标签:相等 lse 类型 习惯 count info 用户输入 demo str
实验三 String类的应用
1.已知字符串:"this is a test of java".按要求执行以下操作:(要求源代码、结果截图。)
package java实验报告三1; /* * 查找指定字符串中指定字符出现的次数 */ public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str="this is a test of java"; int count=0; char c[]=str.toCharArray(); for(int i=0;i<c.length;i++){ if(c[i]==‘s‘){ //char类型赋值用单引号 count++; } } System.out.println("s出现了"+count+"次"); } }
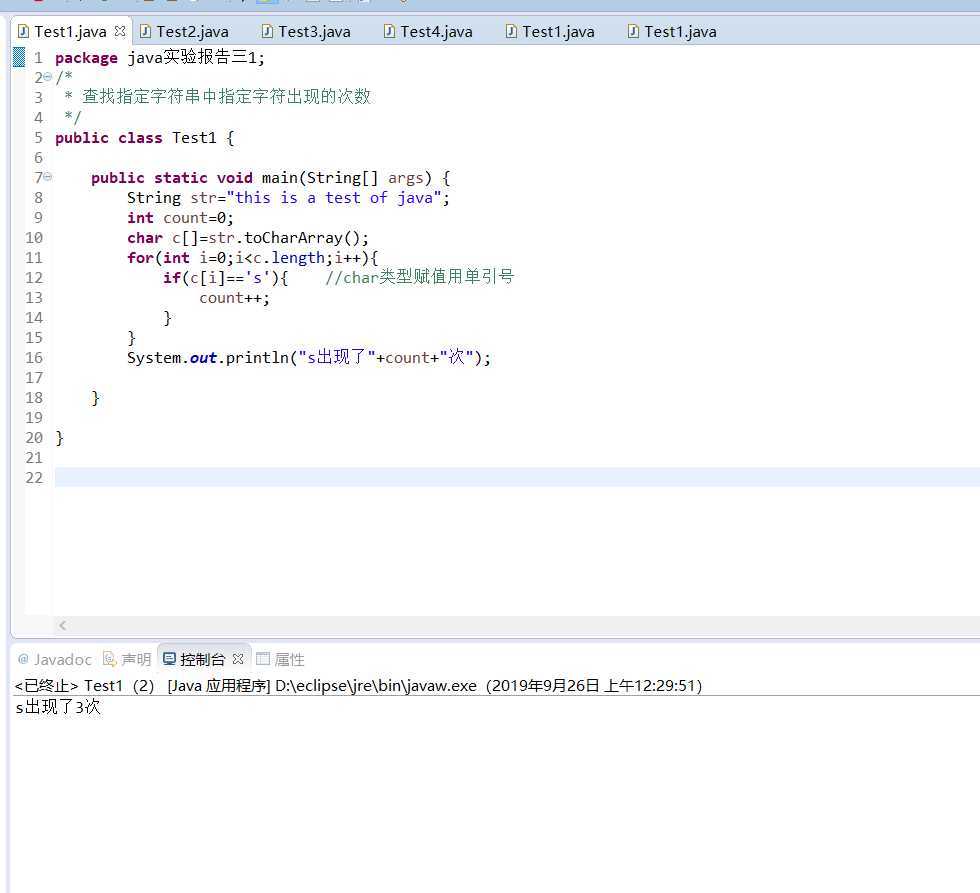
package java实验报告三1; /* * 查找一段字符串中指定字符串出现的次数 */ public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "this is a test of java"; int count = 0, index = 0; while (true) { int n = str.indexOf("is", index); // 从指定位置查找指定字符串的位置 if (n != -1) { index = n + 1; count++; } else { break; } } System.out.print("is出现了" + count + "次"); } }
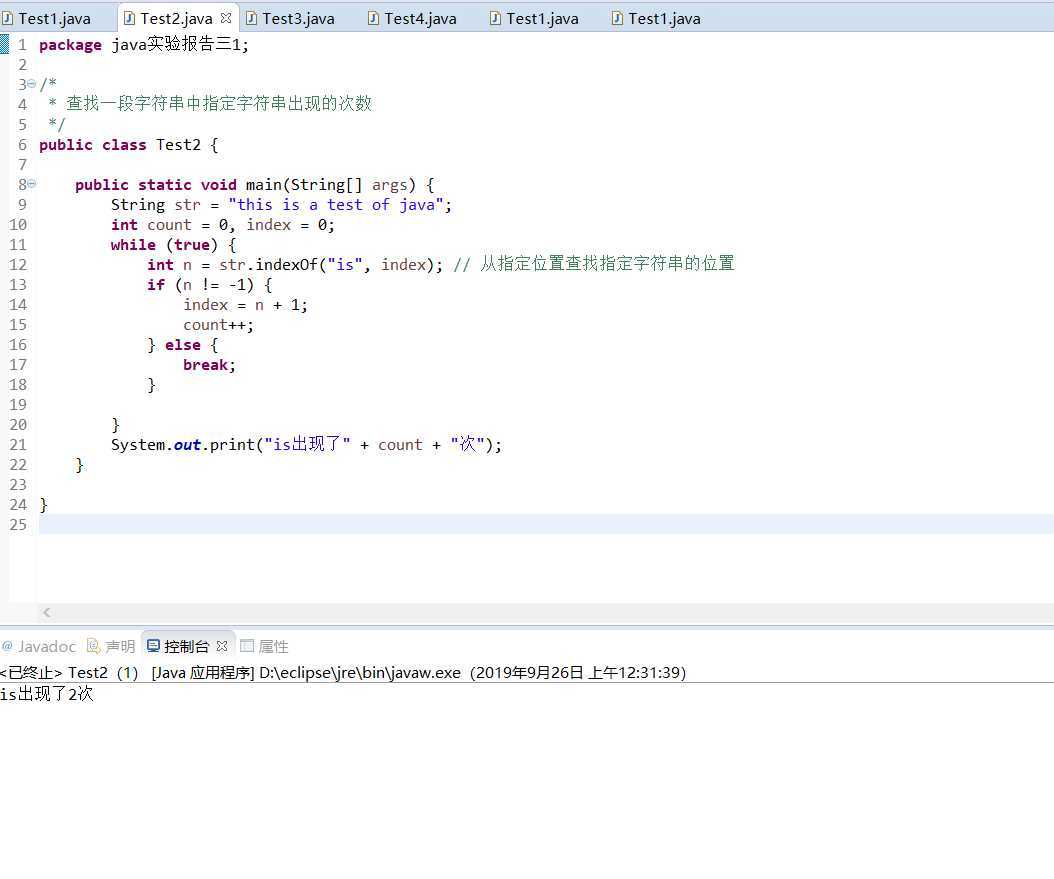
3.统计该字符串中单词“is”出现的次数。
package java实验报告三1; /* * 查找一句话中单词的出现次数 */ public class Test3 { public static void main(String[] args) { int count=0; String str="this is a test of java"; String s[]=str.split(" "); for(int i=0;i<s.length;i++){ if(s[i].equals("is")){ //判断内容相等 count++; } } System.out.println(count); } }
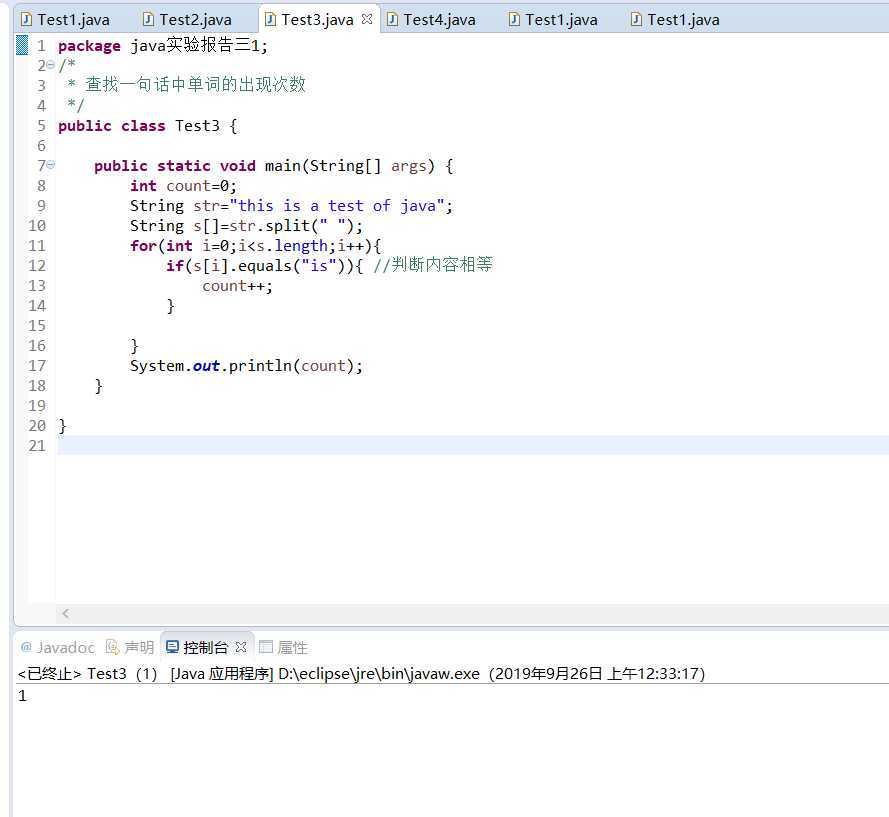
4. 实现该字符串的倒序输出。
package java实验报告三1; public class Test4 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "this is a test of java"; char s[] = str.toCharArray(); for (int i=s.length-1;i>=0;i--) { System.out.print(s[i]); } } }
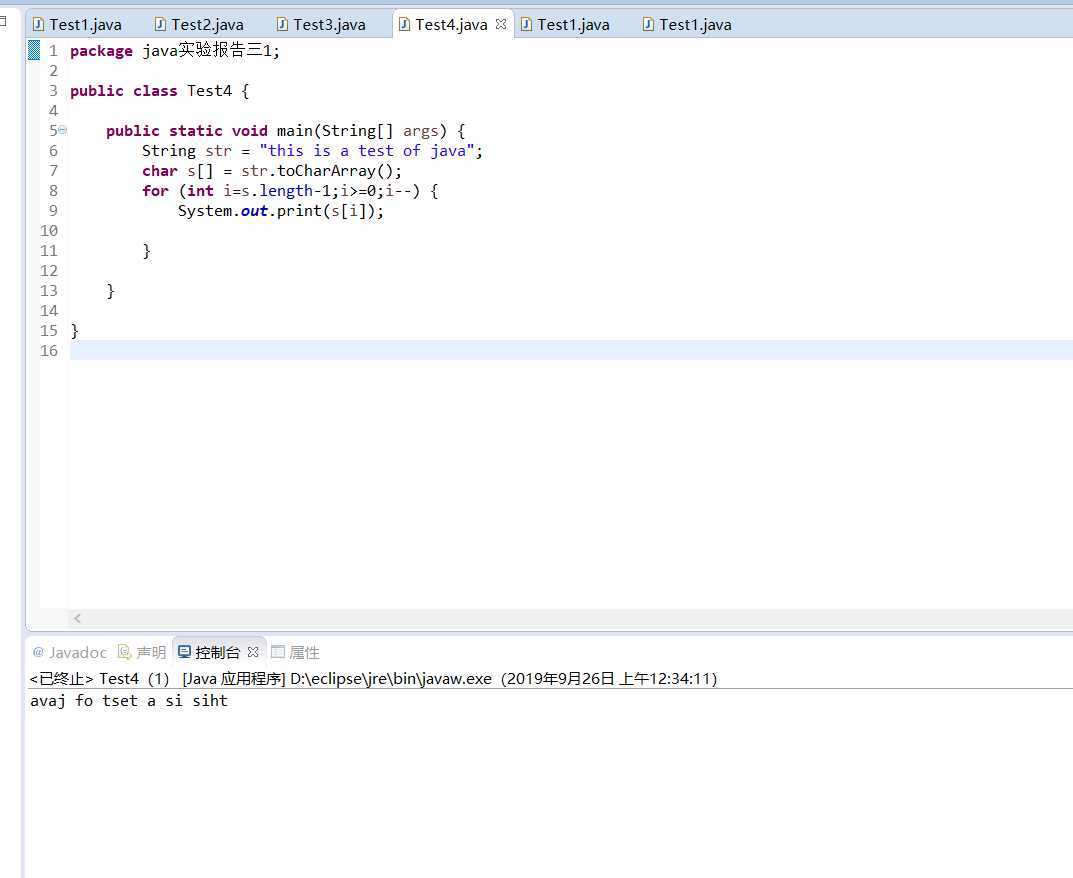

2.请编写一个程序,使用下述算法加密或解密用户输入的英文字串。要求源代码、结果截图。
package java实验报告三demo2; import java.util.Scanner; public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.print("输入一个字符串:"); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String str1 = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println(str1); char c[] = str1.toCharArray(); int ASCII; char c1; for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) { ASCII = c[i] + 3; // 字符转换为整型得到ASCII码并后移3位 // System.out.print(ASCII+" "); c1 = (char) ASCII; // 整型强制转换为字符型 // System.out.print(c1+" "); String s = String.valueOf(c1); // char型转换为String类型 System.out.print(s); } } }
总结:ASCII码是个有趣的东西。注意加密后的字符要连起来,所以经过几波操作后又变为String类型。

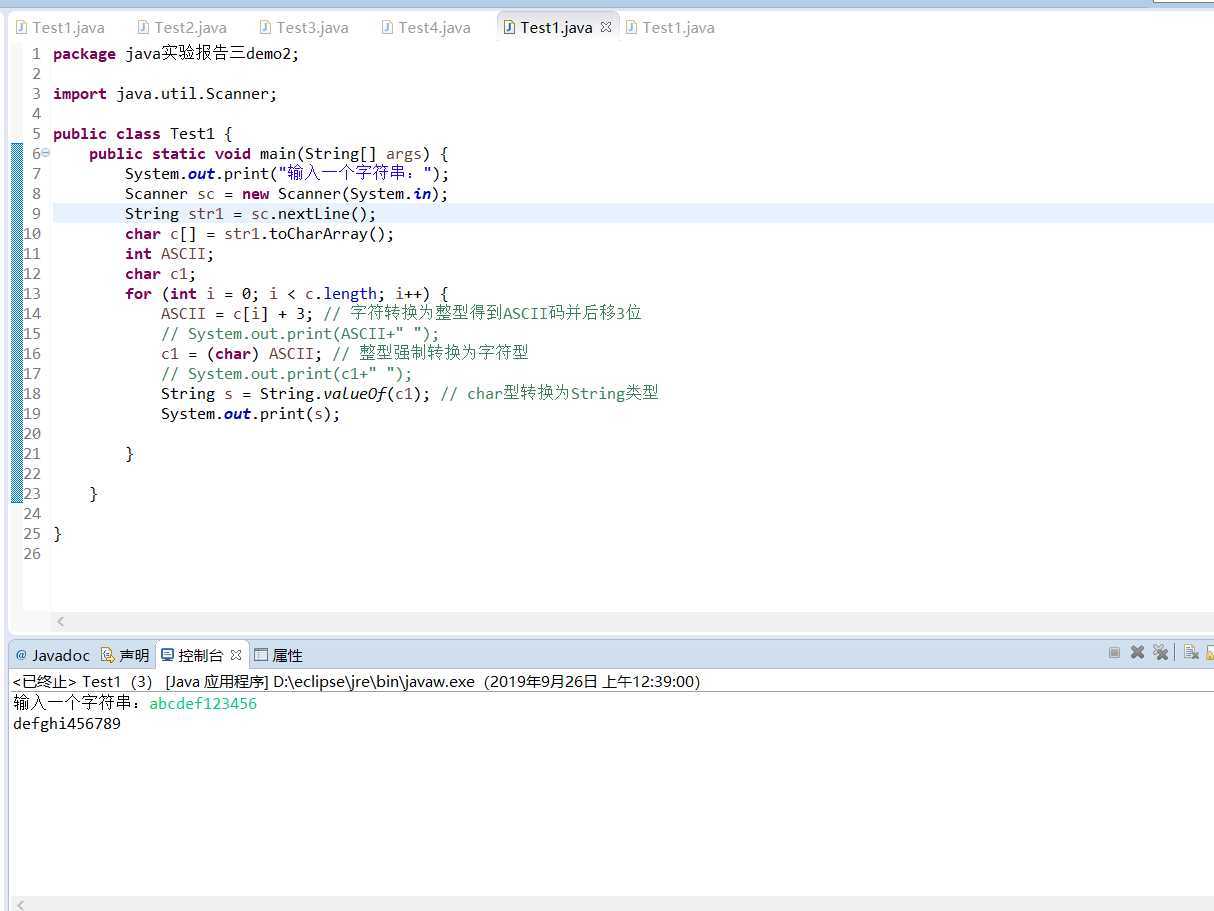
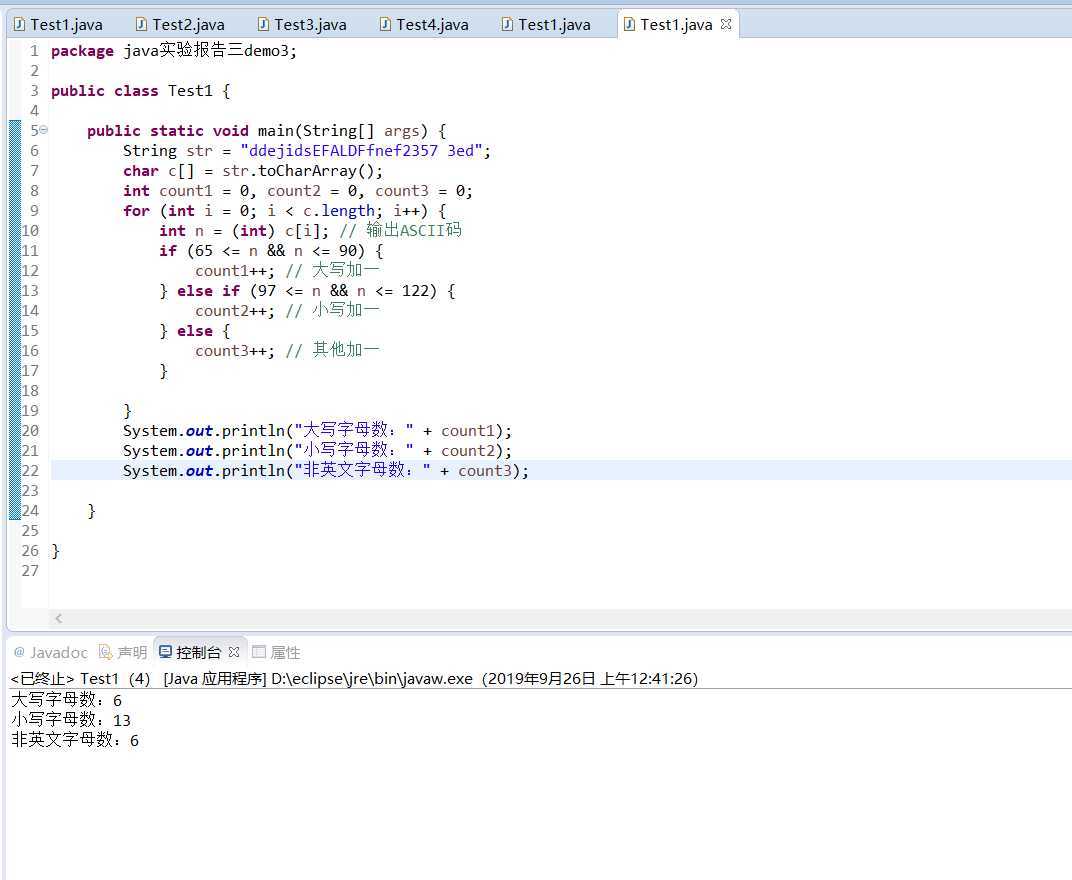
3.已知字符串“ddejidsEFALDFfnef2357 3ed”。输出字符串里的大写字母数,小写英文字母数,非英文字母数。
package java实验报告三demo3; public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "ddejidsEFALDFfnef2357 3ed"; char c[] = str.toCharArray(); int count1 = 0, count2 = 0, count3 = 0; for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) { int n = (int) c[i]; // 输出ASCII码 if (65 <= n && n <= 90) { count1++; // 大写加一 } else if (97 <= n && n <= 122) { count2++; // 小写加一 } else { count3++; // 其他加一 } } System.out.println("大写字母数:" + count1); System.out.println("小写字母数:" + count2); System.out.println("非英文字母数:" + count3); } }
总结:已知大写小写字母在ASCII表里的范围分别是65~90、97~122,所以只要转换一下再判断就OK。

本周总结:我主要学到了String类中常用的方法,整体来说还是很简单的,基本按照书上的套路来就对了,如果不会用这些方法,写特定程序的难度将大大增加,还有要养成看jdk文档的习惯。
标签:相等 lse 类型 习惯 count info 用户输入 demo str
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yanzi404/p/11588571.html