标签:tin efi nod lag dijkstra sizeof 重构 div 编号
重构代码2次终于AC了

你是说这个吗?
思路1:暴力搜索
错,大力搜索
BFS,把图存下来
期望得分:0 实际得分:15
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct node{ int step; int x,y;//空白格坐标 int chx,chy;//特殊格坐标 }; int n,m,Q; bool used[35][35]; int h=1,t=0; node q[5000005]; node st,ed,wh; bool flag=0; int ans=2147483647; int dx[4]={1,-1,0,0}; int dy[4]={0,0,1,-1}; void bfs(){ while(h<=t){ node u; u=q[h++]; if(u.step>17) continue; if(used[u.x][u.y]==0) continue; if(u.x<1&&u.x>n&&u.y<1&&u.y>m){ continue; } if(u.chx==ed.x&&u.chy==ed.y){ flag=1; ans=u.step; return; } for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ node v=u; v.step++; v.x+=dx[i],v.y+=dy[i]; if(v.x>=1&&v.x<=n&&v.y>=1&&v.y<=m){ if(used[u.x][u.y]==1&&used[v.x][v.y]==1){ if(u.chx==v.x&&u.chy==v.y){ v.chx=u.x,v.chy=u.y; } //cout<<u.x<<" "<<u.y<<" "<<v.step<<" "<<v.x<<" "<<v.y<<" "<<used[u.x][u.y]<<endl; q[++t]=v; } } } } } int main(){ //freopen("puzzle.in","r",stdin); //freopen("puzzle.out","w",stdout); scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&Q); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ scanf("%d",&used[i][j]); } } while(Q--){ scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d",&wh.x,&wh.y,&st.x,&st.y,&ed.x,&ed.y); h=1,t=0; q[++t]=wh; q[t].step=0; q[t].chx=st.x; q[t].chy=st.y; flag=0; ans=2147483647; bfs(); if(flag==0) printf("-1\n"); else printf("%d\n",ans); } return 0; } /* 3 4 2 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 3 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 3 2 */
我有一个彩色的评测!
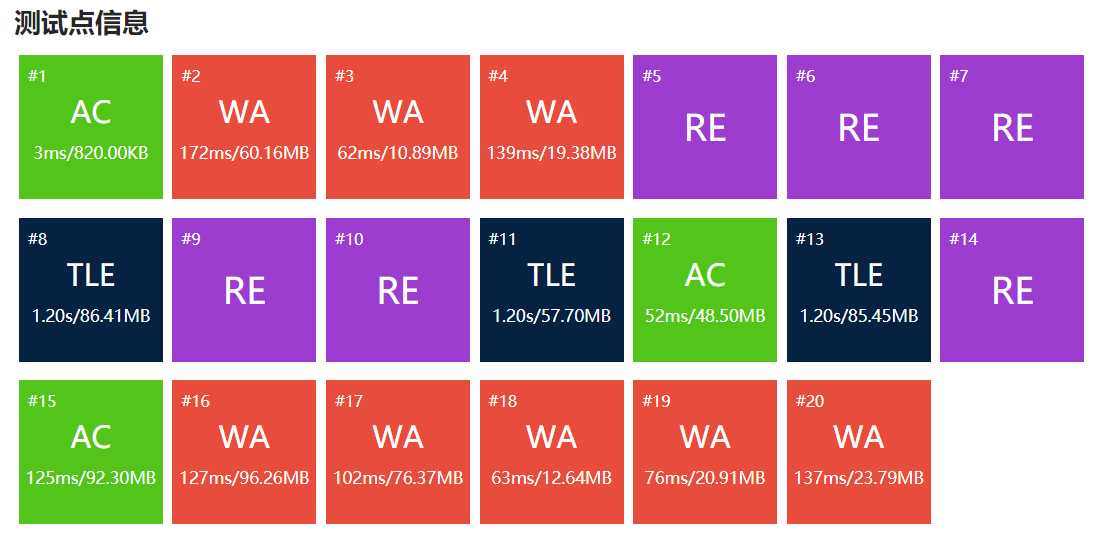
。。。。。。
然后我们想到只专注于空白格子和特殊格子,把他们离散化,跑最短路
期望得分:100 实际得分:60
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int N=35; const int M=3000005; #define re register struct node{ int state; int step; }; node q[M]; int h=1,t=0; struct cacha{ int po1,po2,po3,po4; }E[M]; int s[N][N]; int dis[M]; int n,m,Q; int pop[10]; int hush[N][N][N][N]; //hush[i][j][k][l]表示空格在i,j,绿在k,l时的离散化值 int num=0; int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1}; int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; int hed[M],tal[M],nxt[M],cnt=0; inline void addege(int x,int y){ cnt++; tal[cnt]=y; nxt[cnt]=hed[x]; hed[x]=cnt; } inline int bfs(int S,int ed_x,int ed_y){ memset(dis,-1,sizeof(dis)); h=1,t=0; q[++t].step=0,q[t].state=S; dis[S]=0; while(h<=t){ node u=q[h]; h++; //cout<<E[u.state].po1<<" "<<E[u.state].po2<<" "<<E[u.state].po3<<" "<<E[u.state].po4<<endl; for(re int i=hed[u.state];i;i=nxt[i]){ // cout<<"**"<<endl; int v=tal[i]; if(dis[v]>0) continue; dis[v]=dis[u.state]+1; if(E[v].po3==ed_x&&E[v].po4==ed_y){ return dis[v]; } t++; q[t].state=v; q[t].step=dis[v]; } } return -1; } int main(){ scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&Q); for(re int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(re int j=1;j<=m;j++){ scanf("%d",&s[i][j]); } } for(re int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(re int j=1;j<=m;j++){ for(re int k=1;k<=n;k++){ for(re int l=1;l<=m;l++){ if(s[i][j]==0||s[k][l]==0) continue; num++; hush[i][j][k][l]=num; E[num].po1=i; E[num].po2=j; E[num].po3=k; E[num].po4=l; } } } } for(re int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(re int j=1;j<=m;j++){ for(re int k=1;k<=n;k++){ for(re int l=1;l<=m;l++){ if(s[i][j]==0||s[k][l]==0) continue; for(re int o=0;o<4;o++){ int x,y; x=i+dx[o],y=j+dy[o]; if(s[x][y]==0) continue; if(x<1||y<1||x>n||y>m) continue; if(x==k&&y==l){ addege(hush[i][j][k][l],hush[k][l][i][j]); } else{ addege(hush[i][j][k][l],hush[x][y][k][l]); } } } } } } //cout<<num<<"**"<<endl; while(Q--){ for(re int i=1;i<=6;i++) scanf("%d",&pop[i]); int ans=bfs(hush[pop[1]][pop[2]][pop[3]][pop[4]],pop[5],pop[6]); printf("%d\n",ans); } return 0; }
打的我好辛苦,可惜就是A不了
但是,想想你玩的华容道
你一定是先把空白格子移到特殊格子边上,再继续
所以我们优化状态:f[x][y][z]表示特殊格子再xy,空白格子在z方向的哈希值
对于连边,有两种:
1.xy不变,换一个方向
记住:特殊格子不能走!
BFS计算长度
2.空白格子和特殊格子交换
边长为1,xy->x‘y‘ z->opposite_z
最后跑一边最短路
细节:
1.如果空白格子一开始就在特殊格子边上,就不用移动了
2.如果不用移动,输出0
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define re register #define il inline const int N=33; const int MAXN=990; const int M=500005; struct point{ int x,y; }; struct node{ int x,y; int step; }; //operator int n,m,Q; bool c[N][N];//原图 int h=1,t=0; node que[MAXN]; int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1};//移动数组 int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; bool vis[N][N];//是否到达过这一个点 int f[N][N][5];//f[i][j][k]:特殊块在i,j,白格子在k方向的编号 int hed[M],tal[M],val[M],nxt[M],cnt=0; int dis[M]; bool used[M]; il void addege(int x,int y,int z){ //printf("%d->%d(%d) #@!&^#&^#@&\n",x,y,z); if(y==0||x==0) return; cnt++; tal[cnt]=y; val[cnt]=z; nxt[cnt]=hed[x]; hed[x]=cnt; } il int bfs(int fromx,int fromy,int tox,int toy){//距离函数 if(fromx==tox&&fromy==toy) return 0; h=1,t=0; que[++t].step=0; que[t].x=fromx,que[t].y=fromy; memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); vis[fromx][fromy]=1; if(c[fromx][fromy]==0) return -1; while(h<=t){ node u=que[h]; h++; for(re int p=0;p<4;p++){ node v=u; v.step=u.step+1; v.x+=dx[p],v.y+=dy[p]; if(v.x<1||v.y<1||v.x>n||v.y>m) continue; if(vis[v.x][v.y]) continue; if(c[v.x][v.y]==0) continue; vis[v.x][v.y]=1; if(v.x==tox&&v.y==toy) return v.step; t++; que[t]=v; } } return -1; } struct aa { int v,pos; } ; bool operator<(const aa &a,const aa &b) { return a.v>b.v; } priority_queue<aa> q; void push(int v,int pos) { aa a; a.pos=pos,a.v=v; q.push(a); } il bool ischeck(point x){ if(x.x<1||x.y<1||x.x>n||x.y>m) return 0; if(c[x.x][x.y]==0) return 0; return 1; } inline int dijkstra(point W,point C,point T){ for(int i=0;i<M-2;i++) dis[i]=2147483647; memset(used,0,sizeof(used)); if(C.x==T.x&&C.y==T.y) return 0; for(int d=0;d<4;d++){ point W_=C; W_.x+=dx[d],W_.y+=dy[d]; if(!ischeck(W_)) continue; c[C.x][C.y]=0; int sum=bfs(W_.x,W_.y,W.x,W.y); c[C.x][C.y]=1; if(sum==-1) continue; push(sum,f[C.x][C.y][d]); dis[f[C.x][C.y][d]]=sum; //cout<<sum<<" #@&&^#^"<<endl; } while(!q.empty()) { aa u=q.top(); q.pop(); if(used[u.pos]==1) continue; used[u.pos]=1; //cout<<u.pos<<" "<<u.v<<" *@*&8"<<endl; for(re int i=hed[u.pos];i;i=nxt[i]){ int v=tal[i]; if(used[v]==0&&dis[v]>u.v+val[i]) { dis[v]=dis[u.pos]+val[i]; push(dis[v],v); } } } int ans=2147483647; for(int d=0;d<4;d++){ point W_=T; W_.x+=dx[d],W_.y+=dy[d]; if(!ischeck(W_)) continue; ans=min(ans,dis[f[T.x][T.y][d]]); } if(ans==2147483647) ans=-1; return ans; } il void debug1(){ int u; cin>>u; while(u--){ int x,y,z,i; scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z,&i); cout<<bfs(x,y,z,i)<<endl; } } int main(){ scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&Q); for(re int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(re int j=1;j<=m;j++){ scanf("%d",&c[i][j]); } } //debug1();check! int cttt=0; for(re int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(re int j=1;j<=m;j++){ if(c[i][j]==0) continue; for(re int d=0;d<4;d++){ point u; u.x=i+dx[d]; u.y=j+dy[d]; //if(!ischeck(u)) continue; cttt++; f[i][j][d]=cttt; } } } c[2][1]=0; c[2][1]=1; for(re int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(re int j=1;j<=m;j++){ if(c[i][j]==0) continue; for(re int d1=0;d1<4;d1++){ for(re int d2=0;d2<4;d2++){ if(d1==d2) continue; point x,y; x.x=i+dx[d1],x.y=j+dy[d1]; y.x=i+dx[d2],y.y=j+dy[d2]; if(!ischeck(x)) continue; if(!ischeck(y)) continue; c[i][j]=0; int ans=bfs(x.x,x.y,y.x,y.y); c[i][j]=1; if(ans==-1) continue; addege(f[i][j][d1],f[i][j][d2],ans); } } } } for(re int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(re int j=1;j<=m;j++){ if(c[i][j]==0) continue; for(re int d1=0;d1<4;d1++){ int opd; if(d1==0) opd=1; if(d1==1) opd=0; if(d1==2) opd=3; if(d1==3) opd=2; point bx,by; bx.x=i,bx.y=j; by.x=i+dx[d1],by.y=j+dy[d1]; if(!ischeck(bx)) continue; if(!ischeck(by)) continue; addege(f[bx.x][bx.y][d1],f[by.x][by.y][opd],1); } } } while(Q--){ point W,C,T; scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d",&W.x,&W.y,&C.x,&C.y,&T.x,&T.y); printf("%d\n",dijkstra(W,C,T)); } return 0; }
标签:tin efi nod lag dijkstra sizeof 重构 div 编号
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/QYJ060604/p/11618592.html