标签:string 类型 条件 符号 技术 efault 子程序 tput 出错
一、实验目的:
利用C语言编制递归下降分析程序,并对简单语言进行语法分析。
编制一个递归下降分析程序,实现对词法分析程序所提供的单词序列的语法检查和结构分析。
二、实验原理
每个非终结符都对应一个子程序。
该子程序根据下一个输入符号(SELECT集)来确定按照哪一个产生式进行处理,再根据该产生式的右端:
三、实验要求说明
输入单词串,以“#”结束,如果是文法正确的句子,则输出成功信息,打印“success”,否则输出“error”,并指出语法错误的类型及位置。
例如:
输入begin a:=9;x:=2*3;b:=a+x end #
输出success
输入x:=a+b*c end #
输出‘end‘ error
四、实验步骤
1.待分析的语言的语法(参考P90)
2.将其改为文法表示,至少包含
–语句
–条件
–表达式
3. 消除其左递归
4. 提取公共左因子
5. SELECT集计算
6. LL(1)文法判断
7. 递归下降分析程序
代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void judge();
void T();
void E1();
void T1();
void F();
char input[100],output[10]; //输入输出数组
char word;
int code,row,num,p,i,k;
char *reserve[6]={"begin","if","then","while","do","end"};
int flag=0;
void judge(){
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
output[i]=NULL;
word=input[p++];
while(word==‘ ‘){//空格则忽略
word=input[p];
p++;
}
if((word>=‘a‘&&word<=‘z‘)||(word>=‘A‘&&word<=‘Z‘)){//判断字母
k=0;
while((word>=‘0‘&&word<=‘9‘)||(word>=‘a‘&&word<=‘z‘)||(word>=‘A‘&&word<=‘Z‘)){
output[k++]=word;
word=input[p++];
}
output[k++]=‘\0‘;//结束字符串
p--;
code=10;
for(i=0;i<6;i++){
if(strcmp(reserve[i],output)==0){//关键字对比
code=i+1;
break;
}
}
}else if(word>=‘0‘&&word<=‘9‘){//判断数字
num=0;
while(word>=‘0‘&&word<=‘9‘){
num=num*10+(word-‘0‘);
word=input[p++];
}
p--;
code=11;
}else switch(word){//判断符号
case ‘+‘:
output[0]=word;code=13;
break;
case ‘-‘:
output[0]=word;code=14;
break;
case ‘*‘:
output[0]=word;code=15;
break;
case ‘/‘:
output[0]=word;code=16;
break;
case ‘:‘:
i=0;
output[i++]=word;
word=input[p++];
if(word==‘=‘){
output[i++]=word;
code=18;
}else{
code=17;
p--;
}
break;
case ‘<‘:
i=0;
output[i++]=word;
word=input[p++];
if(word==‘=‘){
output[i++]=word;
code=21;
}else if(word==‘>‘){
output[i++]=word;
code=22;
}else{
code=20;
p--;
}
break;
case ‘>‘:
i=0;
output[i++]=word;
word=input[p++];
if(word==‘=‘){
output[i++]=word;
code=24;
}else{
code=23;
p--;
}
break;
case ‘=‘:
output[0]=word;code=25;
break;
case ‘;‘:
output[0]=word;code=26;
break;
case ‘(‘:
output[0]=word;code=27;
break;
case ‘)‘:
output[0]=word;code=28;
break;
case ‘#‘:
output[0]=word;code=0;
break;
case ‘\n‘:
code=100;
break;
default:
code=-1;
break;
}
}
//新加
void E(){
if(code==1){
judge();
T();
while(code==26){
judge();
T();
}
if(code==6){
judge();
if(code==0 && flag==0){
printf("成功!\n");
}
}
else{
printf("语法有误,缺少end!\n");
}
}else{
printf("语法有误,缺少begin!\n");
flag=1;
}
return ;
}
void T(){
if(code==10){
judge();
if(code==18){
judge();
E1();
}else{
printf("表达式语法有误!错误是%s\n",output);
flag=1;
}
}else{
if(flag!=1){
printf("表达式语法有误,错误是%s\n",output);
flag=1;
}
}
}
void E1(){
T1();
while(code==13||code==14){
judge();
T1();
}
return ;
}
void T1(){
F();
while(code==15||code==16){
judge();
F();
}
return ;
}
void F(){
if(code==10||code==11){
judge();
}else if(code==27){
judge();
E1();
if(code==28)
judge();
else{
printf("没有‘)‘,语法有误!\n");
flag=1;
}
}
else{
printf("表达式语法有误!错误为:%s\n",output);
flag=1;
}
return ;
}
int main(){
p=0;
printf("输入语句段:");
do{
word=getchar();
input[p++]=word;
}while(word!=‘#‘);
p=0;
judge();
E();
printf("结束!");
getchar();
}
运行结果:
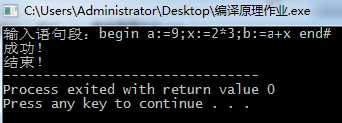
图1-1
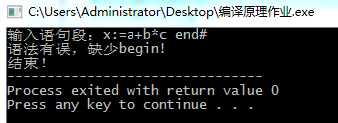
图1-2
标签:string 类型 条件 符号 技术 efault 子程序 tput 出错
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/MRJ1/p/11959307.html