标签:就会 lda enqueue sam ase 常数时间 语法 array 无限
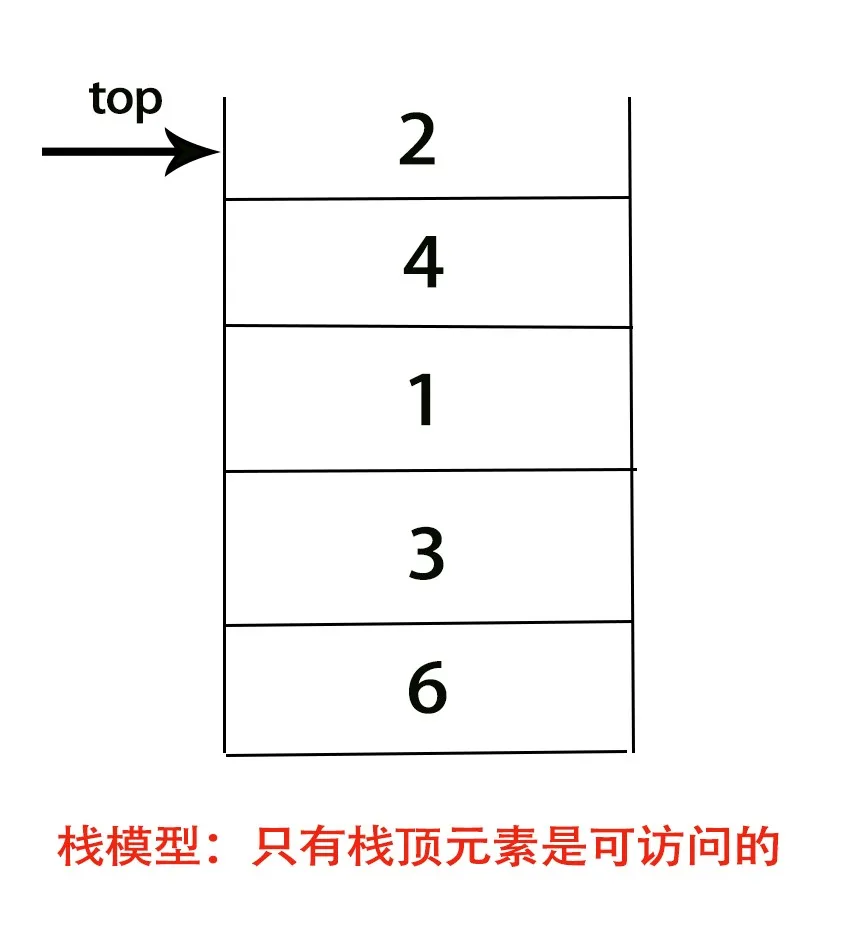
栈(stack)是限制对元素的插入(push)和删除(pop)只能在一个位置上进行的表,该位置是表的末端,叫做栈的栈顶(top)。
栈的基本操作只有两种,压入栈(push)和弹出栈顶(pop),且只能作用于栈顶。(只有栈顶元素是可访问的

你可以把栈结构理解成一个底部封闭,顶部打开的桶。最先进去的元素一定是最后才能取出,最晚进去的元素一定是最先取出。
因此栈又叫做LIFO(后进先出,Last In First Out)表。

栈的操作是常数时间的,而且是以非常快的常数时间。在某些机器上,push和pop都可以写成一条机器指令,现代计算机把栈操作作为它指令的一部分。因此栈是在计算机科学中继数组之后最基本的数据结构。
栈的实现分为数组实现和链表实现。
1` 链表实现
这里我们使用单链表来实现,定义一个first指针指向栈顶,栈的链表实现实际上是简化了单链表实现,具体实现看以下代码。
public class StackImplementByLinklist<AnyType> {
public Node<AnyType> first;
int size;
//内部类定义node
public class Node<AnyType>{
AnyType data;
Node<AnyType> next;
}
//初始化
public void stack(){
first=null;
size=0;
}
public void push(AnyType a){
Node oldNode=first;
first=new Node();
first.data=a;
first.next=oldNode;
size++;
}
public AnyType pop(){
AnyType a=first.data;
first=first.next;
size--;
return a;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size==0;
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
}
2` 数组实现
相比于链表实现,数组实现栈更加的常用。因为数组操作的常数时间极短,而且实现起来更加简单。
public class StackImplementByArray<AnyType> {
AnyType[] arr;
int size;
public void stack(int capacity){
arr=(AnyType[])new Object[capacity];
size=0;
}
public void push(AnyType a){
if(size==arr.length){
changeArray(2*size+1);
}
arr[size]=a;
size++;
}
public AnyType pop(){
if(size==0){
System.out.println("栈顶为空");
System.exit(0);
}
AnyType a=arr[size-1];
arr[size-1]=null;
size--;
return a;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size==0;
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
//由于数组大小是要先确定的,因此当数组满了后要扩大数组容量
public void changeArray(int newCapacity){
AnyType[] newArr=(AnyType[])new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
newArr[i]=arr[i];
}
arr=newArr;
}
}
平衡符号的检测
编译器检查程序符号的语法错误,常常就是通过栈来实现的。
在编程时,我们经常会用到“ ( ),[ ],{ }," " ”这些符号,当这些符号不是配对出现的,编译器就会报错,编译就无法通过。
那么,编译器是怎么知道这些符号有没有配对出现的呢?它通常是这么处理的。
当遇到左符号,如“( [ { " ”这些,就把它压入一个准备好的栈;否则就弹出栈顶,检测当前符号是否与栈顶元素配对。一旦不能配对,直接退出报错。
算术表达式的求值
wiki: 队列,又称为伫列(queue),是先进先出(FIFO, First-In-First-Out)的线性表。在具体应用中通常用链表或者数组来实现。队列只允许在后端(称为rear)进行插入操作,在前端(称为front)进行删除操作。队列的操作方式和堆栈类似,唯一的区别在于队列只允许新数据在后端进行添加。
队列模型就相当于我们日常生活的排队,在队伍的后面入队,在队伍的前端出队。
队列一般分为普通的数组队列,链表队列和循环队列。
链表队列:长度一般是无限的,一般不存在溢出的可能性,用完就销毁,不会浪费内存空间。
普通的数组队列:长度一般是有限的,即数组长度。由于元素出队后其位置的内存空间并不会释放,因此会浪费大量的内存空间。
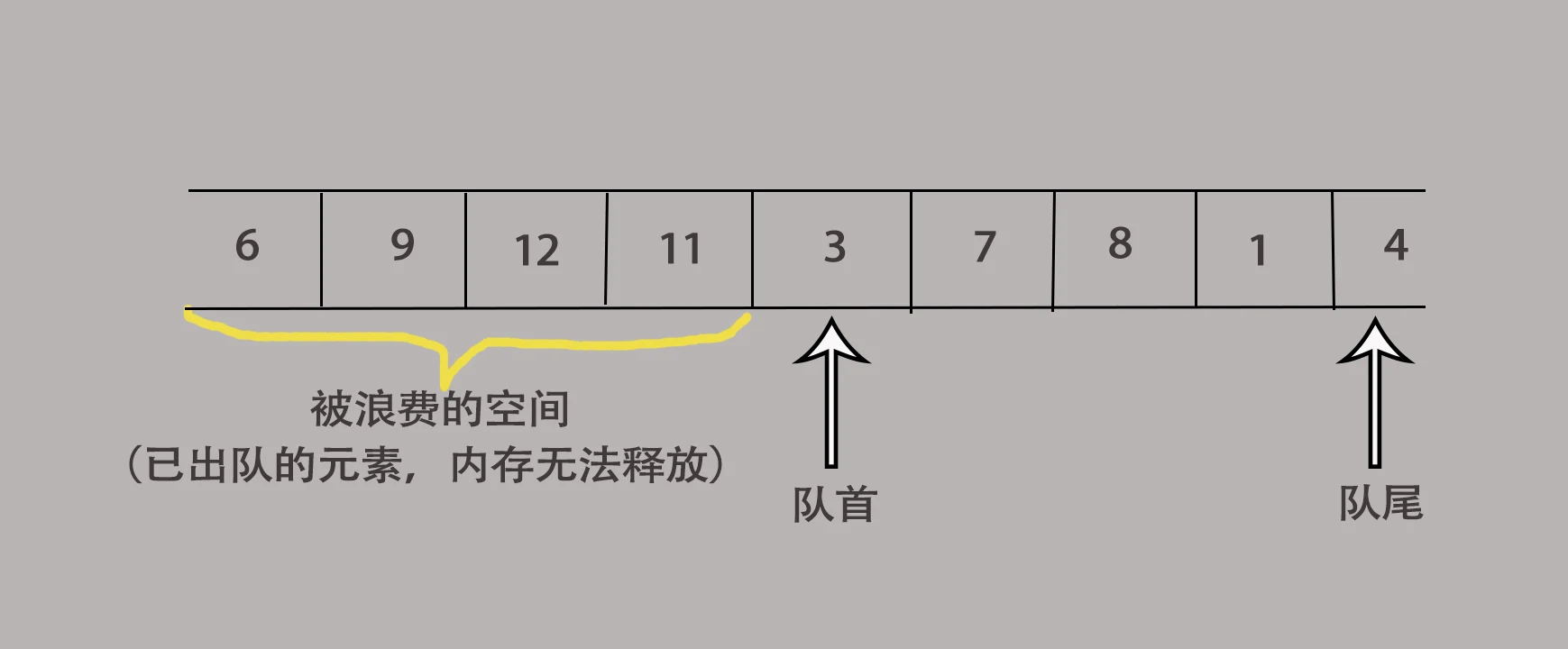
循环队列:特殊的数组队列,由于普通的数组的队列会浪费大量的内存空间,因此出现了循环队列。当循环队列的队尾指针到达数组末尾后,会重新回到数组起始位置,实现了对内存的重复利用。

1` 链表队列
public class QueueImplementByLinkList<AnyType> {
Node first;//队首
Node last;//队尾
int size;
public class Node{
AnyType data;
Node next;
public Node(AnyType data,Node next){
this.data=data;
this.next=next;
}
}
//初始化队列
public void initqueue(){
first=new Node(null,null);
last=first;
size=0;
}
//入队
public void enqueue(AnyType a){
if(size==0){
last.data=a;
size++;
return;
}
Node oldlast=last;
last=new Node(a,null);
oldlast.next=last;
size++;
}
//出队
public AnyType dequeue(){
if(size==0){
System.out.print("队列为空");
System.exit(0);
}
AnyType a=first.data;
first=first.next;
size--;
return a;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size==0;
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
}
2` 数组队列
public class QueueImplementByArray<AnyType> {
AnyType[] arr;
int first;
int last;
int size;
//初始化
public void ininqueue(int capacity){
arr=(AnyType[])new Object[capacity];
first=0;
last=0;
size=0;
}
public void enqueue(AnyType a){
if(size==arr.length){
changeArray(2*size+1);
}
arr[last++]=a;
size++;
}
public AnyType dequeue(){
if(size==0){
System.out.println("队列为空");
System.exit(0);
}
AnyType a=arr[first++];
arr[first-1]=null;
size--;
return a;
}
public void changeArray(int newCapacity){
AnyType[] newArr=(AnyType[])new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
newArr[i]=arr[i];
}
arr=newArr;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size==0;
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
}
3` 循环队列
public class CycleQueue {
int[] arr;
int start;//队首
int end;//队尾
int size=0;
//初始化
public void initqueue(int size){
arr=new int[size];
size=0;
start=0;
end=0;
}
//入队
public void enqueue(int num){
if(size>arr.length){
System.out.println("队列已满");
return;
}
if(end==arr.length){
end=0;
}
arr[end++]=num;
size++;
}
//出队
public int dequeue(){
if(size==0){
System.out.println("队列为空");
System.exit(0);
}
if(start==arr.length){
start=0;
}
size--;
return arr[start++];
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size==0;
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
}
栈和队列是基本的数据结构,是对数组和链表的重新封装和扩展。由于它们的特性和执行速度,栈和队列被广泛的使用。
最后,不要为了使用数据结构而使用使用数据结构,要区分各种数据结构的使用场景,灵活地运用数据结构,可以事半功倍。
标签:就会 lda enqueue sam ase 常数时间 语法 array 无限
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/sang-bit/p/11757553.html