标签:图片 down ip地址 选择 想去 splay mpls next 目标
路由基础认识路由器
路由器的每一个接口都处于不用的网段中,也就是在不用的广播域中 (大部分情况下两台路由器直接相连的接口算一个广播域)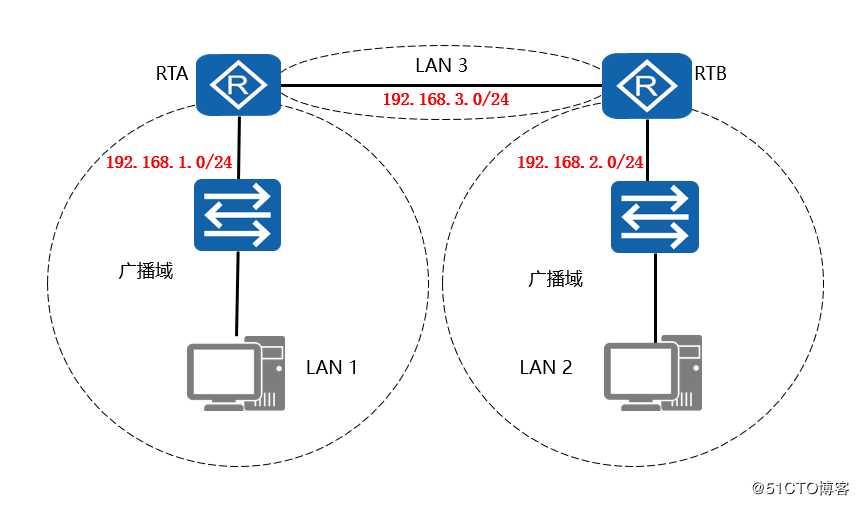
路由就是你想去往目标的一个路径
比如:我在上海这边去往武汉的话 源地址是上海 目标是武汉
? A路径:上海坐高铁到武汉
? B路径:上海作飞机到武汉
? C路径:上海坐船到武汉到底该选择哪一条路径呢?
? 时间或者速度或者距离长短
? 经济也就是钱或者费用
? 方便路由是指导IP报文转发的路径信息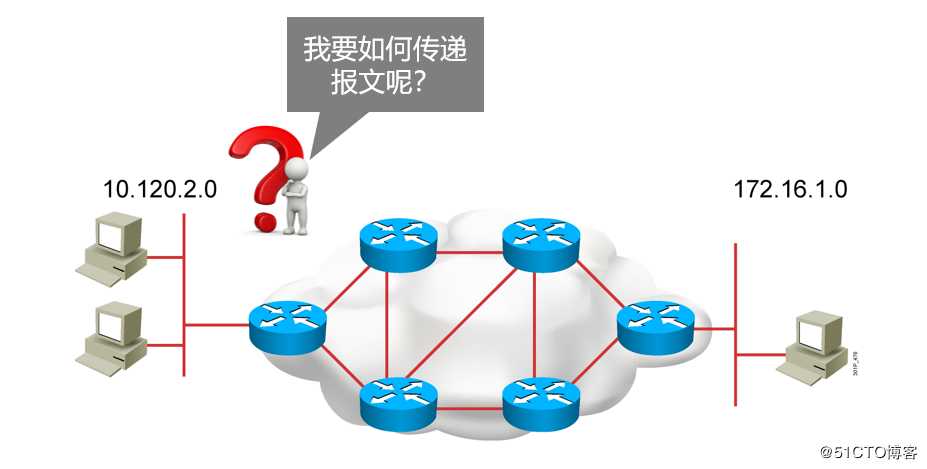
路由的信息都放在路由表当中 就是帮助设备进行选路用的
用命令查看路由器当中路由表
<R1>display ip routing-table
Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Routing Tables: Public
Destinations : 8 Routes : 8
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface
10.1.12.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.12.1 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
10.1.12.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
10.1.12.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
10.1.23.0/24 Static 60 0 RD 10.1.12.2 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
配置IP地址,端口UP状态,形成直连路由
需要静态路由或动态路由,将网段添加到路由表中
<R1>display ip routing-table
Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Routing Tables: Public
Destinations : 8 Routes : 8
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface
10.1.12.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.12.1 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
10.1.12.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
10.1.12.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
10.1.23.0/24 Static 60 0 RD 10.1.12.2 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0Destination/Mask:目标网络:你想去往目标地的网络
Proto:路由来源:要么是通过直连学习到 要么是通过静态或者动态构建出来的
Pre:优先级:直连是0 OSPF是10和150 静态是60 rip是100 BGP是255
Cost:开销值(cost):可以理解为花销成本
Flags:标志位
NextHop:下一跳:你想要去往目标地的下一站 127.0.0.1表示的是抵达设备自身流量
Interface:出接口:数据包发送的接口
注意:一般来说 出接口和下一跳在同一个网段1、被转发的路由条路必须存在
2、根据最长匹配原则进行匹配 也就是掩码越长越好
3、当掩码一样 会比较优先级 优先级是最小最优先
4、当掩码一样 优先级一样的情况下 会比较开销 也就是cost值 这个数值越小越优先
5、当前面的所有原则是一样的情况 负载分担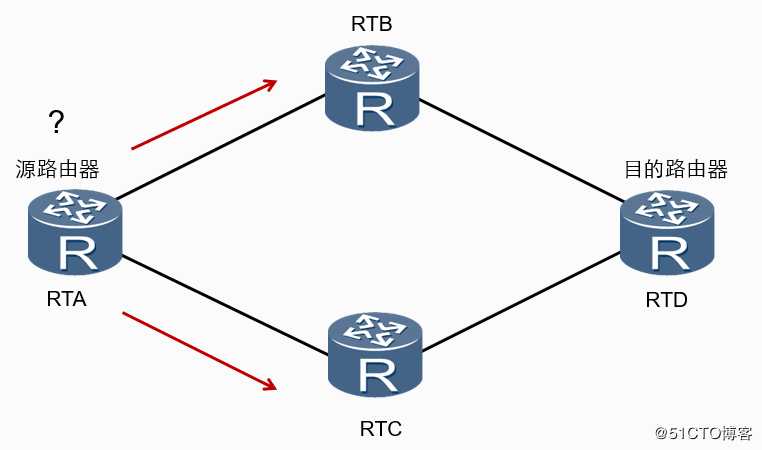
1、接口下面得配置IP地址
2、接口必须UP(就是接口的灯是亮的)1、是所有路由当中优先级最高的(默认情况 直连>OSPF>static等)
2、直连路由可以自动生成出来(只要触发一定条件就可以诞生)不能去往非自己直连的其他网段(地方)
AR1配置
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
[R1]display ip interface brief
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 2
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 2
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 2
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 2
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 192.168.1.1/24 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
[R1]
[R1]display ip routing-table
Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Routing Tables: Public
Destinations : 7 Routes : 7
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
192.168.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 192.168.1.1 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
192.168.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
192.168.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
[R1]控制平面用于控制和管理网络协议的运行,比如OSPF协议、RIP协议、BGP协议、MPLS协议
display ip routing-table 查看IP路由表,属控制平面范畴(路由信息数据库,RIB)转发平面对于数据处理过程中各种具体处理转发过程,比如二层流量或者三层流量等流量转发
display fib 查看最终迭代的出接口,属数据平面范畴(转发信息数据库,FIB) 每个路由器都至少保存着一张路由表(routeing-table)和一张FIB(Forwarding Information Base)表。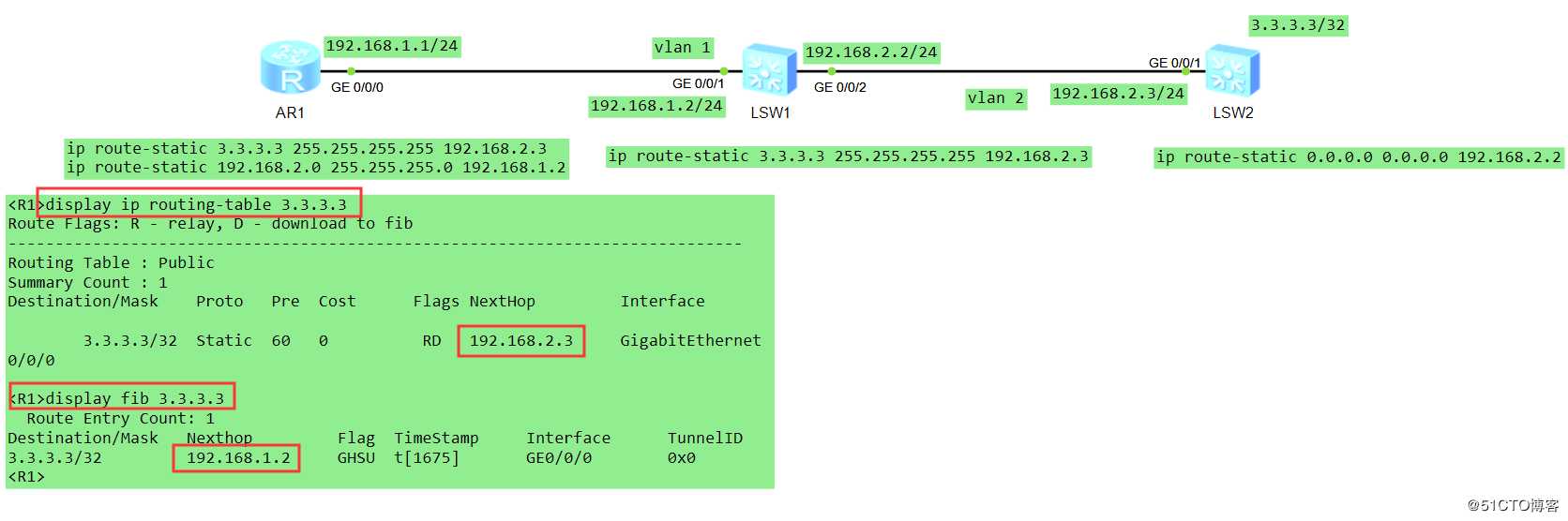
标签:图片 down ip地址 选择 想去 splay mpls next 目标
原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/13817711/2451779