标签:block 一段 har 理解 mic 定位 行修改 res filter
博文大纲:
Nginx专为性能优化而开发,其最大的优点就是它的稳定性和低系统资源消耗,以及对http并发连接的高处理能力,单台物理服务器可支持20000~50000个并发请求,正是如此,大量提供社交网络、新闻资讯、电子商务及虚拟主机等服务的企业纷纷选择Nginx来提供web服务,目前中国大陆使用nginx网站用户有:新浪、网易、腾讯,另外知名的微网志Plurk也使用nginx。
Nginx是一个很牛的高性能Web和反向代理服务器,它具有有很多非常优越的特性:
- 高并发连接:官方测试能支撑5万并发连接,在实际生产环境中跑到2,~3W并发连接。
- 内存消耗少:在3W并发连接下,开启的10个NGINX进程才消耗150M内存(15M*10=150M)
- 配置文件非常简单:风格跟程序一样通俗易懂。
- 成本低廉:Nginx作为开源软件,可以免费使用,而购买F5 BIG-IP、NetScaler等硬件负载均衡交换机则需要十多万至几十万人民币。
- 支持rewrite重写规则:能够根据域名、URL的不同,将HTTP请求分发到不同的后端服务器群组。
内置的健康检查功能:如果Nginx Proxy后端的后台web服务器宕机了,不会影响前端访问。- 节省带宽:支持GZIP压缩,可以添加浏览器本地缓存的Header头。
- 稳定性高:用于反向代理,宕机的概率微乎其微。
对于一个 Web 服务器来说,一个请求的基本过程是:建立连接—接收数据—发送数据,在系统底层看来 :上述过程(建立连接—接收数据—发送数据)在系统底层就是读写事件。
如果采用阻塞调用的方式,当读写事件没有准备好时,那么就只能等待,当前线程被挂起,等事件准备好了,才能进行读写事件。
如果采用非阻塞调用的方式:事件马上返回,告诉你事件还没准备好呢,过会再来吧。过一会,再来检查一下事件,直到事件准备好了为止,在这期间,你就可以先去做其它事情,然后再来看看事件好了没。虽然不阻塞了,但你得不时地过来检查一下事件的状态,你可以做更多的事情了,但带来的开销也是不小的。非阻塞调用指在不能立刻得到结果之前,该调用不会阻塞当前线程
非阻塞通过不断检查事件的状态来判断是否进行读写操作,这样带来的开销很大,因此就有了异步非阻塞的事件处理机制。这种机制让你可以同时监控多个事件,调用他们是非阻塞的,但可以设置超时时间,在超时时间之内,如果有事件准备好了,就返回。这种机制解决了上面阻塞调用与非阻塞调用的两个问题。
以 epoll 模型为例:当事件没有准备好时,就放入 epoll(队列)里面。如果有事件准备好了,那么就去处理;当事件没有准备好时,才在 epoll 里面等着。这样,我们就可以并发处理大量的并发了,当然,这里的并发请求,是指未处理完的请求。线程只有一个,所以同时能处理的请求当然只有一个了,只是在请求之间进行不断地切换而已,切换也是因为异步事件未准备好,而主动让出的。这里的切换是没有任何代价,可以理解为循环处理多个准备好的事件。
多线程方式相比,这种事件处理方式是有很大的优势的,不需要创建线程,每个请求占用的内存也很少,没有上下文切换, 事件处理非常的轻量级,并发数再多也不会导致无谓的资源浪费(上下文切换)。对于 apache 服务器,每个请求会独占一个工作线程,当并发数上到几千时,就同时有几千的线程在处理请求了。这对操作系统来说,是个不小的挑战:因为线程带来的内存占用非常大,线程的上下文切换带来的 cpu 开销很大,自然性能就上不 去,从而导致在高并发场景下性能下降严重。
总结:通过异步非阻塞的事件处理机制,Nginx 实现由进程循环处理多个准备好的事件,从而实现高并发和轻量级。
环境准备:
- centos 7.3,IP地址为192.168.20.5
- 下载我提供的软件包,无需都下载,后面用到什么下载什么即可。
注:Nginx官方下载地址:http://nginx.org/download/
[root@nginx ~]# rz #在xshell中上传所需源码包
[root@nginx ~]# tar zxf nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz -C /usr/src #解包
[root@nginx ~]# cd /usr/src/nginx-1.14.0/ #切换至解压后的目录
[root@nginx nginx-1.14.0]# useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx #创建运行Nginx的用户
[root@nginx nginx-1.14.0]# yum -y erase httpd #卸载系统自带的httpd服务,以免冲突
[root@nginx nginx-1.14.0]# yum -y install openssl-devel pcre-devel
[root@nginx nginx-1.14.0]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module && make && make install
至此,就安装成功了
[root@nginx nginx-1.14.0]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx #启动Nginx服务
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.14.0 #注意,现在版本为nginx/1.14.0
.......................#省略部分信息
[root@nginx ~]# rz #在xshell中上传所需源码包
[root@nginx ~]# tar zxf nginx-1.2.4.tar.gz -C /usr/src #解压
[root@nginx ~]# cd /usr/src/nginx-1.2.4/ #切换至解压后的路径
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module && make
#注意,升级时,不要执行make install 命令,否则会覆盖原有的低版本配置文件
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# pwd #确认当前路径
/usr/src/nginx-1.2.4
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# mv /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx nginx.bak
#将旧版本的服务控制命令进行更名
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# cp objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ #复制新生成的控制命令至指定目录
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# kill -USR2 `cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid`
#生成新的PID号
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# kill -HUP `cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid` #重启Nginx服务
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V #查看是否已经升级
nginx version: nginx/1.2.4 #版本为1.2.4,升级成功一般是为了提高安全性,我们会对客户端进行隐藏Nginx的版本信息,具体操作如下:
#修改前,客户端访问,可以看到我们Nginx服务器的版本等信息,如下:
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# curl -I 127.0.0.1 #获取头部信息
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.2.4 #版本信息显示的很详细
Date: Thu, 17 Oct 2019 14:40:50 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 612
Last-Modified: Thu, 17 Oct 2019 14:20:40 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
Accept-Ranges: bytes
#现在进行修改如下:
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# pwd #确定当前工作路径在源码包中
/usr/src/nginx-1.2.4
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# vim src/core/nginx.h #修改该文件,随便修改即可
#define nginx_version 1002004
#define NGINX_VERSION "666" #这里为版本号信息
#define NGINX_VER "ljz/" NGINX_VERSION #这里原来为Nginx,现更改为ljz
#注意,上述配置项前面的注释符号不用删除
#更改完成后,保存退出即可
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# vim src/http/ngx_http_header_filter_module.c
#编辑该配置文件
static char ngx_http_server_string[] = "Server: ljz" CRLF;
#搜索“nginx”,定位到该行,然后更改其中原来的nginx为ljz,注意,这里必须和前一个配置文件中指定的名字一样
#更改完成后,保存退出即可
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# vim src/http/ngx_http_special_response.c #编辑此配置文件
static u_char ngx_http_error_tail[] = #注意,有一段配置和这段内容非常相似,主要区分这一行即可
#如果改错了,在后面将会报错
"<hr><center>ljz</center>" CRLF #将此行中间的nginx更改为ljz。
"</body>" CRLF
"</html>" CRLF
#更改完成后,保存退出即可
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module && make
#重新配置及编译
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# mv /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx nginx2.bak #将原有的nginx命令改名
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# cp objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ #复制新生成的nginx命令到指定目录
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop #停止nginx服务
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx #启动nginx
[root@nginx nginx-1.2.4]# curl -I 127.0.0.1 #查看其头部信息
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: ljz/666 #已经更改成功
...............#省略部分内容在nginx的主配置文件中,有一个http{ }的段落,在http{ }中还包含了server { },其中一个server { }就代表一个虚拟主机,可以在其中针对某个web服务配置不同的参数,这里说一下location { }的详细配置。
“=”号表示绝对匹配,访问网页的根目录可以但是访问后面带参数就不可以了,比如 127.0.0.1可以访问成功,但是127.0.0.1/html就访问不成功了。
[root@nginx ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/ #切换至指定目录
[root@nginx conf]# vim nginx.conf #编辑主配置文件
http {
...............#省略部分内容
server {
listen 80;
location = / { #这里设置为“= /”
root test;
index index.html index.htm;
}
...............#省略部分内容
}
}
[root@nginx nginx]# ln -sf /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload #多重载两次服务,否则可能不生效
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
[root@nginx nginx]# mkdir test
[root@nginx nginx]# echo "`pwd`/test/index.html" > test/index.html
[root@nginx nginx]# cat test/index.html
/usr/local/nginx/test/index.html客户端访问192.168.20.5进行测试: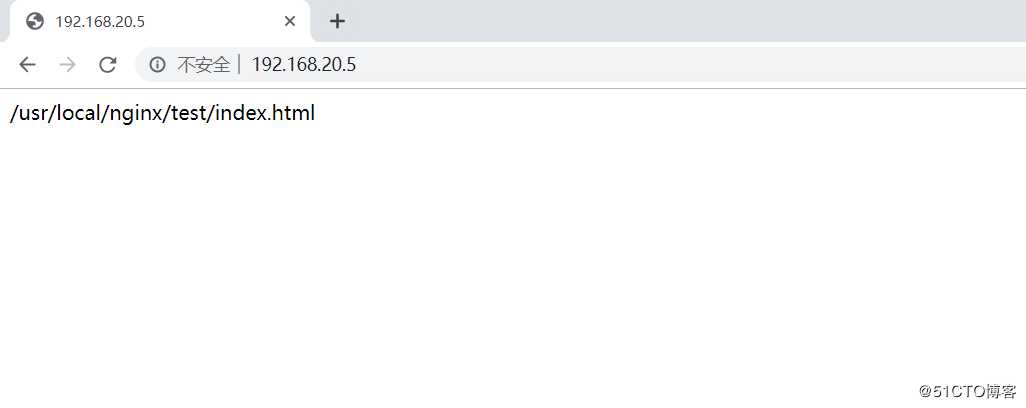
在下面的配置中,“ ^ ”表示以什么开头,“ ~ ”表示使用正则匹配表达式
1)现在将配置文件中的location改为如下内容:
[root@nginx conf]# vim nginx.conf #编辑主配置文件
http {
...............#省略部分内容
server {
listen 80;
location ^~ /www {
root /var/www/html; #当访问127.0.0.1/www时,会寻找/var/www/html路径下的www目录
index index.html index.htm;
}
...............#省略部分内容
}
}
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload #多重载两次服务,否则可能不生效
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
[root@nginx conf]# mkdir -p /var/www/html/www
[root@nginx conf]# echo "/var/www/html/www/index.html" > /var/www/html/www/index.html客户端访问192.168.20.5/www进行测试: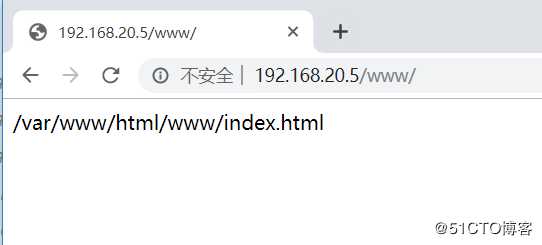
2)现在将配置文件中的location改为如下内容:
[root@nginx conf]# vim nginx.conf #编辑主配置文件
http {
...............#省略部分内容
server {
listen 80;
location ^~ /test02 {
alias /var/www/test02; #访问127.0.0.1/test02会寻找/var/www/test02目录下的网页文件
index index.html index.htm;
}
...............#省略部分内容
}
}
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
[root@nginx conf]# mkdir -p /var/www/test02
[root@nginx conf]# echo "/var/www/test02/index.html" > /var/www/test02/index.html客户端访问192.168.20.5/test02进行测试: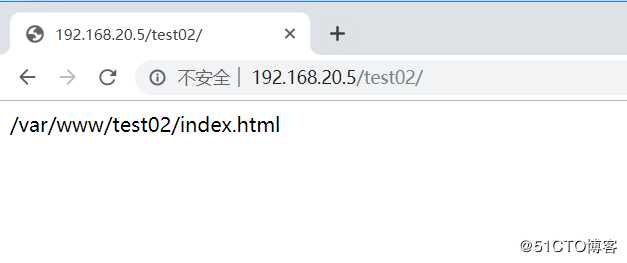
[root@nginx conf]# vim nginx.conf #编辑主配置文件
http {
...............#省略部分内容
server {
listen 80;
location ~* .(gif|jpg|png)$ {
rewrite .(gif|jpg)$ /error.png;
}
#以上表示当访问gif和jpg结尾的文件跳转到/usr/local/nginx/html/error.png
...............#省略部分内容
}
}
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
[root@nginx html]# pwd #查看当前路径
/usr/local/nginx/html
[root@nginx html]# ls #error.png需存放在这个目录下
50x.html error.png index.html客户端访问192.168.20.5/bb.gif进行测试:
[root@nginx conf]# vim nginx.conf #编辑主配置文件
http {
...............#省略部分内容
server {
listen 80;
if ($request_method = TEST) {
return 666;
}
#当客户端以TEST的方式访问时,返回状态码666
...............#省略部分内容
}
}
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload在本机执行命令 curl -X TEST -I 127.0.0.1 进行测试:
可以看到返回了我们指定的状态码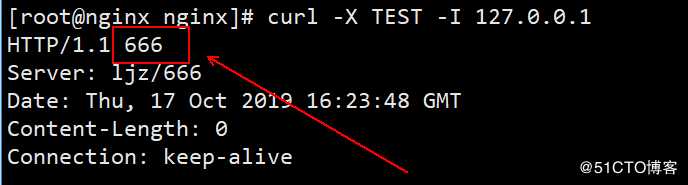
[root@nginx conf]# vim nginx.conf #编辑主配置文件
http {
...............#省略部分内容
server {
listen 80;
if ($host != ‘www.test.com‘){
rewrite ^/(.*)$ https://www.baidu.com/$1;
}
#以上表示当客户端不是通过www.test.com域名访问时,就跳转到百度首页
...............#省略部分内容
}
}
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -t
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload
[root@nginx nginx]# nginx -s reload客户端访问192.168.20.5进行测试:
由于我在截图之前,就访问了一次,所以,这里输入IP时,自动会和百度对应上。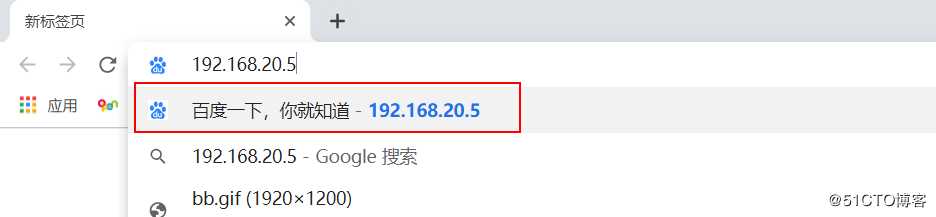
我们都知道http是80端口,https是443端口,由于https更加安全,所以现在大多数web服务都是通过https方式进行访问的,接下来,就配置一下https访问nginx服务器。
由于互联网认证的CA证书需要付费购买,所以这里就自己做一个,没有经过互联网认证的CA证书。
[root@nginx ca]# pwd #切换至指定目录
/usr/local/nginx/ca
[root@nginx ca]# openssl genrsa -out ca.key 4096 #生成秘钥文件
[root@nginx ca]# openssl req -new -x509 -days 7304 -key ca.key -out ca.crt
#以下所有填写的内容,可直接按回车,接收默认值
..................#省略部分内容
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:zh #国家名称
State or Province Name (full name) []:beijing #州或省名(全称)
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:beijing #城市名称
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:test #公司名称
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:operation #所在部门
Common Name (eg, your name or your server‘s hostname) []:test.com #主机名
Email Address []:lv916551516@163.com #邮箱
[root@nginx ca]# ls #确保当前目录下有下面两个文件
ca.crt ca.key
[root@nginx ca]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf #编辑主配置文件
..................#省略部分内容,搜索“HTTPS”定位到下面的配置项,并删除HTTPS下面server{ }所有的注释符号
#更改后如下(共修改两行即可):
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name localhost;
ssl_certificate /usr/local/nginx/ca/ca.crt; #就改这一行,指定ca.crt的绝对路径
ssl_certificate_key /usr/local/nginx/ca/ca.key; #再改这一行,指定ca.key的绝对路径
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
#更改完成后,保存退出即可
[root@nginx ca]# nginx -s reload #重启nginx
[root@nginx ca]# nginx -s reload客户端使用https访问测试(由于证书没有经过互联网认证的,所以会出现下面的警告信息,单击“高级”,选择继续访问即可):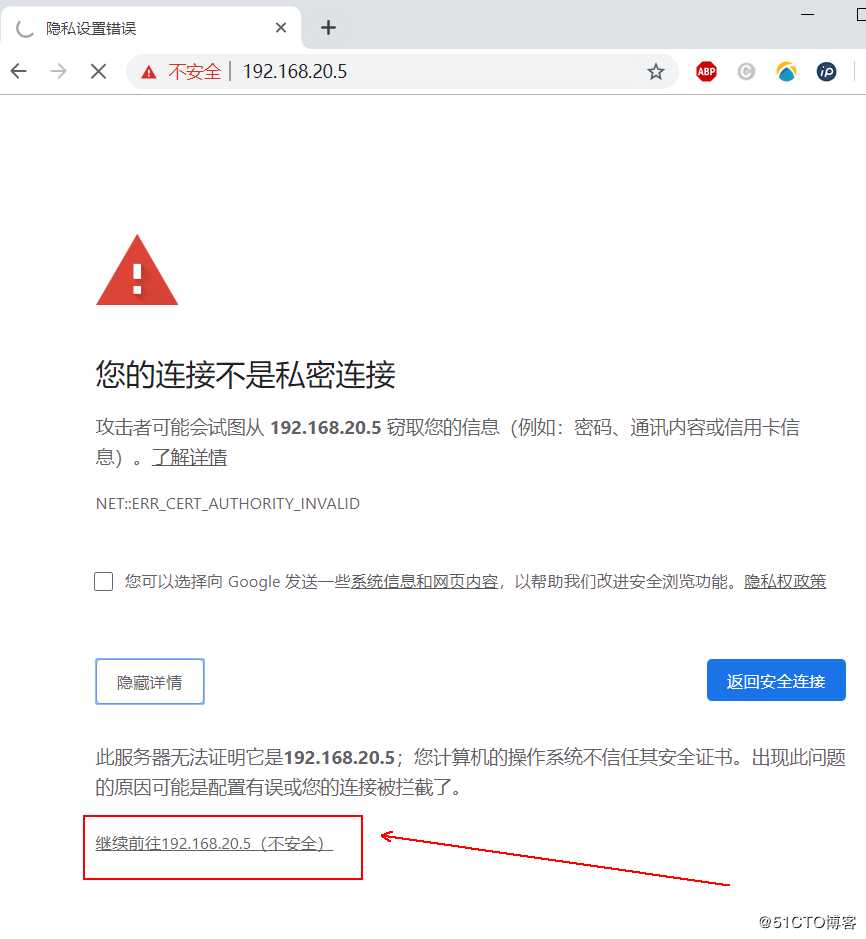
https访问成功: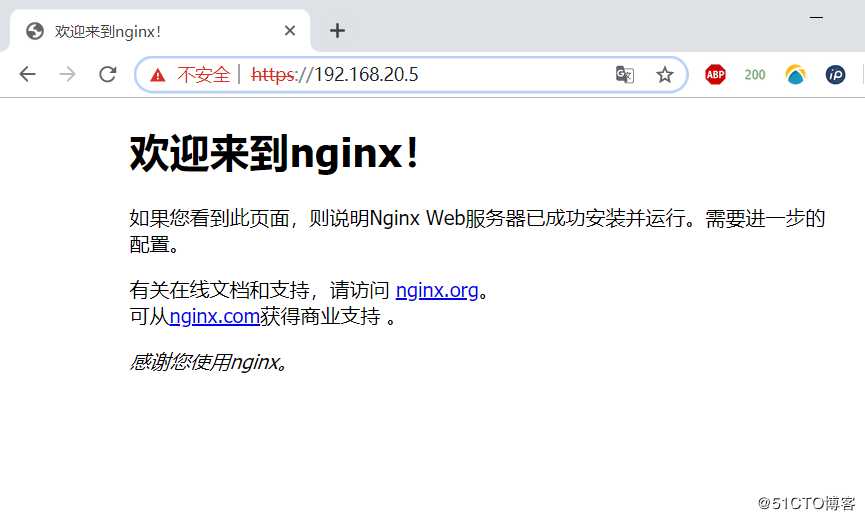
———————— 本文至此结束,感谢阅读 ————————
标签:block 一段 har 理解 mic 定位 行修改 res filter
原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/14154700/2443460