标签:for hashmap 帮助 equal except 根据 赋值 sed and
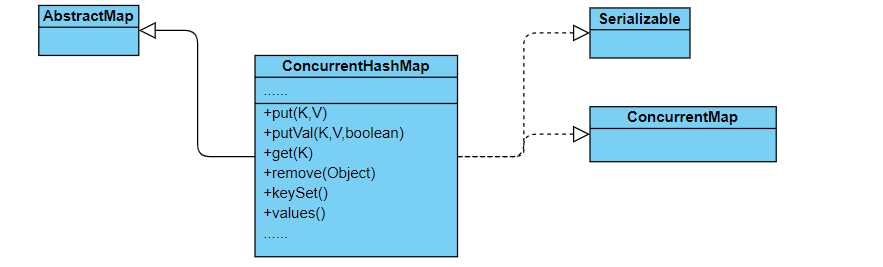
ConcurrentHashMap是1.5引入的用于高并发情况下的检索和更新。本文是基于jdk8的代码进行分析的,从put方法入手,来看下该结构是如何实现的。
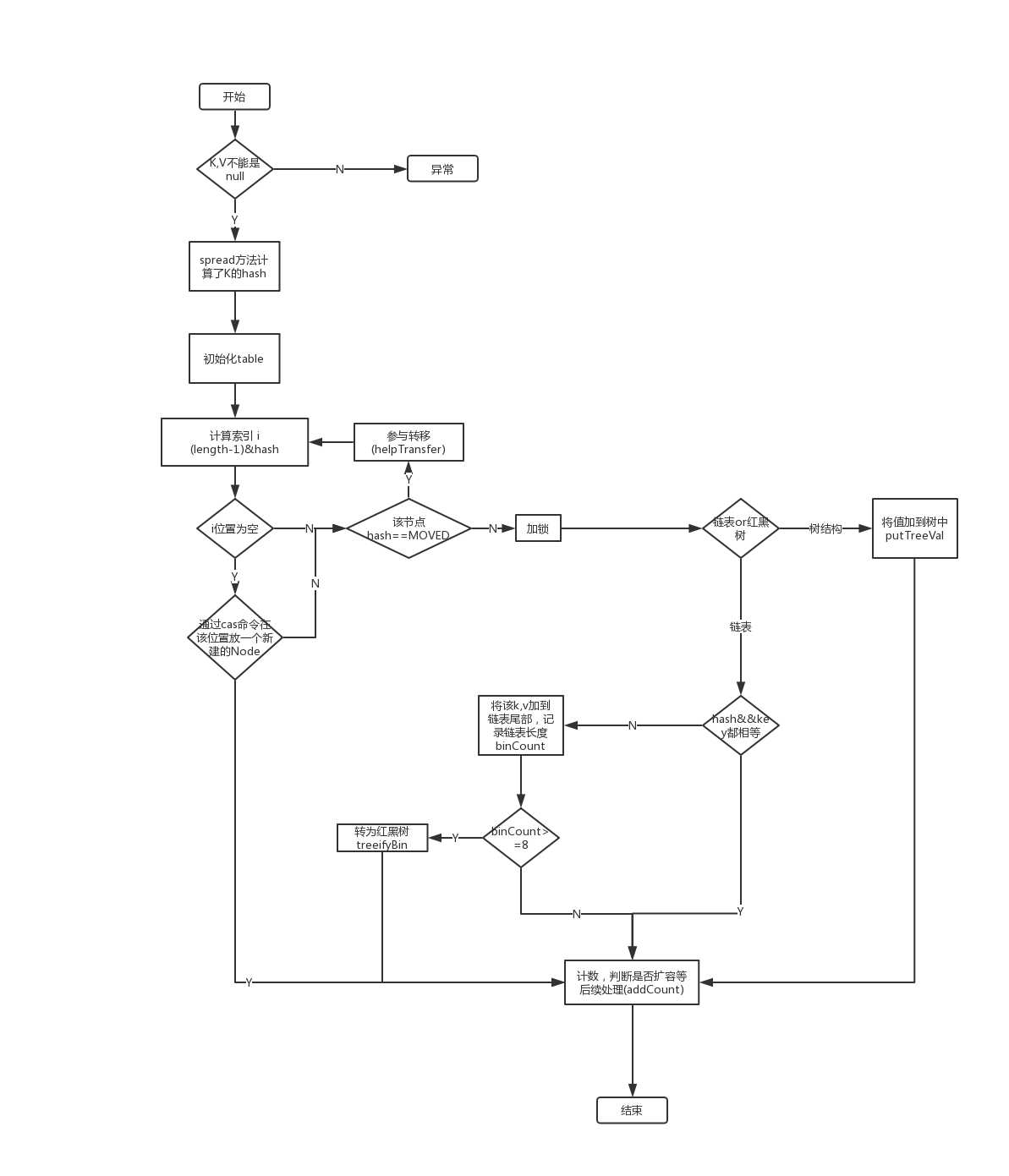
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
//计算hash
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
//默认就是0,代表链表的长度,如果key不碰撞都是0,
int binCount = 0;
//常见的自旋结构
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
//延迟加载tab,用来放Node的数组
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
//i的位置没有值
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
//通过cas将i位置设定为新node
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
//正在扩容的移动阶段
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
//i位置已经有值了
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
//hash和key都相同才认为是相同的key,然后根据onlyIfAbsent的值来决定是否覆盖值
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
//链表尾部添加新node
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
//红黑树结构
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
//将k,v添加到树中
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
//链表长度大于等于8,就将其转为红黑树结构
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
//计数及扩容的代码
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
//sizeCtl 是tab扩容和初始化的控制器,默认是0,可以进行操作,负的话就代表正在初始化或扩容,因为可以多个线程扩容,-N 就代表n个线程正在扩容
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
//CAS 设置 sizectl 设为-1,失败会跳过
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
//sc 为tab长度的 3/4
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
//此时sizeCtl 作为长度的3/4 ,后面作为是否需要扩容的一个判断条件
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
final Node<K,V>[] helpTransfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V> f) {
Node<K,V>[] nextTab; int sc;
//ForwardingNode 是一个空的节点,没有val,是当transfer时插入到头那做标识的,所以这里代表f 正处于transfer 状态。
if (tab != null && (f instanceof ForwardingNode) &&
(nextTab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)f).nextTable) != null) {
//根据tab的长度生成个印记戳
int rs = resizeStamp(tab.length);
while (nextTab == nextTable && table == tab &&
(sc = sizeCtl) < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) {
//具体转移的代码,transfer的入口主要是在addCount里面,该方法是协助transfer的入口。
transfer(tab, nextTab);
break;
}
}
return nextTab;
}
return table;
}
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
//计数器增加x,s为最终长度
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
CounterCell a; long v; int m;
boolean uncontended = true;
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
s = sumCount();
}
//需要检查是否要扩容,默认check为0 ,每次都检查
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
//长度大于sizeCtl,前面说了是长度的是四分之三,并且小于最大容量2^30
//n 为数组长度
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
//待扩容列表长度n的校验戳
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
//正在扩容
if (sc < 0) {
// 待扩容长度n的校验戳不一致 || 长度+1了,其他线程扩容完了 || 超过最大的resizers || 扩容完成(transfer里)||扩容完成(transfer里)
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
//添加帮助扩容线程
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
//扩容
transfer(tab, nt);
}
//将计算出来的校验戳变为sizectl的高位,2是低位,保证了上面 sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs 的可以校验长度不变化
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
s = sumCount();
}
}
} //扩容方法,该方法也比较长
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
int n = tab.length, stride;
//stride 是每个线程可处理的桶的数量,后面决定了nextBound的值
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
//初始化nextTab
if (nextTab == null) { // initiating
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];
//扩容为2倍
nextTab = nt;
//OOM
} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
nextTable = nextTab;
//从后向前遍历,<=0时遍历扩容完成
transferIndex = n;
}
int nextn = nextTab.length;
//table里面某个位置的首节点,代表移动了,会被当作判断条件
ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);
boolean advance = true;
boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab
//bound 是边界
for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int fh;
//获取该线程处理的桶的边界 以及负责向前推进下标i
//advance 是上面操作的控制器
while (advance) {
int nextIndex, nextBound;
// 向前推进下标
if (--i >= bound || finishing)
advance = false;
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
i = -1;
advance = false;
}
//当前参与扩容的线程给nextindex赋值,成功的话,bound设置为nextBound i=transferIndex-1,跳出循环
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
bound = nextBound;
i = nextIndex - 1;
advance = false;
}
}
// i=-1 是上面transferIndex<=0的条件,任务执行完毕
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc;
if (finishing) {
nextTable = null;
table = nextTab;
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);
return;
}
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return;
finishing = advance = true;
//配合上面的>=n 重新计算table和sizeCtl
i = n; // recheck before commit
}
}
//占位
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
//该位置已经处理过,重新计算i bound等,继续向前推进
advance = true; // already processed
else {
//f是当前i位置的节点
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node<K,V> ln, hn;
//fh是f的hash值
//链表操作
if (fh >= 0) {
int runBit = fh & n;
Node<K,V> lastRun = f;
//找到链表中最后一个hash 相同的节点,就是最后一个节点
for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
int b = p.hash & n;
if (b != runBit) {
runBit = b;
lastRun = p;
}
}
//ln 猜测是low node hn认为是 high node ,因为会拆出来两个链表
// hash&n ==0 一个判断标准,符合这样的,就作为ln,不符合的作为hn
if (runBit == 0) {
ln = lastRun;
hn = null;
}
else {
hn = lastRun;
ln = null;
}
//遍历所有节点,符合 hash & n == 0的 就放到ln的前面,不符合的就放到hn的前面
for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
if ((ph & n) == 0)
ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);
else
hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
}
//将ln 放到nexttab的i位置,high 放到i+n位置
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
//原tab 的i位置 放fwd占位
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
//继续往下推进
advance = true;
}
//红黑树操作
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {
int h = e.hash;
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>
(h, e.key, e.val, null, null);
if ((h & n) == 0) {
if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
lo = p;
else
loTail.next = p;
loTail = p;
++lc;
}
else {
if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
hi = p;
else
hiTail.next = p;
hiTail = p;
++hc;
}
}
ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;
hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
标签:for hashmap 帮助 equal except 根据 赋值 sed and
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/june777/p/11597678.html