标签:maximum rtl running 两个栈 fun 就是 catch float sha
Windows内核分析索引目录:https://www.cnblogs.com/onetrainee/p/11675224.html
用户异常与模拟异常的派发
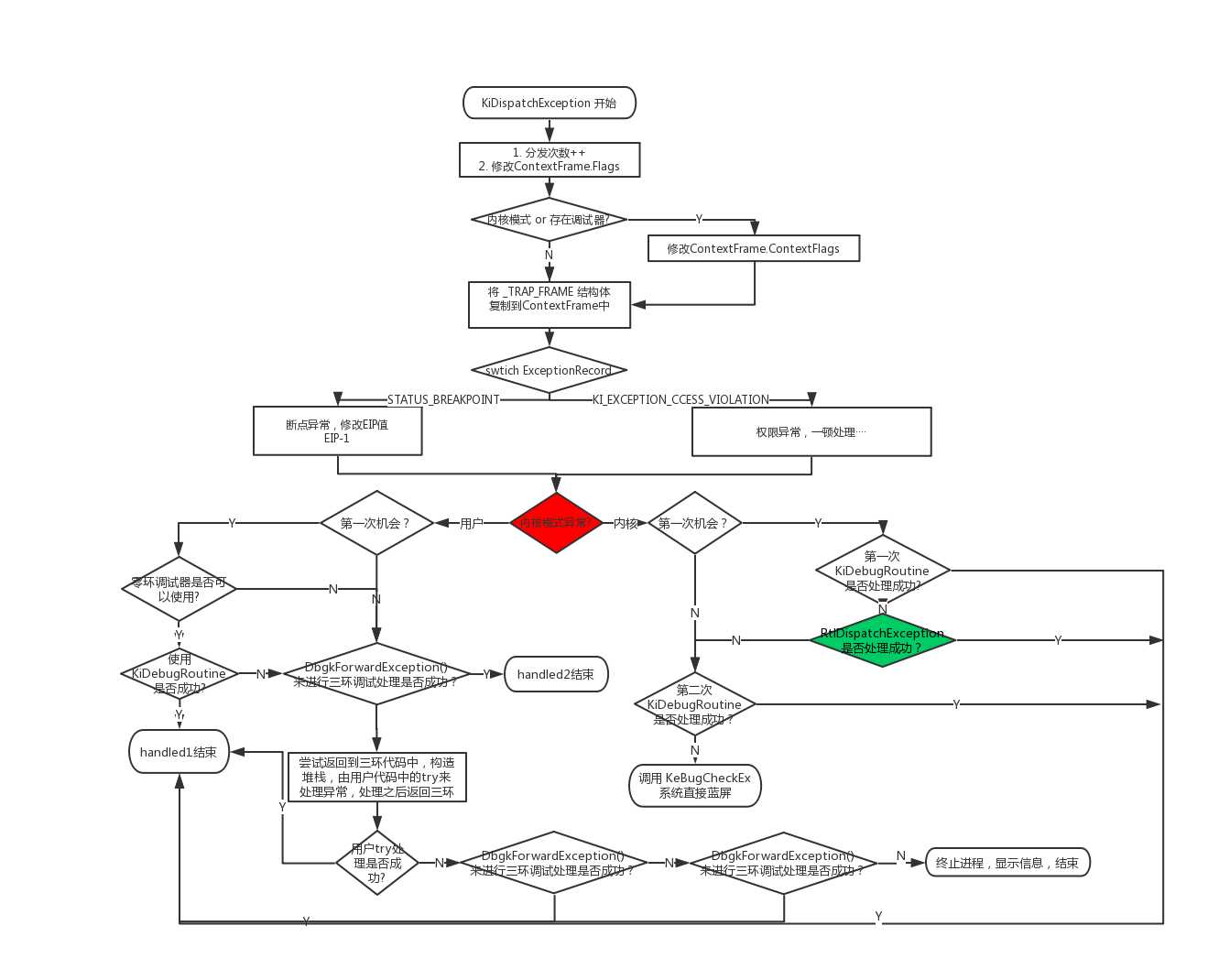
一、KiDispatchException函数处理流程图
无论用户模拟异常还是CPU异常,经过前面分析,在经过记录之后,最终都会经过KiDispatchException这个派发函数中。
在KiDispatchException中会对CPU异常和用户异常分别进行处理。
CPU异常:首先调用内核调试器,如果调用失败则调用RtlDispatchException(该函数后面会有介绍)分发,
RtlDispatchException函数会检查SEH链中是否有该程序的处理函数,如果有则返回成功,
若RtlDispatchException函数处理异常失败,其会尝试第二次调用内核调试器进行调试处理,如果最终处理不了直接蓝屏。
用户异常:先尝试内核调试器,再尝试用户调试器,如果还不行,直接返回用户代码尝试使用try_catch_语法来进行处理,之后还不行再尝试两次用户调试器。
如果最终还是处理不了异常,该进程会关闭并报出错误。(用户异常不会导致蓝屏出现)
二、RtlDispatchException的函数解析代码
1 VOID 2 KiDispatchException ( 3 IN PEXCEPTION_RECORD ExceptionRecord, 4 IN PKEXCEPTION_FRAME ExceptionFrame, 5 IN PKTRAP_FRAME TrapFrame, 6 IN KPROCESSOR_MODE PreviousMode, 7 IN BOOLEAN FirstChance 8 ) 9 10 /*++ 11 12 Routine Description: 13 14 This function is called to dispatch an exception to the proper mode and 15 to cause the exception dispatcher to be called. If the previous mode is 16 kernel, then the exception dispatcher is called directly to process the 17 exception. Otherwise the exception record, exception frame, and trap 18 frame contents are copied to the user mode stack. The contents of the 19 exception frame and trap are then modified such that when control is 20 returned, execution will commense in user mode in a routine which will 21 call the exception dispatcher. 22 23 Arguments: 24 25 ExceptionRecord - Supplies a pointer to an exception record. 26 27 ExceptionFrame - Supplies a pointer to an exception frame. For NT386, 28 this should be NULL. 29 30 TrapFrame - Supplies a pointer to a trap frame. 31 32 PreviousMode - Supplies the previous processor mode. 33 34 FirstChance - Supplies a boolean value that specifies whether this is 35 the first (TRUE) or second (FALSE) chance for the exception. 36 37 Return Value: 38 39 None. 40 41 --*/ 42 43 { 44 CONTEXT ContextFrame; 45 EXCEPTION_RECORD ExceptionRecord1, ExceptionRecord2; 46 LONG Length; 47 ULONG UserStack1; 48 ULONG UserStack2; 49 50 // 51 // Move machine state from trap and exception frames to a context frame, 52 // and increment the number of exceptions dispatched. 53 // 54 55 //-------------------------------------// 56 // 将当前异常分发次数增加1 // 57 // 修改ContextFrame.ContextFlags标志位 // 58 //-------------------------------------// 59 KeGetCurrentPrcb()->KeExceptionDispatchCount += 1; 60 ContextFrame.ContextFlags = CONTEXT_FULL | CONTEXT_DEBUG_REGISTERS; 61 62 //------------------------------------------// 63 // 对于用户模式异常的处理 or 调试器可以执行 // 64 // 标记好Context内容 // 65 //------------------------------------------// 66 if ((PreviousMode == UserMode) || KdDebuggerEnabled) { 67 // 68 // For usermode exceptions always try to dispatch the floating 69 // point state. This allows exception handlers & debuggers to 70 // examine/edit the npx context if required. Plus it allows 71 // exception handlers to use fp instructions without destroying 72 // the npx state at the time of the exception. 73 // 74 // Note: If there‘s no 80387, ContextTo/FromKFrames will use the 75 // emulator‘s current state. If the emulator can not give the 76 // current state, then the context_floating_point bit will be 77 // turned off by ContextFromKFrames. 78 // 79 80 ContextFrame.ContextFlags |= CONTEXT_FLOATING_POINT; 81 if (KeI386XMMIPresent) { 82 ContextFrame.ContextFlags |= CONTEXT_EXTENDED_REGISTERS; 83 } 84 } 85 86 //----------------------------------// 87 // 将TrapFrame转换为ContextFrame // 88 // 接下来都是处理ContextFrame的内容 // 89 // 这部分零环无意义,三环有意义 // 90 // 否则修改返回地址不行了。 // 91 //----------------------------------// 92 KeContextFromKframes(TrapFrame, ExceptionFrame, &ContextFrame); 93 94 // 95 // if it is BREAK_POINT exception, we subtract 1 from EIP and report 96 // the updated EIP to user. This is because Cruiser requires EIP 97 // points to the int 3 instruction (not the instruction following int 3). 98 // In this case, BreakPoint exception is fatal. Otherwise we will step 99 // on the int 3 over and over again, if user does not handle it 100 // 101 // if the BREAK_POINT occured in V86 mode, the debugger running in the 102 // VDM will expect CS:EIP to point after the exception (the way the 103 // processor left it. this is also true for protected mode dos 104 // app debuggers. We will need a way to detect this. 105 // 106 // 107 108 switch (ExceptionRecord->ExceptionCode) { 109 //-------------------------// 110 // 如果为int3断点异常 // 111 // 则修改eip执行原来的位置 // 112 //-------------------------// 113 case STATUS_BREAKPOINT: 114 ContextFrame.Eip--; 115 break; 116 117 //------------------------------// 118 // 执行权限问题而发生的访问违例 // 119 //------------------------------// 120 case KI_EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION: 121 ExceptionRecord->ExceptionCode = STATUS_ACCESS_VIOLATION; 122 if (PreviousMode == UserMode) { 123 if (KiCheckForAtlThunk(ExceptionRecord,&ContextFrame) != FALSE) { 124 goto Handled1; 125 } 126 127 if ((SharedUserData->ProcessorFeatures[PF_NX_ENABLED] == TRUE) && 128 (ExceptionRecord->ExceptionInformation [0] == EXCEPTION_EXECUTE_FAULT)) { 129 130 if (((KeFeatureBits & KF_GLOBAL_32BIT_EXECUTE) != 0) || 131 (PsGetCurrentProcess()->Pcb.Flags.ExecuteEnable != 0) || 132 (((KeFeatureBits & KF_GLOBAL_32BIT_NOEXECUTE) == 0) && 133 (PsGetCurrentProcess()->Pcb.Flags.ExecuteDisable == 0))) { 134 ExceptionRecord->ExceptionInformation [0] = 0; 135 } 136 } 137 } 138 break; 139 } 140 141 // 142 // Select the method of handling the exception based on the previous mode. 143 // 144 145 ASSERT (( 146 !((PreviousMode == KernelMode) && 147 (ContextFrame.EFlags & EFLAGS_V86_MASK)) 148 )); 149 150 //--------------------------// 151 // 如果是内核模式触发的异常 // 152 //--------------------------// 153 if (PreviousMode == KernelMode) { 154 155 // 156 // Previous mode was kernel. 157 // 158 // If the kernel debugger is active, then give the kernel debugger the 159 // first chance to handle the exception. If the kernel debugger handles 160 // the exception, then continue execution. Else attempt to dispatch the 161 // exception to a frame based handler. If a frame based handler handles 162 // the exception, then continue execution. 163 // 164 // If a frame based handler does not handle the exception, 165 // give the kernel debugger a second chance, if it‘s present. 166 // 167 // If the exception is still unhandled, call KeBugCheck(). 168 // 169 170 //----------------------------------// 171 // 给内核调试器第一次机会来处理异常 // 172 //----------------------------------// 173 if (FirstChance == TRUE) { 174 175 if ((KiDebugRoutine != NULL) && 176 (((KiDebugRoutine) (TrapFrame, 177 ExceptionFrame, 178 ExceptionRecord, 179 &ContextFrame, 180 PreviousMode, 181 FALSE)) != FALSE)) { 182 183 //------------------------------// 184 // 如果处理成功,不进行下面处理 // 185 //------------------------------// 186 goto Handled1; 187 } 188 189 // Kernel debugger didn‘t handle exception. 190 191 //--------------------------------------// 192 // 如果第一次调试器不成功,则派发异常 // 193 // 当派发成功之后,也不会处理第二次异常 // 194 //--------------------------------------// 195 if (RtlDispatchException(ExceptionRecord, &ContextFrame) == TRUE) { 196 goto Handled1; 197 } 198 } 199 200 // 201 // This is the second chance to handle the exception. 202 // 203 204 //--------------------------------// 205 // 第二次机会来调用调试器处理异常 // 206 //--------------------------------// 207 if ((KiDebugRoutine != NULL) && 208 (((KiDebugRoutine) (TrapFrame, 209 ExceptionFrame, 210 ExceptionRecord, 211 &ContextFrame, 212 PreviousMode, 213 TRUE)) != FALSE)) { 214 215 //------------------// 216 // 第二次也处理成功 // 217 //------------------// 218 goto Handled1; 219 } 220 221 222 //------------------------------------------------// 223 // 如果两次调试器处理和派发都不成功,系统直接蓝屏 // 224 //------------------------------------------------// 225 KeBugCheckEx( 226 KERNEL_MODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED, 227 ExceptionRecord->ExceptionCode, 228 (ULONG)ExceptionRecord->ExceptionAddress, 229 (ULONG)TrapFrame, 230 0); 231 232 } else { 233 //--------------// 234 // 用户模式异常 // 235 //--------------// 236 237 // 238 // Previous mode was user. 239 // 240 // If this is the first chance and the current process has a debugger 241 // port, then send a message to the debugger port and wait for a reply. 242 // If the debugger handles the exception, then continue execution. Else 243 // transfer the exception information to the user stack, transition to 244 // user mode, and attempt to dispatch the exception to a frame based 245 // handler. If a frame based handler handles the exception, then continue 246 // execution with the continue system service. Else execute the 247 // NtRaiseException system service with FirstChance == FALSE, which 248 // will call this routine a second time to process the exception. 249 // 250 // If this is the second chance and the current process has a debugger 251 // port, then send a message to the debugger port and wait for a reply. 252 // If the debugger handles the exception, then continue execution. Else 253 // if the current process has a subsystem port, then send a message to 254 // the subsystem port and wait for a reply. If the subsystem handles the 255 // exception, then continue execution. Else terminate the process. 256 // 257 258 259 if (FirstChance == TRUE) { 260 261 // 262 // This is the first chance to handle the exception. 263 // 264 265 //-------------------------------------------------------------------------------// 266 // 调用内核调试器有两个条件: // 267 // 1. 当前存在一个调试器 // 268 // 2. (当前进程的调试器端口为NULL && 不忽略异常) or 可以得到当前 ContextFrame ) // 269 //-------------------------------------------------------------------------------// 270 if ((KiDebugRoutine != NULL) && 271 272 //---------------------------------------------------------------// 273 // 三环调试器最终会建立一个调试对象,挂在被调试进程的DebugPort处 // 274 //---------------------------------------------------------------// 275 ((PsGetCurrentProcess()->DebugPort == NULL && 276 !KdIgnoreUmExceptions) || 277 //-------------------------------------// 278 // 判断R3层的INT3是否能进入内核调试器 // 279 //-------------------------------------// 280 (KdIsThisAKdTrap(ExceptionRecord, &ContextFrame, UserMode)))) { 281 // 282 // Now dispatch the fault to the kernel debugger. 283 // 284 285 //------------------------// 286 // 先尝试第一次调试器处理 // 287 //------------------------// 288 if ((((KiDebugRoutine) (TrapFrame, 289 ExceptionFrame, 290 ExceptionRecord, 291 &ContextFrame, 292 PreviousMode, 293 FALSE)) != FALSE)) { 294 295 goto Handled1; 296 } 297 } 298 299 300 //---------------------------------------------------// 301 // 如果零环调试器无法处理 会调用三环调试器来进行处理 // 302 //---------------------------------------------------// 303 if (DbgkForwardException(ExceptionRecord, TRUE, FALSE)) { 304 goto Handled2; 305 } 306 307 // 308 // Transfer exception information to the user stack, transition 309 // to user mode, and attempt to dispatch the exception to a frame 310 // based handler. 311 312 ExceptionRecord1.ExceptionCode = 0; // satisfy no_opt compilation 313 314 //---------------------------------------------------------// 315 // 当内核调试器/用户调试器都处理不了该异常时 // 316 // 返回R3层的用户代码,尝试交给自定的try.catch. 来进行处理 // 317 // 对栈的存储跟APC操作类似 // 318 //---------------------------------------------------------// 319 repeat: 320 try { 321 322 // 323 // If the SS segment is not 32 bit flat, there is no point 324 // to dispatch exception to frame based exception handler. 325 // 326 327 328 if (TrapFrame->HardwareSegSs != (KGDT_R3_DATA | RPL_MASK) || 329 TrapFrame->EFlags & EFLAGS_V86_MASK ) { 330 //-----------------------------------// 331 // 如果TrapFrame保存的不是用户层地址 // 332 // 直接出触发二次异常 // 333 //-----------------------------------// 334 ExceptionRecord2.ExceptionCode = STATUS_ACCESS_VIOLATION; 335 ExceptionRecord2.ExceptionFlags = 0; 336 ExceptionRecord2.NumberParameters = 0; 337 ExRaiseException(&ExceptionRecord2); 338 } 339 340 // 341 // Compute length of context record and new aligned user stack 342 // pointer. 343 // 344 345 //--------------------------------------// 346 // 计算"对齐并提高用户栈的大小"后的指针 // 347 //--------------------------------------// 348 UserStack1 = (ContextFrame.Esp & ~CONTEXT_ROUND) - CONTEXT_ALIGNED_SIZE; 349 350 // 351 // Probe user stack area for writability and then transfer the 352 // context record to the user stack. 353 // 354 355 //--------------------------------------------------------------------// 356 // ProbeForWrite 检测是否可写入,如果可以写入则写入内存,否则抛出异常 // 357 // 将Context结构保存到三环栈帧中,为进入零环时恢复三环的环境做准备 // // 358 //--------------------------------------------------------------------// 359 ProbeForWrite((PCHAR)UserStack1, CONTEXT_ALIGNED_SIZE, CONTEXT_ALIGN); 360 RtlCopyMemory((PULONG)UserStack1, &ContextFrame, sizeof(CONTEXT)); 361 362 // 363 // Compute length of exception record and new aligned stack 364 // address. 365 // 366 367 //----------------------------// 368 // 计算放入异常参数后栈的大小 // 369 //----------------------------// 370 Length = (sizeof(EXCEPTION_RECORD) - (EXCEPTION_MAXIMUM_PARAMETERS - 371 ExceptionRecord->NumberParameters) * sizeof(ULONG) +3) & 372 (~3); 373 UserStack2 = UserStack1 - Length; 374 375 // 376 // Probe user stack area for writeability and then transfer the 377 // context record to the user stack area. 378 // N.B. The probing length is Length+8 because there are two 379 // arguments need to be pushed to user stack later. 380 // 381 382 //----------------------------------------------// 383 // 将参数放入内核中 这里提升8因为后面还需要参数 // 384 //----------------------------------------------// 385 ProbeForWrite((PCHAR)(UserStack2 - 8), Length + 8, sizeof(ULONG)); 386 RtlCopyMemory((PULONG)UserStack2, ExceptionRecord, Length); 387 388 // 389 // Push address of exception record, context record to the 390 // user stack. They are the two parameters required by 391 // _KiUserExceptionDispatch. 392 // 393 394 //----------------------------------------------------------------------// 395 // 将上述两个栈地址压入栈中,将该参数是 _KiUserExceptionDispatch 需要的 // 396 //----------------------------------------------------------------------// 397 *(PULONG)(UserStack2 - sizeof(ULONG)) = UserStack1; 398 *(PULONG)(UserStack2 - 2*sizeof(ULONG)) = UserStack2; 399 400 // 401 // Set new stack pointer to the trap frame. 402 // 403 404 //-------------------------------------------// 405 // 修改_KTRAP_FRAME中寄存器ss与esp寄存器的值 // 406 // 这样返回用户层时栈帧就是修改栈帧的数据了 // 407 //-------------------------------------------// 408 KiSegSsToTrapFrame(TrapFrame, KGDT_R3_DATA); 409 KiEspToTrapFrame(TrapFrame, (UserStack2 - sizeof(ULONG)*2)); 410 411 // 412 // Force correct R3 selectors into TrapFrame. 413 // 414 415 //-------------------------// 416 // 修改 TrapFrame后的数据 // 417 //-------------------------// 418 TrapFrame->SegCs = SANITIZE_SEG(KGDT_R3_CODE, PreviousMode); 419 TrapFrame->SegDs = SANITIZE_SEG(KGDT_R3_DATA, PreviousMode); 420 TrapFrame->SegEs = SANITIZE_SEG(KGDT_R3_DATA, PreviousMode); 421 TrapFrame->SegFs = SANITIZE_SEG(KGDT_R3_TEB, PreviousMode); 422 TrapFrame->SegGs = 0; 423 424 // 425 // Set the address of the exception routine that will call the 426 // exception dispatcher and then return to the trap handler. 427 // The trap handler will restore the exception and trap frame 428 // context and continue execution in the routine that will 429 // call the exception dispatcher. 430 // 431 432 //--------------------------------------// 433 // 修改到返回三环的地址 // 434 // KeUserExceptionDispathcer 这个函数中 // 435 //--------------------------------------// 436 TrapFrame->Eip = (ULONG)KeUserExceptionDispatcher; 437 return; 438 439 } except (KiCopyInformation(&ExceptionRecord1, 440 (GetExceptionInformation())->ExceptionRecord)) { 441 442 // 443 // If the exception is a stack overflow, then attempt 444 // to raise the stack overflow exception. Otherwise, 445 // the user‘s stack is not accessible, or is misaligned, 446 // and second chance processing is performed. 447 // 448 449 if (ExceptionRecord1.ExceptionCode == STATUS_STACK_OVERFLOW) { 450 ExceptionRecord1.ExceptionAddress = ExceptionRecord->ExceptionAddress; 451 RtlCopyMemory((PVOID)ExceptionRecord, 452 &ExceptionRecord1, sizeof(EXCEPTION_RECORD)); 453 goto repeat; 454 } 455 } 456 } 457 458 // 459 // This is the second chance to handle the exception. 460 // 461 462 if (DbgkForwardException(ExceptionRecord, TRUE, TRUE)) { 463 goto Handled2; 464 } else if (DbgkForwardException(ExceptionRecord, FALSE, TRUE)) { 465 goto Handled2; 466 } else { 467 ZwTerminateProcess(NtCurrentProcess(), ExceptionRecord->ExceptionCode); 468 KeBugCheckEx( 469 KERNEL_MODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED, 470 ExceptionRecord->ExceptionCode, 471 (ULONG)ExceptionRecord->ExceptionAddress, 472 (ULONG)TrapFrame, 473 0); 474 } 475 } 476 477 // 478 // Move machine state from context frame to trap and exception frames and 479 // then return to continue execution with the restored state. 480 // 481 482 Handled1: 483 484 KeContextToKframes(TrapFrame, ExceptionFrame, &ContextFrame, 485 ContextFrame.ContextFlags, PreviousMode); 486 487 // 488 // Exception was handled by the debugger or the associated subsystem 489 // and state was modified, if necessary, using the get state and set 490 // state capabilities. Therefore the context frame does not need to 491 // be transferred to the trap and exception frames. 492 // 493 494 Handled2: 495 return; 496 }
标签:maximum rtl running 两个栈 fun 就是 catch float sha
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/onetrainee/p/11797640.html