标签:sorted mapping 发送 sar 增加 目标 try commit concat
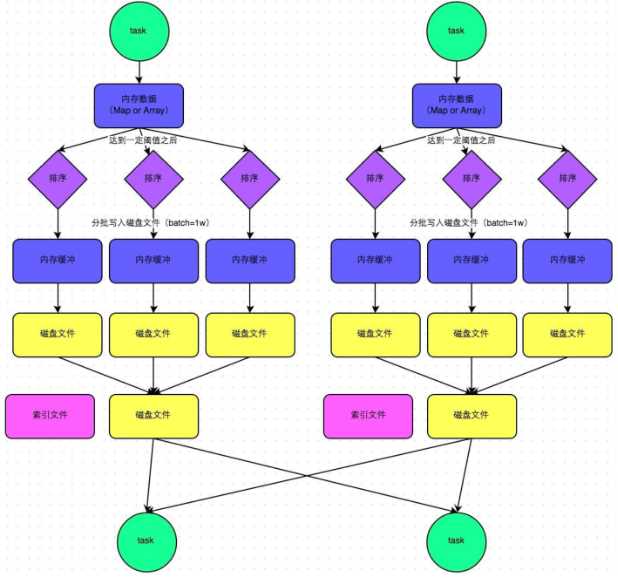
普通机制
示意图
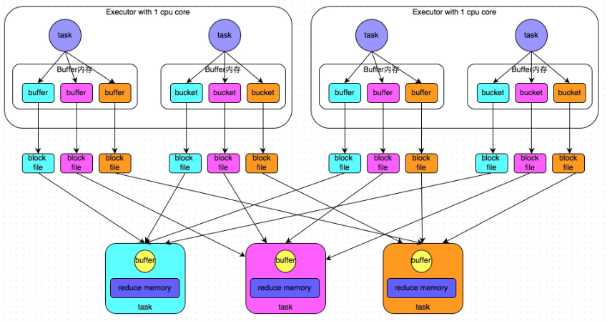
执行流程
总结
存在的问题
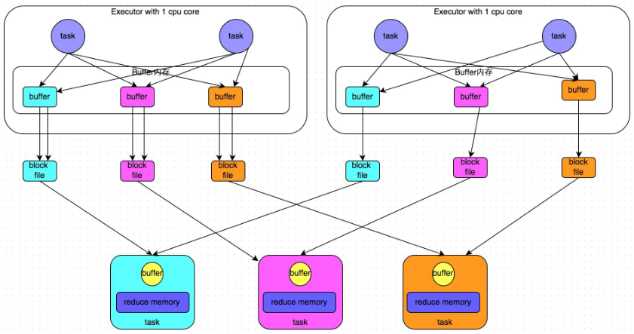
合并机制
合并机制示意图
源码
ShuffleManager(Trait)
package org.apache.spark.shuffle
import org.apache.spark.{ShuffleDependency, TaskContext}
/**
* Pluggable interface for shuffle systems. A ShuffleManager is created
* in SparkEnv on the driver and on each executor, based on the
* spark.shuffle.manager setting.
* shuffle 系统的可植入接口。在 SparkEnv(Spark 环境)中创建了一个
* 基于spark.shuffle.manager 设置的 ShuffleManager
* The driver registers shuffles with it, and executors (or tasks
* running locally in the driver) can ask to read and write data.
* driver 将 shuffle 任务注册, 并且executor进程(或者运行在本地的任务) 可以申
* 请数据的读写
* NOTE: this will be instantiated by SparkEnv so its constructor can
* take a SparkConf and boolean isDriver as parameters.
* 需要注意的是, 以上会被 SparkEnv(Env => Environment) 实例化 从而使它的构
* 造器能够获取一个 SparkConf(Spark 配置文件) 和 是否是 Driver 的标签
*/
private[spark] trait ShuffleManager {
/**
* Register a shuffle with the manager and obtain a handle for it to
* pass to tasks.
* 注册一个 带管理器的 shuffle 任务 并好获取一个将它发送给 任务集的 句柄
*/
//sortShuffle的实现
def registerShuffle[K, V, C](
shuffleId: Int,
numMaps: Int,
dependency: ShuffleDependency[K, V, C]): ShuffleHandle
/** Get a writer for a given partition. Called on executors by map
* tasks.
* 对已得的分区获取一个writer, 通过 map tasks 在 executor 进程上调用
*/
def getWriter[K, V](handle: ShuffleHandle, mapId: Int, context: TaskContext): ShuffleWriter[K, V]
/**
* Get a reader for a range of reduce partitions (startPartition to
* endPartition-1, inclusive).
* 根据一段reduce(规约)分区获取 reader
* Called on executors by reduce tasks.
* 通过 reduce tasks 在 executor进程上调用
*/
def getReader[K, C](
handle: ShuffleHandle,
startPartition: Int,
endPartition: Int,
context: TaskContext): ShuffleReader[K, C]
/**
* Remove a shuffle's metadata from the ShuffleManager.
* 从Shufflemanager 移除一个 shuffle 任务的 元数据
* @return true if the metadata removed successfully, otherwise false.
* 如果元数据被成功移除就返回true, 反之 false
*/
def unregisterShuffle(shuffleId: Int): Boolean
/**
* Return a resolver capable of retrieving shuffle block data based on
* block coordinates.
* 返回一个能基于block坐标来取回 shuffle block 中的数据的解析器
*/
def shuffleBlockResolver: ShuffleBlockResolver
/** Shut down this ShuffleManager.
* 关闭该 shuffleManager
*/
def stop(): Unit
}ShuffleReader(Trait)
package org.apache.spark.shuffle
/**
* Obtained inside a reduce task to read combined records from the
* mappers.
* 从一个 reduce task 内部 获取该 Trait的实例 以 从 mappers 中读取 总共的数据
*/
private[spark] trait ShuffleReader[K, C] {
/** Read the combined key-values for this reduce task
* 读取 此 reduce task 的所有键值对
*/
def read(): Iterator[Product2[K, C]]
/**
* Close this reader.关闭该 reader
* TODO: Add this back when we make the ShuffleReader a developer API
* that others can implement (at which point this will likely be 、
* necessary).
* 当我们将 ShuffleReader 作为一个他人可以实现的开发者的API时 将以下注释放
* 开(在某些情况下这可能是必须的).
*
*/
// def stop(): Unit
}ShuffleWriter
package org.apache.spark.shuffle
import java.io.IOException
import org.apache.spark.scheduler.MapStatus
/**
* Obtained inside a map task to write out records to the shuffle
* system.
* 该类 在一个 map task 获取, 用于将记录写出到Shuffle系统中。
*/
private[spark] abstract class ShuffleWriter[K, V] {
/** Write a sequence of records to this task's output
* 将一系列记录写入到该任务的输出中
*/
@throws[IOException]
//这里有相对应的 ShuffleWriter 实现
def write(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit
/** Close this writer, passing along whether the map completed
* 关闭该writer, 传回该map是否完成的 Boolean 标签
*/
def stop(success: Boolean): Option[MapStatus]SortShuffleManager
package org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap
import org.apache.spark._
import org.apache.spark.internal.Logging
import org.apache.spark.shuffle._
/**
* In sort-based shuffle, incoming records are sorted according to their
* target partition ids, then written to a single map output file.
* 在 sort-based(基于排序) 的 shuffle中, 将到来的记录都会根据他们的目标分区
* id 被排序, 然后被写入到一个简单的 map 输出文件
*
* Reducers fetch contiguous regions of this file in order to
* read their portion of the map output.
* Reducer 获取 该文件相邻的区域从而读取他们的 map 输出部分
*
* In cases where the map output data is too large to fit in memory,
* sorted subsets of the output can are spilled to disk and those on-
* disk files are merged to produce the final output file.
* 当 map 输出文件太大内存装不下时, 排序好的输出的子集可以被溢写到磁盘中, 并且
* 这些在磁盘中的(小)文件会被归并输出为最终文件
*
* Sort-based shuffle has two different write paths for producing its
* map output files:
* Sort-based shuffle 有两种不同的 产生map 输出文件 的 写路径
*
* - Serialized sorting: used when all three of the following
* conditions hold:
* 当以下所有三种 条件成立时, 使用serialized sorting(序列化的排序)
* 1. The shuffle dependency specifies no aggregation or output
* ordering.
* 1. shuffle 的依赖规定了 没有聚合 以及 输出排序
* 2. The shuffle serializer supports relocation of serialized values
* (this is currently supported by KryoSerializer and Spark SQL's custom
* serializers).
* 2. shuffle 的序列器 支持 序列化值的重新分配 (这目前 由 Kryo 序列器 和
* Spark SQK 的客户端序列器 所支持)
* 3. The shuffle produces fewer than 16777216 output partitions.
* 3. shuffle 任务产生了比16777216 更少的输出分区
*
* - Deserialized sorting: used to handle all other cases.
* - 不序列化的排序, 用于处理所有其他情况
* -----------------------
* Serialized sorting mode
* -----------------------
*
* In the serialized sorting mode, incoming records are serialized as
* soon as they are passed to the shuffle writer and are buffered in a
* serialized form during sorting.
* 在序列化的排序模式中, 即将到来的记录会在他们被传送到 shuffle writer 上时就
* 马上被序列化 并 在排序过程中 被缓存为 序列化的形式
*
* This write path implements several optimizations:
* 此写入路径 实现了许多优化
*
* - Its sort operates on serialized binary data rather than Java
* objects, which reduces memory consumption and GC overheads.
* 它的 排序直接操作 序列化的二进制数据 而不是 Java 对象, 这样就会减少内存消耗
* 和 GC(Garbage Collector) 开销
*
* This optimization requires the record serializer to have certain
* properties to allow serialized records to be re-ordered without
* requiring deserialization.
* 此优化需要记录的序列器依据有特定的性质来允许序列化的记录 在 不执行反序列化
* 的情况下被重新排序
*
* See SPARK-4550, where this optimization was first proposed and
* implemented, for more details.
* 该优化在 SPARK-4550 中第一次被提出并且实施, 更多细节请查询它
*
* - It uses a specialized cache-efficient
* sorter([[ShuffleExternalSorter]]) that sorts arrays of compressed
* record pointers and partition ids.
* 它使用了 一个特殊的 高效缓存排序器(ShuffleExternalSorter[外部的 shuffle
* 排序器]), 该排序器 对压缩过的记录点 数组 和 分区 id 数组 进行排序
*
* By using only 8 bytes of space per record in the sorting array, this
* fits more of the array into cache.
* 通过 对每条记录 仅使用 排序数组中 8 字节的 空间, 这使得更多的数组能被传入缓
* 存
*
* The spill merging procedure operates on blocks of serialized
* records that belong to the same partition and does not need to
* deserialize records during the merge.
* 溢写合并过程操作了序列化的记录所在的block(块), 这些记录属于相同分区, 并
* 且不需要 在合并期间将数据反序列化
*
* - When the spill compression codec supports concatenation of
* compressed data, the spill merge simply concatenates the serialized
* and compressed spill partitions to produce the final output
* partition.
* 当溢写压缩代码编译器 支持了 压缩数据 的合并时, 该溢写过程仅仅合并了序列化且
* 压缩的溢写分区来产生最终的输出分区.
*
* This allows efficient data copying methods, like NIO's `transferTo`,
* to be used and avoids the need to allocate decompression or copying
* buffers during the merge.
* 这使得数据能被高效地拷贝, 就像 NIO(Not Blocked IO) 中的 transferTo(转换
* 到), 在被使用时避免了在 合并时 分配解压缩 或 将缓存拷贝。
*
* For more details on these optimizations, see SPARK-7081.
* 对于这些优化的更多细节,请查询 SPARK-7081
*/
private[spark] class SortShuffleManager(conf: SparkConf) extends ShuffleManager with Logging {
if (!conf.getBoolean("spark.shuffle.spill", true)) {
logWarning(
"spark.shuffle.spill was set to false, but this configuration is ignored as of Spark 1.6+." +
" Shuffle will continue to spill to disk when necessary.")
}
/**
* A mapping from shuffle ids to the number of mappers producing
* output for those shuffles.
* 使用一个ConcurrentHashMap 来存储shuffles的中间结果
*/
private[this] val numMapsForShuffle = new ConcurrentHashMap[Int, Int]()
// 重写 shuffleBlock 解析器
override val shuffleBlockResolver = new IndexShuffleBlockResolver(conf)
/**
* Obtains a [[ShuffleHandle]] to pass to tasks.
* 获取一个 shuffle 句柄来传递任务
*/
/**
* SortShuffleManager中有几个重要的方法
* getReader :读取数据
* getWriter :写数据
* registerShuffle : 注册shuffle
*/
override def registerShuffle[K, V, C](
shuffleId: Int,
numMaps: Int,
dependency: ShuffleDependency[K, V, C]): ShuffleHandle = {
//判断是否使用sortShuffle 中的BypassMergeSort
if (SortShuffleWriter.shouldBypassMergeSort(conf, dependency)) {
// If there are fewer than spark.shuffle.sort.bypassMergeThreshold partitions and we don't
// need map-side aggregation, then write numPartitions files directly and just concatenate
// them at the end. This avoids doing serialization and deserialization twice to merge
// together the spilled files, which would happen with the normal code path. The downside is
// having multiple files open at a time and thus more memory allocated to buffers.
/**
* 如果是少于参数 spark.shuffle.sort.bypassMergeThreshold 的分区,不需要map端预聚合,直接向buffer 缓存区中写数据,最后将它们连接起来。
* 这样避免了在shuffle 落地文件合并时的 序列化和反序列 过程。缺点是需要分配更多的内存。
*/
new BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle[K, V](
shuffleId, numMaps, dependency.asInstanceOf[ShuffleDependency[K, V, V]])
} else if (SortShuffleManager.canUseSerializedShuffle(dependency)) {
// Otherwise, try to buffer map outputs in a serialized form, since this is more efficient:
//使用序列化的形式写入buffer缓存区,存的更多,高效
new SerializedShuffleHandle[K, V](
shuffleId, numMaps, dependency.asInstanceOf[ShuffleDependency[K, V, V]])
} else {
// Otherwise, buffer map outputs in a deserialized form:
//不使用序列化直接写入buffer缓存区
new BaseShuffleHandle(shuffleId, numMaps, dependency)
}
}
/**
* Get a reader for a range of reduce partitions (startPartition to 、
* endPartition-1, inclusive).
* 获取一段 reduce 分区的读取器
* Called on executors by reduce tasks.
* 在 executor 进程上被 reduce 任务调用
*/
override def getReader[K, C](
handle: ShuffleHandle,
startPartition: Int,
endPartition: Int,
context: TaskContext): ShuffleReader[K, C] = {
new BlockStoreShuffleReader(
handle.asInstanceOf[BaseShuffleHandle[K, _, C]], startPartition, endPartition, context)
}
/** Get a writer for a given partition. Called on executors by map
* tasks.
* 获取一段分区的写入者 在 executor 进程上被 map 任务调用
*/
override def getWriter[K, V](
handle: ShuffleHandle,
mapId: Int,
context: TaskContext): ShuffleWriter[K, V] = {
numMapsForShuffle.putIfAbsent(
handle.shuffleId, handle.asInstanceOf[BaseShuffleHandle[_, _, _]].numMaps)
val env = SparkEnv.get
handle match {
case unsafeShuffleHandle: SerializedShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked] =>
new UnsafeShuffleWriter(
env.blockManager,
shuffleBlockResolver.asInstanceOf[IndexShuffleBlockResolver],
context.taskMemoryManager(),
unsafeShuffleHandle,
mapId,
context,
env.conf)
case bypassMergeSortHandle: BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked] =>
new BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter(
env.blockManager,
shuffleBlockResolver.asInstanceOf[IndexShuffleBlockResolver],
bypassMergeSortHandle,
mapId,
context,
env.conf)
case other: BaseShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked, _] =>
new SortShuffleWriter(shuffleBlockResolver, other, mapId, context)
}
}
/** Remove a shuffle's metadata from the ShuffleManager. */
override def unregisterShuffle(shuffleId: Int): Boolean = {
Option(numMapsForShuffle.remove(shuffleId)).foreach { numMaps =>
(0 until numMaps).foreach { mapId =>
shuffleBlockResolver.removeDataByMap(shuffleId, mapId)
}
}
true
}
/** Shut down this ShuffleManager. */
override def stop(): Unit = {
shuffleBlockResolver.stop()
}
}
private[spark] object SortShuffleManager extends Logging {
/**
* The maximum number of shuffle output partitions that SortShuffleManager supports when
* buffering map outputs in a serialized form. This is an extreme defensive programming measure,
* since it's extremely unlikely that a single shuffle produces over 16 million output partitions.
* */
val MAX_SHUFFLE_OUTPUT_PARTITIONS_FOR_SERIALIZED_MODE =
PackedRecordPointer.MAXIMUM_PARTITION_ID + 1
/**
* Helper method for determining whether a shuffle should use an optimized serialized shuffle
* path or whether it should fall back to the original path that operates on deserialized objects.
*/
def canUseSerializedShuffle(dependency: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]): Boolean = {
val shufId = dependency.shuffleId
val numPartitions = dependency.partitioner.numPartitions
if (!dependency.serializer.supportsRelocationOfSerializedObjects) {
log.debug(s"Can't use serialized shuffle for shuffle $shufId because the serializer, " +
s"${dependency.serializer.getClass.getName}, does not support object relocation")
false
} else if (dependency.aggregator.isDefined) {
log.debug(
s"Can't use serialized shuffle for shuffle $shufId because an aggregator is defined")
false
} else if (numPartitions > MAX_SHUFFLE_OUTPUT_PARTITIONS_FOR_SERIALIZED_MODE) {
log.debug(s"Can't use serialized shuffle for shuffle $shufId because it has more than " +
s"$MAX_SHUFFLE_OUTPUT_PARTITIONS_FOR_SERIALIZED_MODE partitions")
false
} else {
log.debug(s"Can use serialized shuffle for shuffle $shufId")
true
}
}
}
/**
* Subclass of [[BaseShuffleHandle]], used to identify when we've chosen to use the
* serialized shuffle.
*/
private[spark] class SerializedShuffleHandle[K, V](
shuffleId: Int,
numMaps: Int,
dependency: ShuffleDependency[K, V, V])
extends BaseShuffleHandle(shuffleId, numMaps, dependency) {
}
/**
* Subclass of [[BaseShuffleHandle]], used to identify when we've chosen to use the
* bypass merge sort shuffle path.
*/
private[spark] class BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle[K, V](
shuffleId: Int,
numMaps: Int,
dependency: ShuffleDependency[K, V, V])
extends BaseShuffleHandle(shuffleId, numMaps, dependency) {
}SortShuffleWriter
package org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort
import org.apache.spark._
import org.apache.spark.internal.Logging
import org.apache.spark.scheduler.MapStatus
import org.apache.spark.shuffle.{BaseShuffleHandle, IndexShuffleBlockResolver, ShuffleWriter}
import org.apache.spark.storage.ShuffleBlockId
import org.apache.spark.util.Utils
import org.apache.spark.util.collection.ExternalSorter
private[spark] class SortShuffleWriter[K, V, C](
shuffleBlockResolver: IndexShuffleBlockResolver,
handle: BaseShuffleHandle[K, V, C],
mapId: Int,
context: TaskContext)
extends ShuffleWriter[K, V] with Logging {
private val dep = handle.dependency
private val blockManager = SparkEnv.get.blockManager
private var sorter: ExternalSorter[K, V, _] = null
// Are we in the process of stopping? Because map tasks can call stop() with success = true
// and then call stop() with success = false if they get an exception, we want to make sure
// we don't try deleting files, etc twice.
private var stopping = false
private var mapStatus: MapStatus = null
private val writeMetrics = context.taskMetrics().shuffleWriteMetrics
/** Write a bunch of records to this task's output */
override def write(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
sorter = if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
require(dep.aggregator.isDefined, "Map-side combine without Aggregator specified!")
new ExternalSorter[K, V, C](
context, dep.aggregator, Some(dep.partitioner), dep.keyOrdering, dep.serializer)
} else {
// In this case we pass neither an aggregator nor an ordering to the sorter, because we don't
// care whether the keys get sorted in each partition; that will be done on the reduce side
// if the operation being run is sortByKey.
new ExternalSorter[K, V, V](
context, aggregator = None, Some(dep.partitioner), ordering = None, dep.serializer)
}
//每次数据溢写磁盘
sorter.insertAll(records)
// Don't bother including the time to open the merged output file in the shuffle write time,
// because it just opens a single file, so is typically too fast to measure accurately
// (see SPARK-3570).
//下面就是将数据写往一个文件
val output = shuffleBlockResolver.getDataFile(dep.shuffleId, mapId)
val tmp = Utils.tempFileWith(output)
try {
val blockId = ShuffleBlockId(dep.shuffleId, mapId, IndexShuffleBlockResolver.NOOP_REDUCE_ID)
val partitionLengths = sorter.writePartitionedFile(blockId, tmp)
shuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit(dep.shuffleId, mapId, partitionLengths, tmp)
mapStatus = MapStatus(blockManager.shuffleServerId, partitionLengths)
} finally {
if (tmp.exists() && !tmp.delete()) {
logError(s"Error while deleting temp file ${tmp.getAbsolutePath}")
}
}
}
/** Close this writer, passing along whether the map completed */
override def stop(success: Boolean): Option[MapStatus] = {
try {
if (stopping) {
return None
}
stopping = true
if (success) {
return Option(mapStatus)
} else {
return None
}
} finally {
// Clean up our sorter, which may have its own intermediate files
if (sorter != null) {
val startTime = System.nanoTime()
sorter.stop()
writeMetrics.incWriteTime(System.nanoTime - startTime)
sorter = null
}
}
}
}
private[spark] object SortShuffleWriter {
def shouldBypassMergeSort(conf: SparkConf, dep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]): Boolean = {
// We cannot bypass sorting if we need to do map-side aggregation.
if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
//map 端有预聚合的操作,不能使用bypass 机制
require(dep.aggregator.isDefined, "Map-side combine without Aggregator specified!")
false
} else {
//map 端没有预聚合,但是分区大于 参数 spark.shuffle.sort.bypassMergeThreshold = 200 也不能使用bypass 机制。
val bypassMergeThreshold: Int = conf.getInt("spark.shuffle.sort.bypassMergeThreshold", 200)
dep.partitioner.numPartitions <= bypassMergeThreshold
}
}
}总结
普通机制
示意图
执行流程
总结
bypass机制
示意图
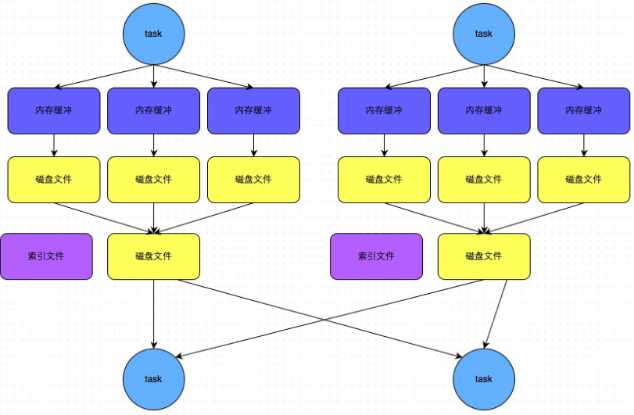
总结
MapOutputTracker
BlockManager
Shuffle文件寻址图
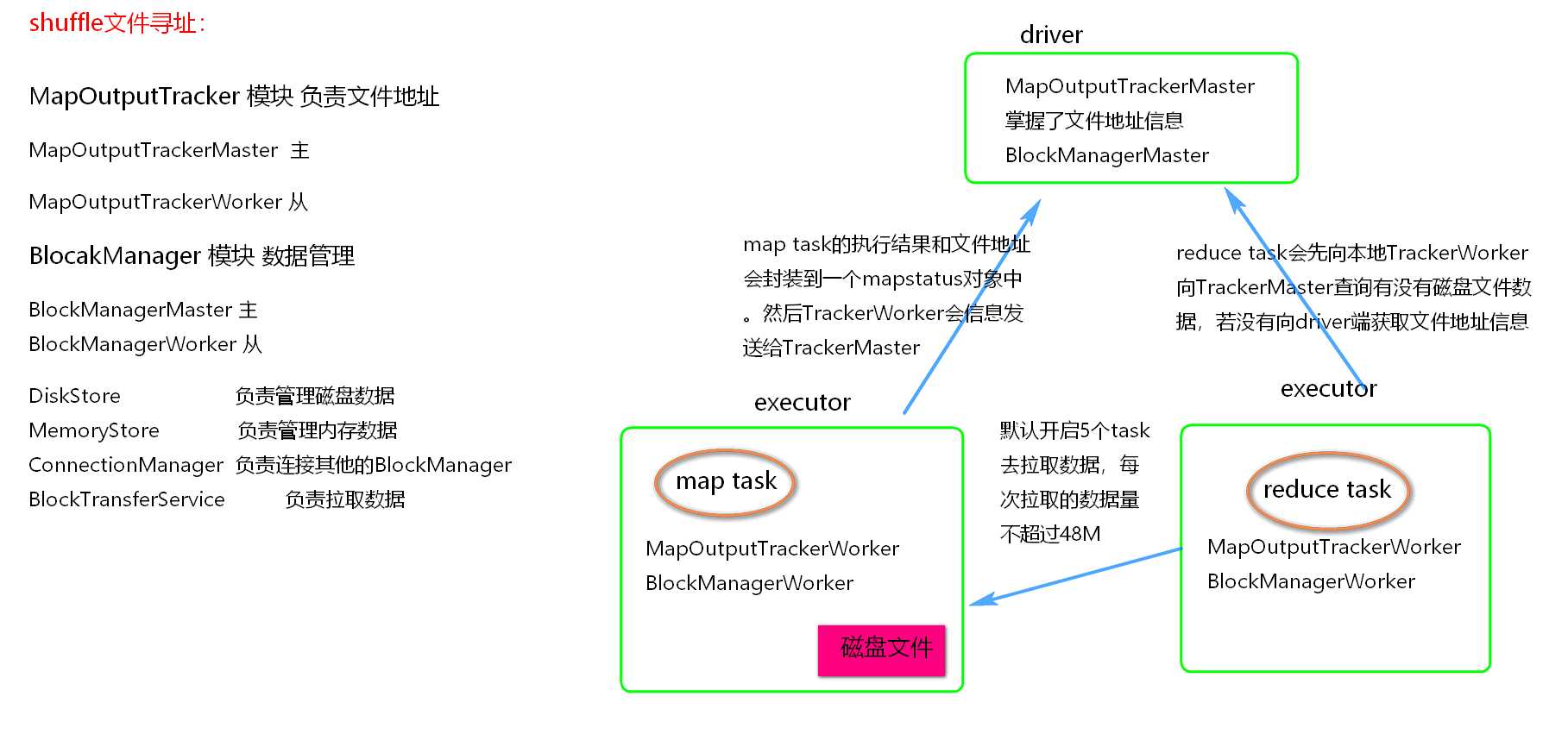
Shuffle 文件寻址流程
标签:sorted mapping 发送 sar 增加 目标 try commit concat
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ronnieyuan/p/11741768.html