标签:not port ORC 删除 初始 div 使用 targe 方便
点云数据结构非常简单,只有点的三维坐标信息和法线信息。下面是一个点云表示的抽象类:
class GPP_EXPORT IPointCloud
{
public:
IPointCloud(){}
virtual Int GetPointCount() const = 0;
virtual Vector3 GetPointCoord(Int pid) const = 0;
virtual void SetPointCoord(Int pid, const Vector3& coord) = 0;
virtual Vector3 GetPointNormal(Int pid) const = 0;
virtual void SetPointNormal(Int pid, const Vector3& normal) = 0;
virtual bool HasNormal() const = 0;
virtual void SetHasNormal(bool has) = 0;
virtual Int InsertPoint(const Vector3& coord) = 0;
virtual Int InsertPoint(const Vector3& coord, const Vector3& normal) = 0;
virtual void SwapPoint(Int pointId0, Int pointId1) = 0;
virtual void PopbackPoints(Int popCount) = 0;
virtual void Clear(void) = 0;
virtual ~IPointCloud(){};
};
IPointCloud是一个抽象类,不能直接使用。用户可以继承这个接口类,实现其成员函数。这样设计的一个好处是,用户无需改变自己已有的数据结构,只要实现了这个接口类,就可以调用Geometry++里所有关于点云的算法了。真正体现了即插即用的特点。比如用户已经有了一个点云类MyPointCloudData,则我们可以定义一个类MyPointCloud,并用它来调用Geometry++里的各种点云算法:
class MyPointCloud : public IPointCloud
{
MyPointCloudData* mData;
MyPointCloud(MyPointCloudData* data) : mData(data)
{}
virtual Int GetPointCount() const
{
mData->GetPointCloud();
}
virtual Vector3 GetPointCoord() const
{
mData->GetPointCoord();
}
virtual void SetPointCoord(Int pid, const Vector& coord)
{
mData->SetPointCoord(pid, coord[0], coord[1], coord[2]);
}
// 其它成员函数类似
};
MyPointCloud pointCloud(myPointCloudData); // 用自己的点云数据初始化MyPointCloud
ErrorCode res = ConsolidatePointCloud::LaplaceSmooth(pointCloud, 0.2, 5); // 调用点云算法API来修改自己的点云数据
res = ConsolidatePointCloud::CalculatePointCloudNormal(pointCloud);
一帧扫描数据是一副深度图,属于灰度图。像素的灰度值代表的是深度信息,可以通过相机参数把每个像素点变换到世界坐标系,这样每个像素就对应一个三维点,有些点是无效的。下图是一个典型的深度点云。

有序点云是一个方阵,如图所示。点云按照方阵一行一行的,从左上角到右下角排列。
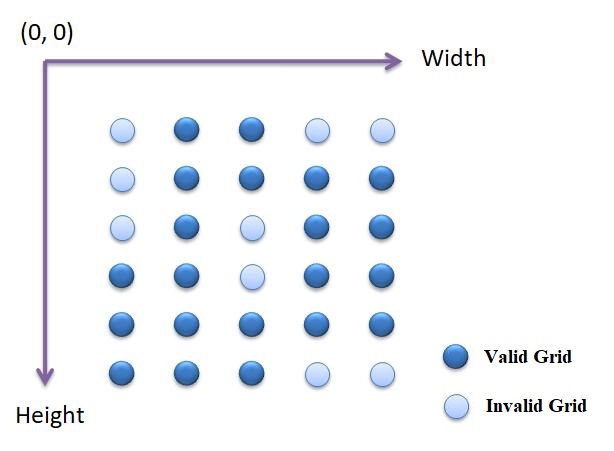
与无序点云相比,有序点云的处理速度可以快很多。
标签:not port ORC 删除 初始 div 使用 targe 方便
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/threepark/p/11746676.html