标签:表示 scan 其他 操作 span bre 平衡 还需 targe
线性表的链式存储表示的特点是用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素
(这组存储单元可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的)。
因此,为了表示每个数据元素 与其直接后继数据元素 之间的逻辑关系,
对数据元素 来说,除了存储其本身的信息之外,
还需存储一个指示其直接后继的信息(即直接后继的存储位置)。
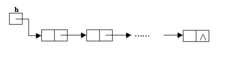
由这两部分信息组成一个"结点"(如概述旁的图所示),表示线性表中一个数据元素。
对于非线性的链表,可以参见相关的其他数据结构,
例如树、图。另外有一种基于多个线性链表的数据结构:
跳表,插入、删除和查找等基本操作的速度可以达到O(nlogn),和平衡二叉树一样。
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> struct node { int data; struct node *next; //后继指针 }; int Length(struct node *head)//求表的长度 { struct node *t=NULL; t=head; int n=0; while(t!=NULL) { t=t->next; n++; } return n; } int search1(struct node *head,int index)//根据序号查找返回值 { struct node *t=NULL; t=head; int j=1; while(t!=NULL&&j<index) { t=t->next; j++; } if(index==j) return t->data; else return 0; } int search2(struct node *head,int x) //按值查找返回位置 { struct node *t=NULL; t=head; int j=1; while(t!=NULL&&t->data!=x) { t=t->next; j++; } if(t->data==x) return j; else return 0; } void Delete(struct node *head,int index) //删除链表中某个位置的 { struct node *t=NULL,*q=NULL; t=head; int j=1; while(t!=NULL&&j<index-1) { t=t->next; j++; } q=t->next; t->next=q->next; free(t); t=head; while(t!=NULL) { printf("%d ",t->data); t=t->next; } } void AllDelete(struct node *head) //整个表的删除 { struct node *t=NULL,*q=NULL; t=head; while(t!=NULL) { q=t->next; free(t); t=q; } head=NULL; } int main() { struct node *head=NULL,*p,*q=NULL,*t=NULL; //初始化为空 int n,i,a; scanf("%d",&n); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d",&a); p=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); //分配动态空间 p->data=a; p->next=NULL; if(head==NULL) head=p; else q->next=p; //q作为临时保存 q=p; } printf("表的长度:%d\n",Length(head)); printf("位置1的值:%d\n",search1(head,1)); printf("值为4的位置%d\n",search2(head,4)); Delete(head,3);//删除位置为3的节点 scanf("%d",&a); //插入 t=head; while(t!=NULL) { if(t->next->data>a) //找到位置 { p=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); p->data=a; p->next=t->next; //后接 t->next=p; //前接 break; } t=t->next; } //输出 t=head; while(t!=NULL) { printf("%d ",t->data); t=t->next; } AllDelete(head); //删除整个表 }
标签:表示 scan 其他 操作 span bre 平衡 还需 targe
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/julyzqy/p/11877102.html