标签:结果 lex 不同 real 介绍 因此 自定义数据类型 方式 实现
多态是指同样的消息被不同类型的对象接收时导致不同的行为。
例如:使用同样的加号"+",就可以实现整型数之间、浮点数之间、双精度浮点数之间的加法,以及这几种数据类型混合的加法运算。
分为4类:重载多态、强制多态、包含多态和参数多态
该部分用来介绍如何通过运算符重载来扩充运算符的作用
运算符的重载形式有两种,即重载为类的非静态成员函数和重载为非成员函数。运算符重载为类的成员函数的一般语法形式为:
返回类型 operator运算符(形参表)
{
函数体
}运算符重载为非成员函数的一般语法形式为同上
以实现自定义数据类型复数的相加减为例
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex { //复数类定义
public: //外部接口
Complex(double r=0.0,double i=0.0):real(r),imag(i){} //构造函数
Complex operator+(const Complex& c2) const; //运算符+重载成员函数
Complex operator-(const Complex& c2) const; //运算符-重载成员函数
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Complex& c);//运算符<<重载非成员函数
private: //私有数据成员
double real; //复数实部
double imag; //复数虚部
};
Complex Complex::operator+(const Complex& c2)const {
return Complex(real + c2.real, imag + c2.imag);
}
Complex Complex::operator-(const Complex& c2)const {
return Complex(real - c2.real, imag - c2.imag);
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Complex& c) {
out << "(" << c.real << "," << c.imag << ")";
return out;
}
int main() {
Complex c1(5, 4), c2(2, 10), c3;
cout << "c1=" << c1 << endl;
cout << "c2=" << c2 << endl;
c3 = c1 + c2;
cout << "c1+c2=" << c3 << endl;
c3 = c1 - c2;
cout << "c1-c2=" << c3 << endl;
return 0;
}程序分析:
运算符“+”和“-”的重载都是作为成员函数,并创建一个临时无名对象作为返回值
运算符"<<"是作为非成员函数,并设置为类的友元函数来使用
运行结果:
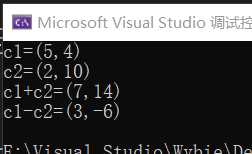
可以看出成功实现了复数+复数的运算。
拓展:通过重载运算符成员函数,实现“复数+实数”、“复数-实数”的功能
以上述代码为基础,添加以下函数:
Complex Complex::operator + (double& b) {
return Complex(real + b, imag);
}
Complex Complex::operator - (double& b) {
return Complex(real - b, imag);
}主函数添加:
double i = -2;
c3 = c1 + i;
cout << "c1+i=" << c3 << endl;
c3 = c2 - i;
cout << "c2-i=" << c3 << endl;运行结果:

可以看出实现了复数+/-实数的目的
本质:覆盖基类函数(不是重载)
注意:静态成员函数、构造函数不能是虚函数;要由成员函数来调用或者是通过指针、引用来访问虚函数
通过一个例题来说明:
请编写一个抽象类Shape,在此基础上派生出类Rectangle和Circle,二者都有计算对象面积的函数getArea()、计算对象周长的函数getPerim()
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define PI 3.1415926;
class Shape //抽象类的 定义
{
public:
virtual double GetArea() = 0; //纯虚函数
virtual double GetPerim() = 0; //纯虚函数
};
class Rectangle : public Shape //矩形类,公有继承
{
public: Rectangle(double aa, double bb) //带参数的 构造函数
{
a = aa;
b = bb;
cout << "长" << a << "宽" << b << endl;
}
virtual double GetArea()
{
return a * b;
}
virtual double GetPerim()
{
return 2 * (a + b);
}
private:
double a;
double b;
};
class Circle : public Shape //圆类,公有继承
{
public: Circle(double rr) //带参数的 构造函数
{
r = rr;
cout << "半径" << r << endl;
}
virtual double GetArea()
{
return r * r * PI;
}
virtual double GetPerim()
{
return 2 * r * PI;
}
private:
double r;
};
void main()
{
double length, width;
cout << "输入长和宽: ";
cin >> length >> width;
Rectangle rect(length, width);
cout << "面积是:" << rect.GetArea() << endl << "周长是:" << rect.GetPerim() << endl;
double rr;
cout << "输入半径: ";
cin >> rr;
Circle cir(rr);
cout << "面积是:" << cir.GetArea() << endl << "周长是:" << cir.GetPerim() << endl;
}程序分析:
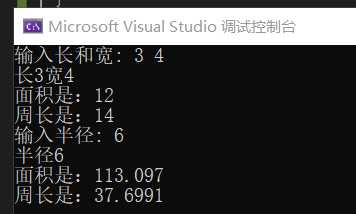
对上述程序进行修改,使得父类的对象调用更新过后的成员函数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Shape //抽象类的 定义
{
public:
virtual double GetArea() = 0; //纯虚函数
virtual double GetPerim() = 0; //纯虚函数
};
class Rectangle : public Shape //矩形类,公有继承
{
public: Rectangle(double aa, double bb) //带参数的 构造函数
{
a = aa;
b = bb;
cout << "长" << a << "宽" << b << endl;
}
virtual double GetArea()
{
return a * b;
}
virtual double GetPerim()
{
return 2 * (a + b);
}
private:
double a;
double b;
};
void main()
{
double length, width;
cout << "输入长和宽: ";
cin >> length >> width;
Shape* r = Rectangle(length, width);
cout << "r_Area=" << r->GetArea() << " " << "r_Perim=" << r->GetPerim() << endl;
}程序分析:
rectangle类公有继承shape类并对计算周长、面积函数进行了具体化展示。在主函数中定义了一个父类的对象指针指向了子类rectangle,在后续调用了计算面积、周长的函数
运行结果:
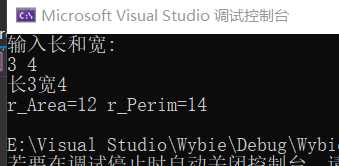
从中可以看出,父类的对象指针成功调用了子类的成员函数,而原因就是虚函数的使用
标签:结果 lex 不同 real 介绍 因此 自定义数据类型 方式 实现
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/YuShiqicodelife/p/11742385.html