标签:释放 实现 数组名 -- %s printf size 字符串 color
1//指针申请动态空间 最后释放空间
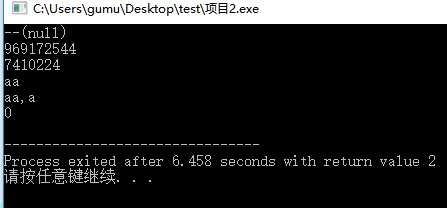
char *u=NULL; printf("--%s\n",u); //一个字符指针 默认为空 null不打印 当给--后会打印出来 char *p; printf("%d\n",p); //在为赋值前 打印为随机地址 p=(char *)malloc(sizeof(char)); // 动态申请空间 printf("%d\n",p); //任然是随机数 scanf("%s",p); //输入 printf("%s,%c\n",p,*p); //打印指针所指代的数字 和当前指针的代表变量 free(p); //释放空间 printf("%c\n",p); //打印为 0
2//指针操作字符串
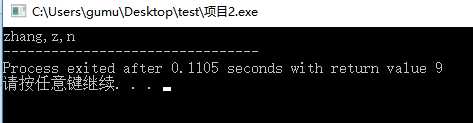
char *p="zhang"; printf("%s,%c,%c",p,*p,*(p+3));
3//字符串数组的初始化
char s1[]="I is array"; //字符数组 char s2[6]="array"; //数组长度=字符串长度+1,因为字符串末尾会自动添‘\0‘ printf("%s,%c\n",s1,s2[2]); //array,r
4//指针+数组+scanf
//指针+数组+scanf char str[60], *sp=str;//将数组的首地址str赋给指针变量sp scanf("%s",sp); printf("%s,%c,%c\n",sp,*sp,*(sp+3));//pointer,p,n printf("%s,%c,%c\n",str,str[0],str[3]);//pointer,p,n
5//控制台终止运行
char *sp;//sp未初始化指向不明 scanf("%s\n",sp); printf("%s\n",sp);
6//用scanf和gets(字符数组名或指针)进行输入的区别
char str1[60],str2[60]; gets(str1); //gets()函数将接收输入的整个字符串直到遇到换行为止 printf("%s\n",str1); scanf("%s\n",str2);//scanf如果输入了空格会认为字符串结束,空格后的字符将作为下一个输入项处理 printf("%s\n",str2);
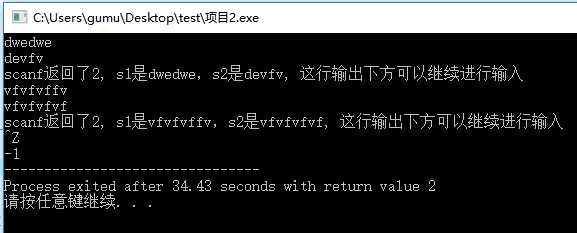
7//使用while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){ }实现多组测试数据输入,而不在输入完一组数据后退出控制台
char s1[60],s2[60]; int cnt; //用来测试scanf返回被输入函数成功赋值的变量个数 while((cnt=scanf("%s%s",s1,s2))!=EOF){ //当按下ctr+z终止输入时,scanf会返回EOF(-1)\n printf("scanf返回了%d, s1是%s,s2是%s, 这行输出下方可以继续进行输入\n",cnt,s1,s2); //scanf若成功输入str1和str2则返回2 } printf("%d",cnt);//当按下ctr+z后会执行该条输出-1
标签:释放 实现 数组名 -- %s printf size 字符串 color
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/myfriend/p/11976988.html