标签:RoCE tle 更新 add txt 作用 mod 函数 二维
线性回归

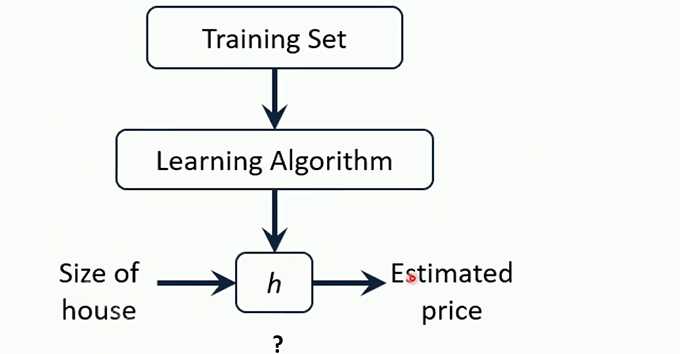
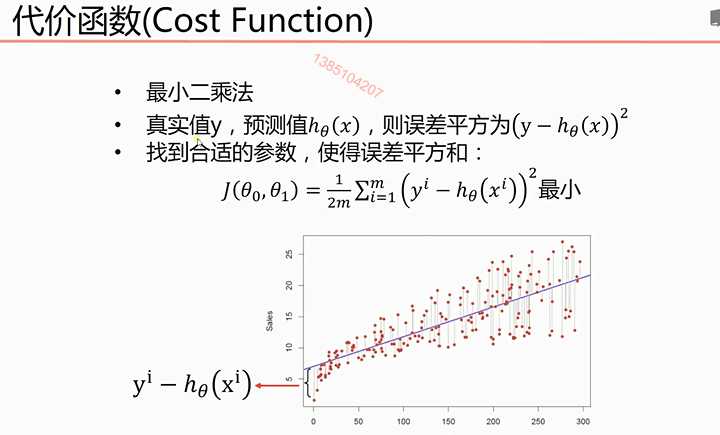
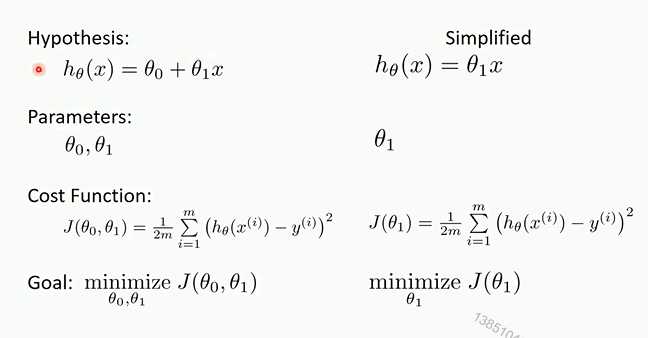
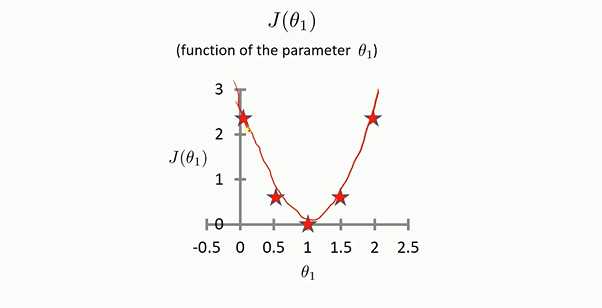

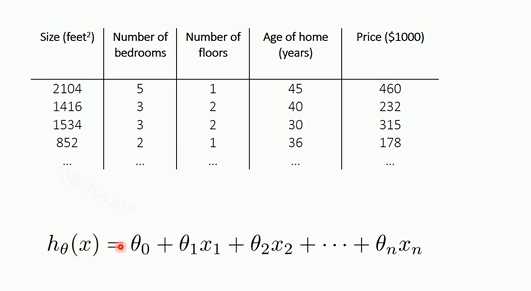
对于多元线性回归和一元线性回归推导理论是一致的,只不过参数是多个参数而已
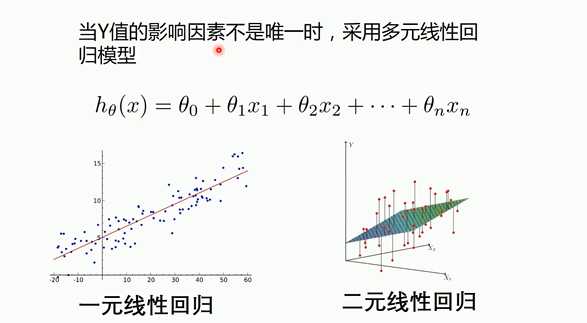
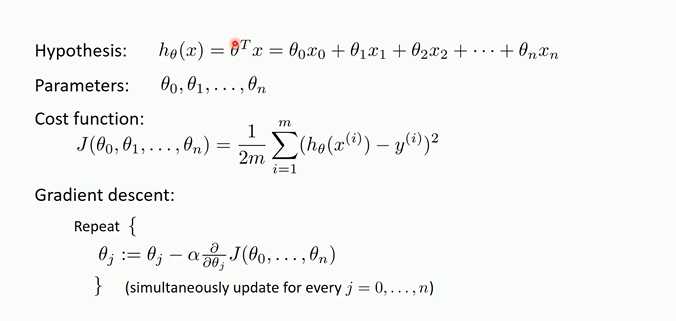
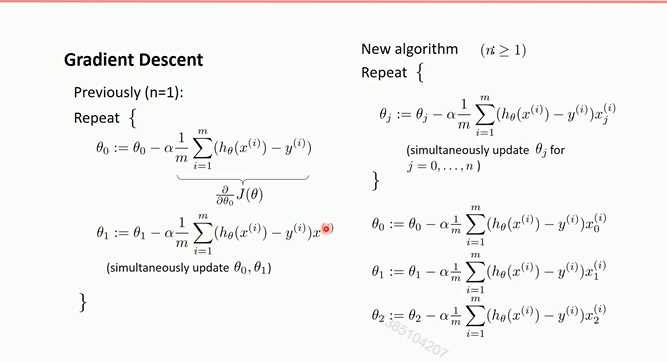
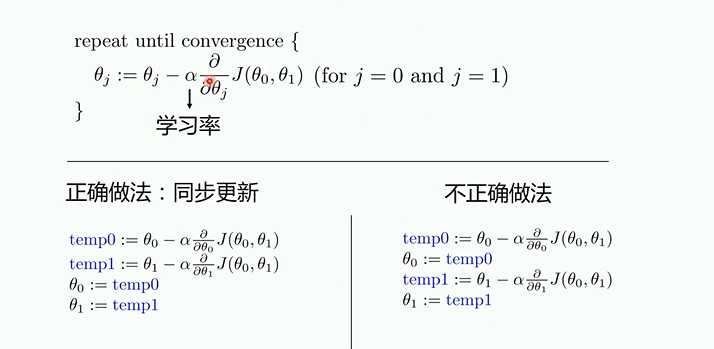
梯度下降

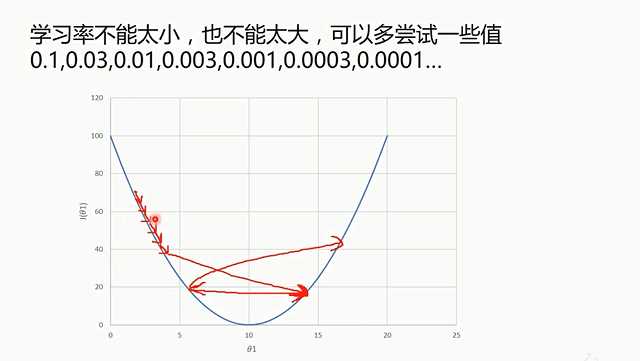

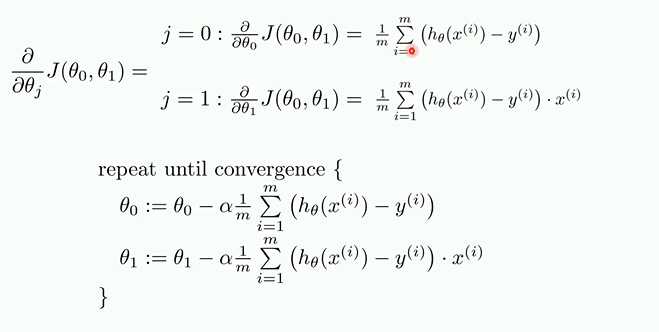
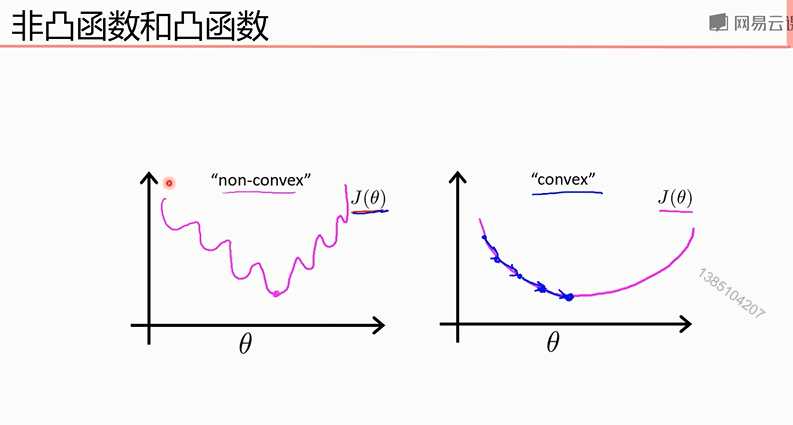
凸函数使用局部下降法一定可以到全部最小值,所以不存在局部最小值才可以
下面两个demo是一元函数的拟合
1使用梯度下降法的数学公式进行的机器学习代码
1 import numpy as np 2 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 3 #读取数据 4 data = np.genfromtxt(‘data.csv‘,delimiter=‘,‘) 5 x_data = data[:, 0] 6 y_data = data[:, 1] 7 #plt.scatter(x_data, y_data) 8 #plt.show() 9 lr = 0.0001 10 k = 0 11 b = 0 12 epochs = 500 13 def compute_loss(x_data, y_data, b, k):#计算损失函数 14 m = float(len(x_data)) 15 sum = 0 16 for i in range(0, len(x_data)): 17 sum += (y_data[i] - (k*x_data[i] + b))**2 18 return sum/(2*m) 19 def gradient(x_data, y_data, k, b, lr, epochs):#进行梯度下降 20 m = float(len(x_data)) 21 22 for i in range(0,epochs): 23 k_gradient = 0 24 b_gradiet = 0 25 for j in range(0,len(x_data)): 26 k_gradient += (1/m)*((x_data[j] * k + b) - y_data[j]) 27 b_gradiet += (1/m)*((x_data[j] * k + b) - y_data[j]) * x_data[j] 28 k -= lr * k_gradient 29 b -= lr * b_gradiet 30 31 32 if i % 50 == 0: 33 print(i) 34 plt.plot(x_data, y_data, ‘b.‘) 35 plt.plot(x_data, k*x_data + b, ‘r‘) 36 plt.show() 37 38 return k, b 39 40 k,b = gradient(x_data, y_data, 0, 0, lr, epochs) 41 plt.plot(x_data, k * x_data + b, ‘r‘) 42 plt.plot(x_data, y_data, ‘b.‘) 43 print(‘loss =:‘,compute_loss(x_data, y_data, b, k),‘b =:‘,b,‘k =:‘,k) 44 plt.show()
2 使用Python的sklearn库
1 import numpy as np 2 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 3 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression 4 #读取数据 5 data = np.genfromtxt(‘data.csv‘,delimiter=‘,‘) 6 x_data = data[:, 0] 7 y_data = data[:, 1] 8 plt.scatter(x_data, y_data) 9 plt.show() 10 x_data = data[:, 0, np.newaxis]#使一位数据编程二维数据 11 y_data = data[:, 1, np.newaxis] 12 model =LinearRegression() 13 model.fit(x_data, y_data)#传进的参数必须是二维的 14 plt.plot(x_data, y_data, ‘b.‘) 15 plt.plot(x_data, model.predict(x_data), ‘r‘)#画出预测的线条 16 plt.show()
3使用梯度下降法完成多元线性回归(以二元为例)
1 import numpy as np 2 from numpy import genfromtxt 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D #用来画3D图的包 5 # 读入数据 6 data = genfromtxt(r"Delivery.csv",delimiter=‘,‘) 7 print(data) 8 # 切分数据 9 x_data = data[:,:-1] 10 y_data = data[:,-1] 11 print(x_data) 12 print(y_data) 13 # 学习率learning rate 14 lr = 0.0001 15 # 参数 16 theta0 = 0 17 theta1 = 0 18 theta2 = 0 19 # 最大迭代次数 20 epochs = 1000 21 22 # 最小二乘法 23 def compute_error(theta0, theta1, theta2, x_data, y_data): 24 totalError = 0 25 for i in range(0, len(x_data)): 26 totalError += (y_data[i] - (theta1 * x_data[i,0] + theta2*x_data[i,1] + theta0)) ** 2 27 return totalError / float(len(x_data)) 28 29 def gradient_descent_runner(x_data, y_data, theta0, theta1, theta2, lr, epochs): 30 # 计算总数据量 31 m = float(len(x_data)) 32 # 循环epochs次 33 for i in range(epochs): 34 theta0_grad = 0 35 theta1_grad = 0 36 theta2_grad = 0 37 # 计算梯度的总和再求平均 38 for j in range(0, len(x_data)): 39 theta0_grad += (1/m) * ((theta1 * x_data[j,0] + theta2*x_data[j,1] + theta0) - y_data[j]) 40 theta1_grad += (1/m) * x_data[j,0] * ((theta1 * x_data[j,0] + theta2*x_data[j,1] + theta0) - y_data[j]) 41 theta2_grad += (1/m) * x_data[j,1] * ((theta1 * x_data[j,0] + theta2*x_data[j,1] + theta0) - y_data[j]) 42 # 更新b和k 43 theta0 = theta0 - (lr*theta0_grad) 44 theta1 = theta1 - (lr*theta1_grad) 45 theta2 = theta2 - (lr*theta2_grad) 46 return theta0, theta1, theta2 47 print("Starting theta0 = {0}, theta1 = {1}, theta2 = {2}, error = {3}". 48 format(theta0, theta1, theta2, compute_error(theta0, theta1, theta2, x_data, y_data))) 49 print("Running...") 50 theta0, theta1, theta2 = gradient_descent_runner(x_data, y_data, theta0, theta1, theta2, lr, epochs) 51 print("After {0} iterations theta0 = {1}, theta1 = {2}, theta2 = {3}, error = {4}". 52 format(epochs, theta0, theta1, theta2, compute_error(theta0, theta1, theta2, x_data, y_data))) 53 ax = Axes3D(plt.figure())#和下面的代码功能一样 54 #ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111, projection=‘3d‘)#plt.figure().add_subplot和plt.subplot的作用是一致的 55 ax.scatter(x_data[:, 0], x_data[:, 1], y_data, c=‘r‘, marker=‘o‘, s=100) # 点为红色三角形 56 x0 = x_data[:, 0] 57 x1 = x_data[:, 1] 58 # 生成网格矩阵 59 x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(x0, x1)#生成一个网格矩阵,矩阵的每个点的第一个轴的取值来自于x0范围内,第二个坐标轴的取值来自于x1范围内 60 z = theta0 + x0 * theta1 + x1 * theta2 61 # 画3D图 62 ax.plot_surface(x0, x1, z) 63 # 设置坐标轴 64 ax.set_xlabel(‘Miles‘) 65 ax.set_ylabel(‘Num of Deliveries‘) 66 ax.set_zlabel(‘Time‘) 67 68 # 显示图像 69 plt.show()
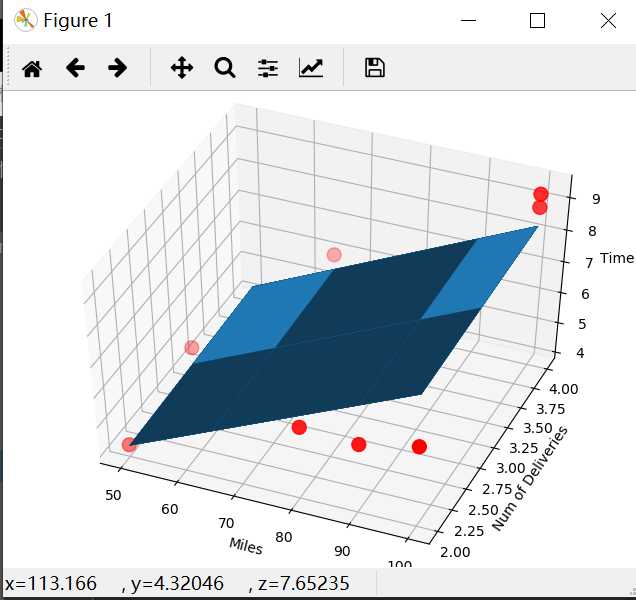
4:使用Python的sklearn库完成多元线性回归
import numpy as np from numpy import genfromtxt from sklearn import linear_model import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D # 读入数据 data = genfromtxt(r"Delivery.csv",delimiter=‘,‘) print(data) # 切分数据 x_data = data[:,:-1] y_data = data[:,-1] print(x_data) print(y_data) # 创建模型 model = linear_model.LinearRegression() model.fit(x_data, y_data) # 系数 print("coefficients:",model.coef_) # 截距 print("intercept:",model.intercept_) # 测试 x_test = [[102,4]] predict = model.predict(x_test) print("predict:",predict) ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111, projection=‘3d‘) ax.scatter(x_data[:, 0], x_data[:, 1], y_data, c=‘r‘, marker=‘o‘, s=100) # 点为红色三角形 x0 = x_data[:, 0] x1 = x_data[:, 1] # 生成网格矩阵 x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(x0, x1) z = model.intercept_ + x0*model.coef_[0] + x1*model.coef_[1] # 画3D图 ax.plot_surface(x0, x1, z)#参数是二维的,而model.prodict(x_data)是一维的。 # 设置坐标轴 ax.set_xlabel(‘Miles‘) ax.set_ylabel(‘Num of Deliveries‘) ax.set_zlabel(‘Time‘) # 显示图像 plt.show()
5 多项式回归拟合
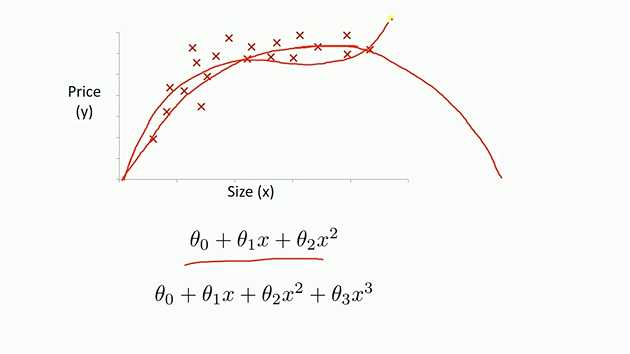
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures#多项式 4 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression 5 6 # 载入数据 7 data = np.genfromtxt("job.csv", delimiter=",") 8 x_data = data[1:,1] 9 y_data = data[1:,2] 10 plt.scatter(x_data,y_data) 11 plt.show() 12 x_data 13 x_data = x_data[:,np.newaxis] 14 y_data = y_data[:,np.newaxis] 15 x_data 16 # 创建并拟合模型 17 model = LinearRegression() 18 model.fit(x_data, y_data) 19 # 画图 20 plt.plot(x_data, y_data, ‘b.‘) 21 plt.plot(x_data, model.predict(x_data), ‘r‘) 22 plt.show() 23 # 定义多项式回归,degree的值可以调节多项式的特征 24 poly_reg = PolynomialFeatures(degree=5) 25 # 特征处理 26 x_poly = poly_reg.fit_transform(x_data) 27 # 定义回归模型 28 lin_reg = LinearRegression() 29 # 训练模型 30 lin_reg.fit(x_poly, y_data) 31 # 画图 32 plt.plot(x_data, y_data, ‘b.‘) 33 plt.plot(x_data, lin_reg.predict(poly_reg.fit_transform(x_data)), c=‘r‘) 34 plt.title(‘Truth or Bluff (Polynomial Regression)‘) 35 plt.xlabel(‘Position level‘) 36 plt.ylabel(‘Salary‘) 37 plt.show() 38 # 画图 39 plt.plot(x_data, y_data, ‘b.‘) 40 x_test = np.linspace(1,10,100) 41 x_test = x_test[:,np.newaxis] 42 plt.plot(x_test, lin_reg.predict(poly_reg.fit_transform(x_test)), c=‘r‘) 43 plt.title(‘Truth or Bluff (Polynomial Regression)‘) 44 plt.xlabel(‘Position level‘) 45 plt.ylabel(‘Salary‘) 46 plt.show()
标签:RoCE tle 更新 add txt 作用 mod 函数 二维
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/henuliulei/p/11762064.html