标签:阈值 情况 rac The 如何 als 重要 接下来 appears
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
主要讲一下在JDK8中,ConcurrentLikedQueue是如何入队,出队的。
首先我们要明白,ConcurrentLikedQueue是一种安全的没有边界的基于链表的队列,有头节点head,尾结点tail。
类似于 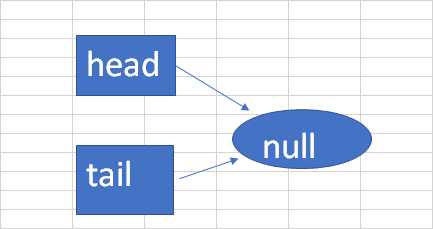 ,上图是创建一个空的队列,只有head和tail节点,以下为源码:
,上图是创建一个空的队列,只有head和tail节点,以下为源码:
public ConcurrentLinkedQueue() {
head = tail = new Node<E>(null);
}
对于入队来说,我们要了解的是tail节点不一定是最后一个节点,这是非常重要的。一般来说,当tail节点的next不为空时,在队尾加入新节点,更新tail的位置为最后一个节点;当tail的next节点为空时,在队尾加入新节点,不更新tail的位置。
源码中有一个注释:Both head and tail are permitted to lag. In fact, failing to update them every time one could is a significant optimization (fewer CASes). As with LinkedTransferQueue (see the internal documentation for that class), we use a slack threshold of two; that is, we update head/tail when the current pointer appears to be two or more steps away from the first/last node.
大概的意思是说不用每次都更新头尾节点,这是一个非常重要的优化。 使用的松弛阈值为2;
也就是说,当当前指针距离第一个/最后一个节点有两个或更多节点的距离时,我们更新head/tail。
在入队的时候,我们就能够很容易的看到上述所描述tail的特点。
入队:
1 /**
2 * Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue.
3 * As the queue is unbounded, this method will never return {@code false}.
4 * 将指定的元素插入到此队列的末尾。因为队列是无界的,所以这个方法永远不会返回{@code false}。
5
6 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
7 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
8 */
9 public boolean offer(E e) {
10 checkNotNull(e);
11 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e); //入队前构建节点
12
13 //从尾结点开始入队
14 for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t;;) {
15 Node<E> q = p.next;
16 if (q == null) { //tail是尾结点
17 // p is last node
18 //如果p是尾结点,设置p节点的next为newNode
19 if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) { //如果新节点添加入尾节点后面
20 // Successful CAS is the linearization point
21 // for e to become an element of this queue,
22 // and for newNode to become "live".
23 //成功的CAS是使e成为这个队列的一个元素,使newNode成为“活的”的线性化点。
24 if (p != t) // hop two nodes at a time一次跳转两个节点
25 casTail(t, newNode); // Failure is OK.
26 return true;
27 }
28 // Lost CAS race to another thread; re-read next
29 //丢失的CAS争用到另一个线程;重读next
30 }
31 else if (p == q)
32 // We have fallen off list. If tail is unchanged, it
33 // will also be off-list, in which case we need to
34 // jump to head, from which all live nodes are always
35 // reachable. Else the new tail is a better bet.
36 //我们从list上掉下来了。
37 //如果tail不变,它也是off-list,
38 //在这种情况下,我们需要跳转到head,从head可以到达所有活动节点。
39 //否则,新tail是个更好的选择。
40
41 p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head;
42 else
43 // Check for tail updates after two hops.
44 p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q;
45 }
46 }
上述的offer(E e)方法,即是向队列尾部添加元素。
首先,入队前构建结点newNode,接下来无限for循环,保证入队成功,所以该方法返回总是true。
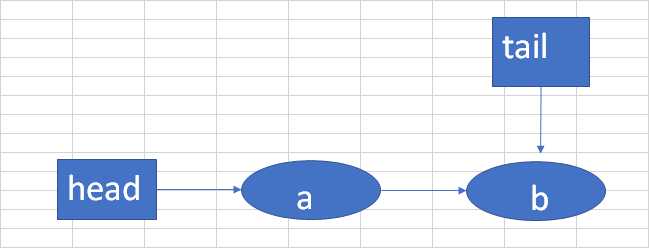
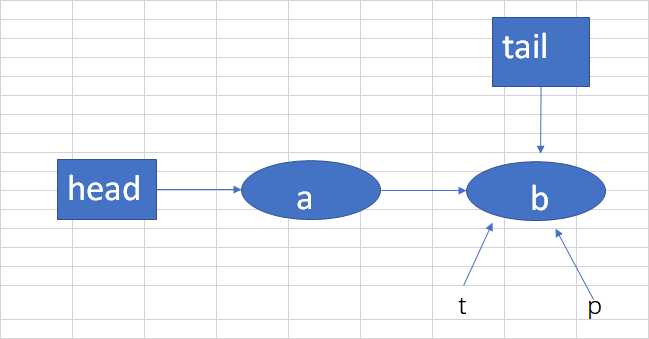
假设现在队列中有两个结点a,b,tail指向b。假如要加入一个c结点。t->tail,p->t,如下图:
标签:阈值 情况 rac The 如何 als 重要 接下来 appears
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xp1234/p/11735603.html