标签:mic block cli back rev log click 部分 梯度下降
另外一种线性回归,它是利用矩阵求导的方式来实现梯度下降算法一样的效果。
首先定义![]() 表示m×n的矩阵,那么对该矩阵进行求导可以用下式表示,可以看出求导后的矩阵仍然为m×n
表示m×n的矩阵,那么对该矩阵进行求导可以用下式表示,可以看出求导后的矩阵仍然为m×n
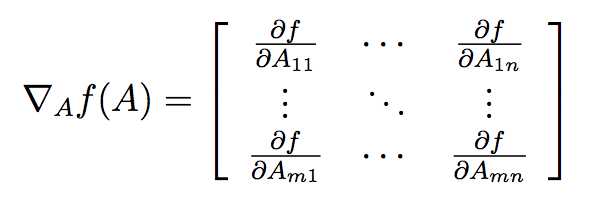
这里要用到矩阵迹的特性,trace. 对于一个n阶的方阵(n×n),它的迹(tr)为对角线元素之和:
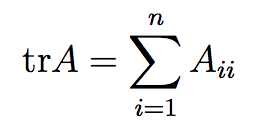
1. 对于一个实数,它的迹即为它本身
tr a = a
2. 如果AB是一个方阵,那么
tr AB = tr BA
3. 由此可推导出
trABC = trCAB = trBCA
trABCD = trDABC = trCDAB = trBCDA
4. 假设A 和 B为方阵,a为实数,那么又可以推导出以下的特性:
trA = trAT
tr(A + B) = trA + trB
tr aA = atrA
5.对迹进行求导,具有以下特性:
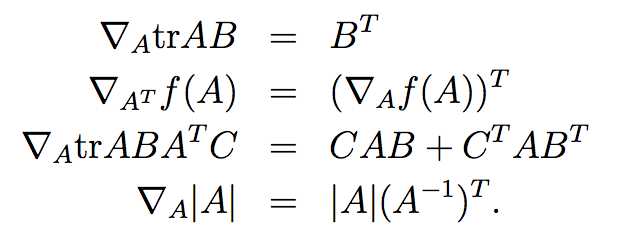
现在就可以利用1中矩阵求导的相关知识来重新求解线性回归问题。
假设训练样本:
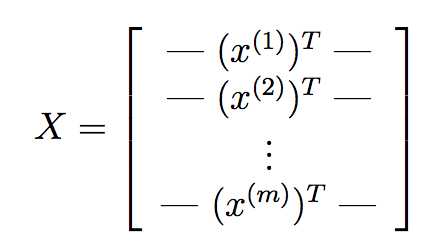
定义目标集合:
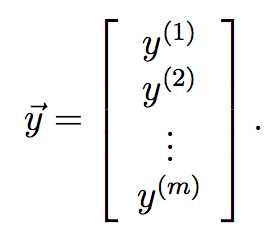
因为![]() ,所以
,所以
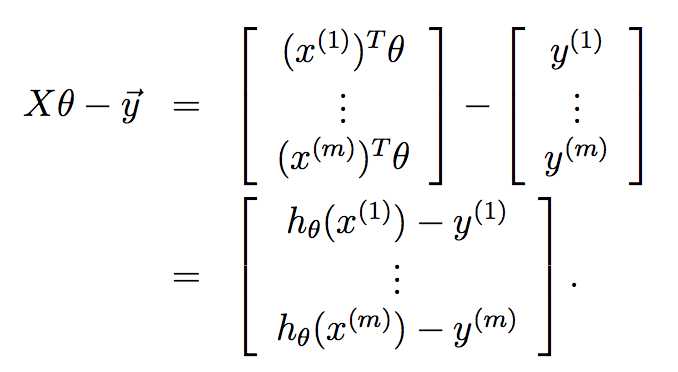
又因为![]() ,根据最小二乘规则,代价函数可以写成:
,根据最小二乘规则,代价函数可以写成:
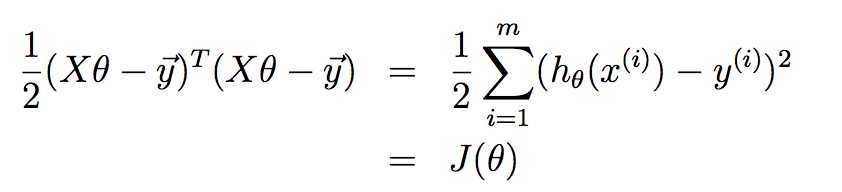
对J(θ)进行求导:
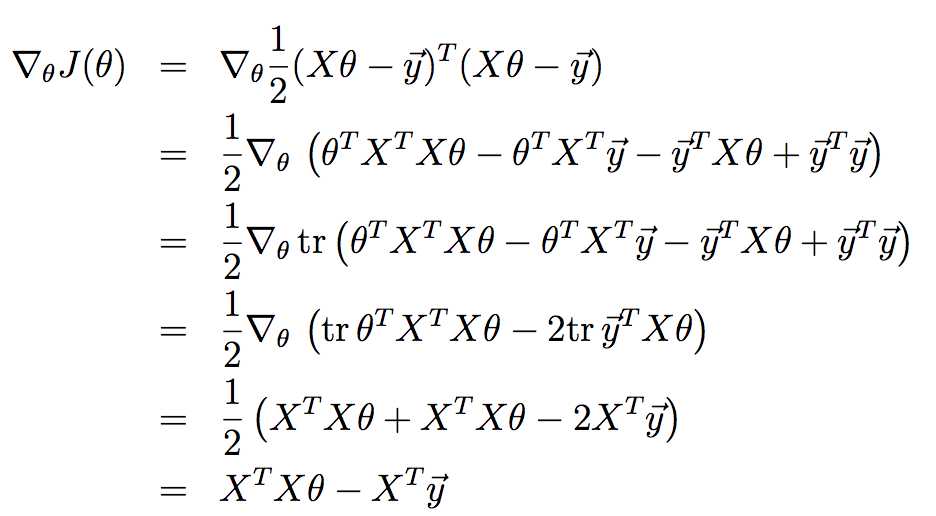
上述推导使用了第1部分的特性。
miniminzes J(θ) 即
![]()
![]()
![]()
python代码实现
1 # coding=utf-8 2 #!/usr/bin/python 3 4 ‘‘‘ 5 Created on 2014年9月10日 6 7 @author: Ryan C. F. 8 9 ‘‘‘ 10 11 import numpy 12 13 #Training data set 14 #each element in x represents (x0,x1,x2) 15 #x = [(1,0.,3) , (1,1.,3) ,(1,2.,3), (1,3.,2) , (1,4.,4)] 16 #y[i] is the output of y = theta0 * x[0] + theta1 * x[1] +theta2 * x[2] 17 #y = [95.364,97.217205,75.195834,60.105519,49.342380] 18 19 def linearRegression(X,Y): 20 A=numpy.dot(X.T,X) #XT*X X的转置矩阵点乘X 21 Ai=A.I #(XT*X)-1 求逆 22 B=numpy.dot(Ai,X.T) #(XT*X)-1 XT 点乘 23 C=numpy.dot(B,Y.T) #((XT.X)-1)XT点乘Y 24 return C 25 26 if __name__ == "__main__": 27 X=numpy.matrix([[1,0.,3], 28 [1,1.,3], 29 [1,2.,3], 30 [1,3.,2], 31 [1,4.,4]]); 32 print X.transpose(); 33 34 Y=numpy.matrix([95.364,97.217205,75.195834,60.105519,49.342380]); 35 print Y; 36 37 print numpy.dot(numpy.dot(numpy.dot(X.T,X).I,X.T),Y.T) 38 39 print (linearRegression(X,Y))
输出结果
1 X: 2 [[ 1. 0. 3.] 3 [ 1. 1. 3.] 4 [ 1. 2. 3.] 5 [ 1. 3. 2.] 6 [ 1. 4. 4.]] 7 8 Y: 9 [[ 95.364 97.217205 75.195834 60.105519 49.34238 ]] 10 11 linear Regression result: 12 [[ 98.10408328] 13 [-13.02877437] 14 [ 1.13281768]]
http://www.cnblogs.com/rcfeng/
标签:mic block cli back rev log click 部分 梯度下降
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/bind/p/11957972.html