标签:sea ted 之间 string begin ack 总结 size monitor
纪念第一次正式参加,听说这次题目很水,感觉确实不是很难,一般前两题都很简单,这次,到第三题的时候,都还可以做,emm......

实际代码记录:

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <math.h> #include <string> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; /* * 功能:初始化m行n列的二维vector * 参数:m,n,vector */ void init(int m, int n, vector<vector<int> > &vc) { //初始化一个数组m行 n列 vector<int> level; level.resize(n); vc.resize(m, level); for (int i = 0; i < m;i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { cin >> vc[i][j]; } } } /* * 功能:输出vector * 参数:vector */ void vecPrint(const vector<vector<int> > vc) { //输出 cout << "The vector vc is as follow:" << endl; int m = vc.size(); int n = vc[0].size(); for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { cout << vc[i][j] << "\t"; } cout << endl; } } int minTimeToVisitAllPoints(vector<vector<int> >& points) { int m = points.size(); int n = 2; //只存在横纵坐标,两个 int cost_time = 0; //记录总时间 int x1, x2, y1, y2; for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) { //记录两个点 x1 = points[i - 1][0]; y1 = points[i - 1][1]; x2 = points[i][0]; y2 = points[i][1]; //计算两个点之间的最小时间 if (x1 == x2) { //位于同一条直线上 cost_time += abs(y1-y2); } else if (y1 == y2) { cost_time += abs(x1 - x2); } else if (x1 < x2 && y1 < y2) { //位于右上方 while (x1 < x2 && y1 < y2) { x1++; y1++; cost_time++; } //底下至少有一个为0 cost_time += abs(x1 - x2); cost_time += abs(y1 - y2); } else if (x1 > x2 && y1 < y2) { //位于左上方 while (x1 > x2 && y1 < y2) { x1--; y1++; cost_time++; } //底下至少有一个为0 cost_time += abs(x1 - x2); cost_time += abs(y1 - y2); } else if (x1 > x2 && y1 > y2) { //位于左下方 while (x1 > x2 && y1 > y2) { x1--; y1--; cost_time++; } //底下至少有一个为0 cost_time += abs(x1 - x2); cost_time += abs(y1 - y2); } else if (x1 < x2 && y1 > y2) { //位于右下方 while (x1 < x2 && y1 > y2) { x1++; y1--; cost_time++; } //底下至少有一个为0 cost_time += abs(x1 - x2); cost_time += abs(y1 - y2); } } return cost_time; } int countServers(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { //对每行没列进行标记 int result = 0; int i, j, k; for (i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) { for (j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) { if (grid[i][j] == 1) { //看i行或j列是否存在i int flag = 0; for (k = 0; k < grid.size(); k++) { if (k != i && grid[k][j] == 1) { result += 1; flag = 1; //表示行找到了 break; } } if (flag == 0) { //如果行没有找到,需要找列 for (k = 0; k < grid[0].size(); k++) { if (k != j && grid[i][k] == 1) { result += 1; break; } } } } } } return result; } /* int main() { int m, n; cin >> m >> n; vector<vector<int> > vc; init(m,n,vc); vecPrint(vc); //cout << minTimeToVisitAllPoints(vc) << endl; cout << countServers(vc) << endl; return 0; } */ vector<vector<string> > suggestedProducts(vector<string>& products, string searchWord) { vector<vector<string> > result; //vector<string> level = products; //处理level //sort排序试试 sort(products.begin(), products.end()); //输出查看效果 int i; /* for (i = 0; i < products.size(); i++) { cout << products[i] << endl; } */ //排序结束,然后进行查找 int len = searchWord.length(); int k=1; while (len--) { int count = 0; string condistr; //候选字符串 condistr = searchWord.substr(0, k); //cout << "候选模式串为:" << condistr << endl; vector<string> level; for (i = 0; i < products.size(); i++) { if (products[i].substr(0, k) == condistr) { if (count < 3) { level.push_back(products[i]); count++; cout << products[i] << " "; } } } cout << endl; result.push_back(level); level.clear(); k++; } return result; } /* int main() { vector<string> result; string str; int k; cin >> k; while (k--) { cin >> str; result.push_back(str); } suggestedProducts(result,"mouse"); return 0; } */ /* 5 mobile mouse moneypot monitor mousepad */
题目:(前三题比较简单,只总结最后一题)
有一个长度为 arrLen 的数组,开始有一个指针在索引 0 处。
每一步操作中,你可以将指针向左或向右移动 1 步,或者停在原地(指针不能被移动到数组范围外)。
给你两个整数 steps 和 arrLen ,请你计算并返回:在恰好执行 steps 次操作以后,指针仍然指向索引 0 处的方案数。
由于答案可能会很大,请返回方案数 模 10^9 + 7 后的结果。
示例 1:
输入:steps = 3, arrLen = 2
输出:4
解释:3 步后,总共有 4 种不同的方法可以停在索引 0 处。
向右,向左,不动
不动,向右,向左
向右,不动,向左
不动,不动,不动
理解:
方案一、(自己的想法)
拿到这道题的第一想法是,枚举解答树,只有三种走法,左走,不动,右走,那么我可以申请一个数组d[3],初始化该数组为d[3]={-1,0,1},即可以将当前的索引位置想象成数轴上的原点坐标,当前位置为pos,往左走一步,位置变为pos-1,不动的情况位置仍为pos,往右走一步,位置变为pos+1。利用一个解答树,判断走了steps步以后,是否为原点0,即可求得最终解;
以示例1为例,我们可以画一棵树,如下所示:
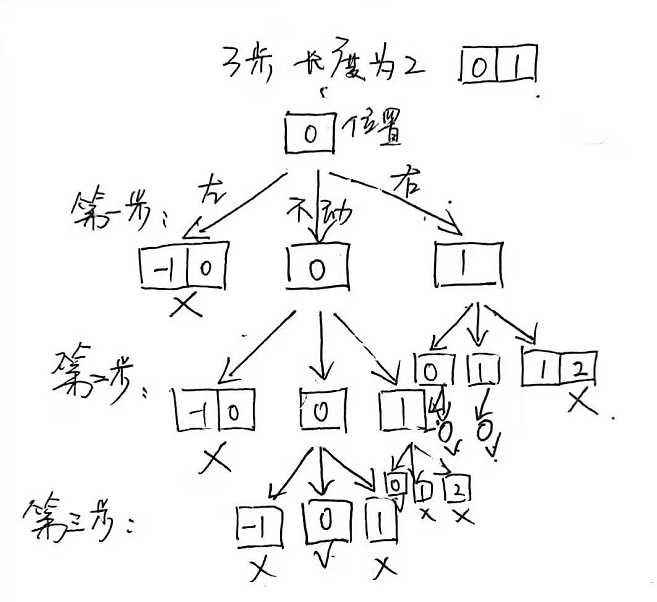
注意:1.当位于原点0时,向左走到了-1的位置,超出了最左限制,当位于数组末尾时,向右走到了2的位置,超出了最右限制;
2.当遍历到最后一步,即最后一层时,我们如果总和sum等于0,说明经过上三步之后,仍位于原点位置,否则直接return。
因此,我们总结出如下代码:(不考虑模100000007的结果)
代码如下:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int d[3] = { 0,-1,1 }; //不动,左,右 4 int count = 0; 5 int sum = 0; 6 int numWays(int steps, int arrLen) { 7 dfs(0,steps,arrLen,sum); 8 return count; 9 } 10 11 12 void dfs(int depth,int step,int arrLen,int sum) //step 13 { 14 if (depth >= step) 15 { 16 if (sum == 0) 17 count++; 18 return; 19 } 20 if (sum < 0 || sum >= arrLen) 21 return; 22 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) 23 { 24 dfs(depth + 1,step,arrLen,sum+d[i]); 25 } 26 } 27 };
很遗憾,这样的递归遍历方式,在27步的时候,就超时了,但是贴到这儿是为了学习,哈哈!
方案二、(学习别人的动态规划思想)
学会再来补充啦~
标签:sea ted 之间 string begin ack 总结 size monitor
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/cnyulei/p/11922461.html