标签:out hadoop2 demo net 进入 throws 创建文件 客户 支持
FileChannel主要用于对本地文件进行IO操作, 常见方法有:
一个简单demo
示意图
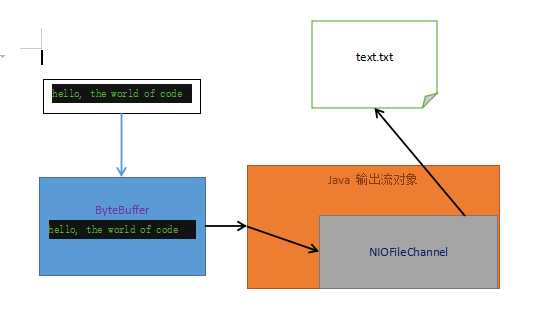
写入案例代码
package com.ronnie.nio;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannel01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str = "hello, the world of code";
// 创建一个输出流 -> channel
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:/fun/nio/doc/text.txt");
// 通过 fileOutputStream获取对应的 FileChannel
// 需要注意的是: 此fileChannel真实类型是 FileChannelImpl
FileChannel fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
// 创建缓冲区 ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 将 str 放入 byteBuffer
byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());
// 对byteBuffer进行反转(flip)
byteBuffer.flip();
// 将byteBuffer 数据写入到channel
fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}细节
fileOutputStream.getChannel()获取的 fileChannel 真实类型是 FileChannelImpl, 是FileChannel的实现类, FileChannel本身只是一个抽象类。
getChannel()方法:
/**
* Returns the unique {@link java.nio.channels.FileChannel * FileChannel} object associated with this file output stream.
* 返回与此文件输出流相关的唯一FileChannel对象
*
* <p> The initial {@link java.nio.channels.FileChannel#position()
* position} of the returned channel will be equal to the
* number of bytes written to the file so far unless this stream is
* in append mode, in which case it will be equal to the size of the
* file.
* 返回的channel的初始位置与写入到此文件此文件的byte数一致(除非这个流式可
* 添加模式, 该模式下channel的初始位置会与该文件的大小一致)
* Writing bytes to this stream will increment the channel's position
* accordingly.
* 将字节码写入到该流会增加该channel的位置
* Changing the channel's position, either explicitly or by
* writing, will change this stream's file position.
* 改变管道的位置, 无论是显示的修改还是通过写入修改, 都会改变此流的文件位置
*
* @return the file channel associated with this file output stream
*
* @since 1.4
* @spec JSR-51
*/
public FileChannel getChannel() {
// 同步锁锁了当前输出流对象
synchronized (this) {
// 如果管道为空
if (channel == null) {
// 就创建一个新的FileChannelImpl对象赋给channel
channel = FileChannelImpl.open(fd, path, false, true, append, this);
}
return channel;
}
}FileChannelImpl.open()方法:
public static FileChannel open(FileDescriptor var0, String var1, boolean var2, boolean var3, boolean var4, Object var5) {
return new FileChannelImpl(var0, var1, var2, var3, var4, var5);
}读取案例代码
package com.ronnie.nio;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannel02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建文件输入流
File file = new File("E:/fun/nio/doc/text.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
// 通过fileInputStream 获取对应的fileChannel -> 实际类型 FileChannelImpl
FileChannel fileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
// 创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) file.length());
// 将通道的数据读入到buffer中
fileChannel.read(byteBuffer);
// 将字节数据转成String
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
一个Buffer完成文件读取案例
示意图

代码
package com.ronnie.nio;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannel03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("1.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("2.txt");
FileChannel channel01 = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel channel02 = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
// 循环读取
while (true){
// 非常重要的操作, 复位(重置标志位)
// 如果没写, 当position与limit相等时, read永远为0, 进入死循环
byteBuffer.clear();
int read = channel01.read(byteBuffer);
if (read == -1){
break;
}
// 将buffer 中的数据写入到 channel02
byteBuffer.flip();
channel02.write(byteBuffer);
}
// 关闭流
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
使用transferFrom()方法拷贝文件案例
package com.ronnie.nio;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannel04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建线管的流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:/fun/nio/doc/hadoop.jpg");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:/fun/nio/doc/hadoop2.jpg");
// 获取各个流对应的fileChannel
FileChannel sourceChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel destinationChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
// 使用transferFrom完成拷贝
destinationChannel.transferFrom(sourceChannel, 0, sourceChannel.size());
// 关闭相关通道和流
sourceChannel.close();
destinationChannel.close();
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}Buffer 和 Channel的注意事项和细节
ByteBuffer支持类型化的put和get, put放入的是什么数据类型, get就应该使用相应的数据类型来取出, 否则可能有 BufferUnderflowException 异常
package com.ronnie.nio;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
public class NIOByteBufferPutGet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个Buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);
// 类型化放入数据
buffer.putInt(100);
buffer.putLong(9);
buffer.putChar('w');
buffer.putShort((short) 4);
// 取出
buffer.flip();
System.out.println();
System.out.println(buffer.getInt());
System.out.println(buffer.getLong());
System.out.println(buffer.getChar());
System.out.println(buffer.getShort());
// 加个没的, 让它报错
System.out.println(buffer.getLong());
}
}100
9
w
4
Exception in thread "main" java.nio.BufferUnderflowException
at java.nio.Buffer.nextGetIndex(Buffer.java:506)
at java.nio.HeapByteBuffer.getLong(HeapByteBuffer.java:412)
at com.ronnie.nio.NIOByteBufferPutGet.main(NIOByteBufferPutGet.java:26)可以将一个普通Buffer转成只读Buffer, 转换后不能再写入
package com.ronnie.nio;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
public class ReadOnlyBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++){
buffer.put((byte) i);
}
// 读取
buffer.flip();
// 得到一个只读的Buffer
ByteBuffer readOnlyBuffer = buffer.asReadOnlyBuffer();
System.out.println(readOnlyBuffer.getClass());
// 读取
while (readOnlyBuffer.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(readOnlyBuffer.get());
}
// 会抛出ReadOnlyBufferException
readOnlyBuffer.put((byte) 100);
}
}NIO还提供了 MappedByteBuffer, 可以让文件直接在内存(堆外的内存)中进行修改。
package com.ronnie.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* MappedByteBuffer 可让文件直接在堆外内存修改, 操作系统无需将数据拷贝到用户态内存中,
* 即零拷贝, kafka底层就是依靠netty实现了零拷贝
*/
public class MappedByteBufferTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile("1.txt", "rw");
// 获取对应的通道
FileChannel channel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
/**
* 参数1: FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE 使用的读写模式
* 参数2: 0: 可以直接修改的起始位置
* 参数3: 5: 是映射到内存的大小(不是索引位置), 即将 1.txt 的多少个字节映射到
* 内存
* 可以直接修改的范围就是0~5, 不到5
*/
MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 5);
mappedByteBuffer.put(0, (byte) 'S');
mappedByteBuffer.put(3, (byte) '8');
// mappedByteBuffer.put(5, (byte) 'G'); 会抛出数组越界异常
randomAccessFile.close();
System.out.println("修改成功");
}
}
之前所说的读写操作都是通过一个Buffer完成的, NIO还支持通过多个Buffer(即Buffer数组) 完成读写操作, 即Scattering(分散) 和 Gathering(聚合)
案例代码:
package com.ronnie.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.Buffer;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Scattering: 将数据写入到buffer时, 可以采用buffer数组, 依次写入 [分散]
* Gathering: 从buffer读取数据时, 可以采用buffer数组, 依次读
*/
public class ScatteringAndGatheringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 使用 ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel 网络
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(7000);
// 绑定端口到socket, 并启动
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress);
// 创建Buffer数组
ByteBuffer[] byteBuffers = new ByteBuffer[2];
byteBuffers[0] = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
byteBuffers[1] = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
// 等待客户端连接(telnet)
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
// 假定从客户端接收8个字节
int messageLength = 8;
// 循环的读取
while (true){
int byteRead = 0;
while (byteRead < messageLength){
long l = socketChannel.read(byteBuffers);
// 累计读取的字节数
byteRead += 1;
System.out.println("byteRead = " + byteRead);
// 使用流打印, 查看当前buffer的position和limit
Arrays.stream(byteBuffers).map(buffer -> "position = " + buffer.position() + ", limit = " + buffer.limit()).forEach(System.out::println);
}
// 将所有的buffer进行反转(flip)
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(Buffer::flip);
// 将数据读出显示到客户端
long byteWrite = 0;
while(byteWrite < messageLength){
long l = socketChannel.write(byteBuffers);// 回写
byteWrite += 1;
}
// 将所有的 buffer 进行 clear操作
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(Buffer::clear);
System.out.println("byteRead := " + byteRead + " byteWrite = " + byteWrite + ", messageLength = " + messageLength);
}
}
}
windows的话打开win + R输入cmd, telnet 127.0.0.1 7000, 就就可以发送数据, 没有开启的请: 控制面板 -> 程序 -> 启用或关闭 Windows功能 -> 开启Telnet Client
标签:out hadoop2 demo net 进入 throws 创建文件 客户 支持
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ronnieyuan/p/12001383.html