标签:元素 完成后 表示 pre alt 方法 引用 节点数据 dem
根据索引取得数据:public 数据类型 get(int index)
通过以上的代码测试发现,链表里面保存了多个String类的对象,在程序里面只有数组可以保存多个对象。现在使用的链表与数据相比较,优势没有长度限制,所以链表严格意义上来讲就是动态对象数组,既然链表属于动态对象数组,那么也应该具备像数组那样,可以根据索引取得元素的功能。
由于是动态对象数组,所以数组中的每一个元素的索引的内容都一定是动态生成的
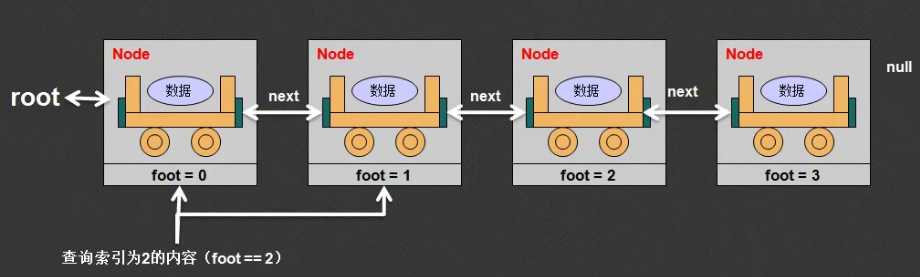
在Link类里面增加一个foot的属性,表示每一个Node元素的编号
private int foot = 0;
在每一次查询的时候(一个链表可能查询多次),那么foot在每次查询前都应该从根节点开始
public String get (int index){ if (index > this.count){ // 超过了查询的范围 return null; } this.foot = 0; // 表示从前向后查询 return this.root.getNode(index); // 查询过程交给Node类处理 }
在Node类里面实现getNode(index)方法,内部类和外部类之间可以方便的进行私有属性的互相访问
class Link{ // 链表类,外部只能看这一个类 // 定义在内部,主要为Link类服务 private class Node{ // 定义的节点类 private String data; // 保存数据 private Node next; // 引用关系 public Node(String data){ this.data = data; } public void AddNode(Node newNode){ if(this.next == null){ // 当前的下一个节点为空 this.next = newNode; }else{ // 向后继续保存 this.next.AddNode(newNode); } } public void printNode(){ // 打印Node信息 System.out.println(this.data); if( this.next != null){ this.next.printNode(); } } // 第一次调用(Link): this = Link.root // 第二次调用 (Node) : this = Link.root.next public boolean containsNode(String data){ if (data.equals(this.data)){ // 当前节点数据为要查询数据 return true; //后面不再查询了 }else{ //当前节点数据不满足查询要求 if (this.next != null){ // 有后续节点 return this.next.containsNode(data); }else{ // 没有后续节点了 return false; // 没得查了 } } } public String getNode(int index){ // 使用当前的foot内容与要查询的索引进行比较 // 随后将foot的内容自增,目的是为了下次查询方便 if (Link.this.foot++ == index){ // 如果等于,为查询的索引 return this.data; // 返回当前节点数据 }else{ // 现在应该继续向后查询 return this.next.getNode(index); } } // ===================以上为内部类============================ } private Node root; // 根结点 private int count = 0; // 保存元素的个数 private int foot = 0; public String get (int index){ if (index > this.count){ // 超过了查询的范围 return null; } this.foot = 0; // 表示从前向后查询 return this.root.getNode(index); // 查询过程交给Node类处理 } public void add(String data){ // 假设不允许有null if (data == null){ return ; } Node newNode = new Node(data); // 要保存的数据 if (this.root == null){ // 如果当前没有根节点,则设置为根节点 this.root = newNode; // 保存根节点 }else{ // 存在根节点,则到下一节点找保存数据 this.root.AddNode(newNode); } this.count ++; // 每一次保存完成后数量加一 } public int size(){ // 取得保存的数据量 return this.count; } public boolean isEmpty(){ //判断链表是否为空 return this.root == null; } public boolean contains(String data){ // 现在没有要查询的数据,要节点也不保存数据 if ( data == null || this.root == null ) { return false; //没有查询结果 } return this.root.containsNode(data); } public void print(){ // 打印所有Node信息 this.root.printNode(); } } public class LinkDemo{ public static void main(String args[]){ Link all = new Link(); all.add("Hello"); all.add("World"); all.add("World"); all.add("World"); System.out.println(all.get(1)); System.out.println(all.get(10)); } }
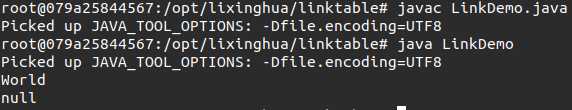
这样的话和数组的联系紧密了
标签:元素 完成后 表示 pre alt 方法 引用 节点数据 dem
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/anyux/p/11878013.html