FAST_ALLOC_VALUE) {
newBits |= FAST_ALLOC;
}
bits = oldBits | newBits;
}
}
bool canAllocFast() {
return bits & FAST_ALLOC;
}
#else
size_t fastInstanceSize() {
abort();
}
void setFastInstanceSize(size_t) {
// nothing
}
bool canAllocFast() {
return false;
}
#endif
void setClassArrayIndex(unsigned Idx) {
#if SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA
// 0 is unused as then we can rely on zero-initialisation from calloc.
assert(Idx > 0);
data()->index = Idx;
#endif
}
unsigned classArrayIndex() {
#if SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA
return data()->index;
#else
return 0;
#endif
}
bool isAnySwift() {
return isSwiftStable() || isSwiftLegacy();
}
bool isSwiftStable() {
return getBit(FAST_IS_SWIFT_STABLE);
}
void setIsSwiftStable() {
setBits(FAST_IS_SWIFT_STABLE);
}
bool isSwiftLegacy() {
return getBit(FAST_IS_SWIFT_LEGACY);
}
void setIsSwiftLegacy() {
setBits(FAST_IS_SWIFT_LEGACY);
}
};
struct class_rw_t {
// Be warned that Symbolication knows the layout of this structure.
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t version;
const class_ro_t *ro;
method_array_t methods; //二维数组,方法列表
property_array_t properties; //二维数组,属性列表
protocol_array_t protocols; //二维数组,协议列表
Class firstSubclass;
Class nextSiblingClass;
char *demangledName;
#if SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA
uint32_t index;
#endif
void setFlags(uint32_t set)
{
OSAtomicOr32Barrier(set, &flags);
}
void clearFlags(uint32_t clear)
{
OSAtomicXor32Barrier(clear, &flags);
}
// set and clear must not overlap
void changeFlags(uint32_t set, uint32_t clear)
{
assert((set & clear) == 0);
uint32_t oldf, newf;
do {
oldf = flags;
newf = (oldf | set) & ~clear;
} while (!OSAtomicCompareAndSwap32Barrier(oldf, newf, (volatile int32_t *)&flags));
}
};struct class_ro_t {
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t instanceStart;
uint32_t instanceSize;
#ifdef __LP64__
uint32_t reserved;
#endif
const uint8_t * ivarLayout;
const char * name; // 类名
method_list_t * baseMethodList; //一维数组
protocol_list_t * baseProtocols; //一维数组
const ivar_list_t * ivars; //声明定义的一些类的成员变量,一维数组
const uint8_t * weakIvarLayout;
property_list_t *baseProperties; //一维数组
method_list_t *baseMethods() const {
return baseMethodList;
}
};
struct method_t {
SEL name; //名称
/*
类型,返回值和参数的组合,对应四要素中的返回值和参数
Type Encodings技术
规顺序则:返回值 | 参数1 | 参数2.... 参数n
eg: -(void)aMethod; v@:
*/
const char *types;
MethodListIMP imp; //无类型的函数指针,对应四要素中的函数体
struct SortBySELAddress :
public std::binary_function<const method_t&,
const method_t&, bool>
{
bool operator() (const method_t& lhs,
const method_t& rhs)
{ return lhs.name < rhs.name; }
};
};总体来说,iOS对象中内存分布如下图
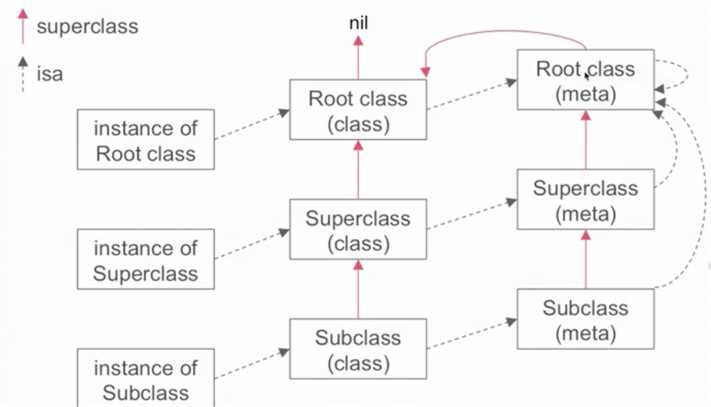
如图,当进行实例方法查找时会按照红线的走向在类对象中查找,进行类方法查找时会根据红线指向在元类中查找,如果在根元类中仍未找到对应的方法则会进行实例方法的查找
消息传递的机制?
消息转发流程
void countFindMethod() {
NSLog(@"未找到实例函数实现");
}
static void countFindClassMethod() {
NSLog(@"未找到类函数实现");
}
+ (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel
{
if ([NSStringFromSelector(sel) isEqualToString:@"unrealizeMethod"]) {
SEL aSel = NSSelectorFromString(@"unrealizeMethod");
//给方法添加
class_addMethod(objc_getMetaClass([NSStringFromClass(self) UTF8String]), aSel, countFindClassMethod, "v@");
return YES;
}
return NO;
}
//给开发者提供添加或调用其它方法的机会
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel
{
if ([NSStringFromSelector(sel) isEqualToString:@"unrealizeMethod"]) {
SEL aSel = NSSelectorFromString(@"unrealizeMethod");
//给方法添加
class_addMethod(self, aSel, countFindMethod, "v@");
return YES;
}
return NO;
}
//如果上面没有对消息进行处理,则进入该方法,该方法用于返回相应对象,如果不进行处理则进入methodSignatureForSelector:方法
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
// Student * std = [[Student alloc] init];
return nil;
}
//通过检查不是此方法本身的选择器并且不发送可能调用此方法的任何消息,请务必在必要时避免无限循环。aSelector,例如,如果您的代理只是将消息转发给名为的实例变量,它可以像这样实现:realObjectmethodSignatureForSelector:
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
return [realObject methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation
{
[anInvocation setTarget:realObject];
[anInvocation invoke];
}
//如果在上面的方法中仍未实现对消息的处理则会进入此步骤抛出错误
- (void)doesNotRecognizeSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
}
+ (void)load
{
Method method1 = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(test1));
Method method2 = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(test2));
method_exchangeImplementations(method1, method2);
}
- (void)test1
{
NSLog(@"test1函数");
}
- (void)test2
{
NSLog(@"test2函数");
}@dynamic与@synthesize的最基本的理解
//动态 添加类的名称
Class TestClass = objc_allocateClassPair([NSObject class], "LGClass", 0);
NSString * name = @"name";
//给类添加属性
class_addIvar(TestClass,name.UTF8String,sizeof(id),log2(sizeof(id)),@encode(id));
//注册类,在注册之前可以增加实例变量等内容,但是注册之后就无法添加实例变量了
objc_registerClassPair(TestClass);
id p = [TestClass alloc];
[p setValue:@"xiyangyag" forKey:@"name"];
NSLog(@"%@", [p valueForKey:@"name"]);标签:fas reference 内存 The ons extra sha 继承 交换
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/GoodmorningMr/p/11558706.html