标签:nod cstring 分解 发放 数字 ini als 数学 scanf
一篇迟到的题解,本以为大家兴趣不大,但是有同学问了,本人觉得还是应该写一下。
T酱和他的数学题
要求判断末尾有多少个0
我们分析一下就可以知道0只能是来自2 和 5 的乘积。
对于每一个数字我们只需要去判断可以分解出多少个2和5就可以,其中5的出现次数一定会小于2的出现次数。
由于是阶乘的阶乘
所以我们只需要暴力一遍,维护5出现次数的前缀和的前缀和就可以了
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 int cal(int x) 3 { 4 int res = 0; 5 while(x) 6 { 7 if(x%5) break; 8 x /= 5; 9 res++; 10 } 11 return res; 12 } 13 int main() 14 { 15 long long res, tmp; 16 int n; 17 while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) 18 { 19 res = tmp = 0; 20 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 21 { 22 tmp += cal(i); 23 res += tmp; 24 } 25 printf("%lld\n", res); 26 } 27 }
Vic和骑士
自己手推一下 n = 4 和n = 5的情况, 就会发现规律,只要RB交错排列就可以
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 int T, n, ca = 0; 10 while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) 11 { 12 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 13 { 14 if(i%2) 15 for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) 16 if(j%2) putchar(‘B‘); 17 else putchar(‘R‘); 18 if(i%2==0) 19 for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) 20 if(j%2) putchar(‘R‘); 21 else putchar(‘B‘); 22 23 putchar(‘\n‘); 24 } 25 putchar(‘\n‘); 26 } 27 28 }
Vic与水题
根据题目输出就可以, 但是我们提交的输出样例显示有点问题,在题面里也说明了
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 int main() 4 { 5 int T, n, flag; 6 cout<<"#include<stdio.h>"<<endl; 7 cout<<"int main()"<<endl; 8 cout<<"{"<<endl; 9 cout<<"int n;"<<endl; 10 cout<<"n = 10;"<<endl; 11 cout<<"printf(\"%d\", n);"<<endl; 12 cout<<"return 0;"<<endl; 13 cout<<"}"; 14 }
保护牛奶
对于这一题,我们可以发现,牛奶被放成了一圈,并且只能取连续的。
贪心策略是利用圆的对称性来反制对手,所以只有当数量为1 或 2 或 3 时, 先手才赢的机会
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 int T, n, flag; 7 while(scanf("%d", &T) != EOF) 8 { 9 while(T--) 10 { 11 scanf("%d", &n); 12 if(n<=3&&n>=1) cout<<"milk will die!!!"<<endl; 13 else cout<<"milk is alive!!!"<<endl; 14 } 15 16 } 17 18 }
当老板
这个题目是一个二分题,但是相对于传统的二分,我们需要计算上界或者下界来保证二分的顺利进行.
讲一下二分的思路,主要是check比较难
对于check的值 我们假设是X,每一个员工的可接受的工资是[Li, Ri]
那么对于Li>X 的员工只能是让他排在中位数的右边
对于Ri<X的员工只能是让他排在中位数的左边
然后剩下的我们进行最优分配,如果左边此时还没达到要求人数的一半,那么应该补足左边,这些人发放最小工资,右边的人则是发放X的工资。最后判读这样的分配下花费是否够用可以。
具体看代码吧
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <set> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 struct node 8 { 9 int l, r; 10 bool operator < (struct node a) 11 { 12 return l < a.l; 13 } 14 }a[200009]; 15 typedef long long ll; 16 int T, n, l, r, mid; 17 ll sum; 18 bool check(int x) 19 { 20 vector <struct node> ve; 21 ve.clear(); 22 int num = 0; 23 ll res = 0; 24 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 25 if(a[i].r<x) 26 { 27 res += a[i].l; 28 num++; 29 } 30 else if(a[i].l>x) 31 { 32 res += a[i].l; 33 }else ve.push_back(a[i]); 34 35 if(num>=n/2+1) return false; 36 37 int size = ve.size(); 38 39 for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) 40 if(num<n/2) 41 { 42 res += ve[i].l; 43 num++; 44 }else res += x; 45 46 return res <= sum; 47 } 48 49 int main() 50 { 51 scanf("%d", &T); 52 while(T--) 53 { 54 scanf("%d %lld", &n, &sum); 55 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 56 scanf("%d %d", &a[i].l, &a[i].r); 57 58 r = 1e9; 59 60 sort(a+1, a+1+n); 61 l = a[n/2+1].l; 62 // printf("%d %d\n", l, r); 63 while(l<=r) 64 { 65 mid = (l+r) / 2; 66 if(check(mid)) 67 { 68 if(!check(mid+1)) break; 69 l = mid+1; 70 }else r = mid - 1; 71 } 72 73 printf("%d\n", mid); 74 } 75 }
滴答滴答
这是一个暴力模拟的题目,具体的只需要按题意敲就可以,但是比较难处理的是涉及到了大数,我们用数组模拟一下就可以了,考虑到新生赛的难度,所以还是比较好处理的
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <string.h> 4 const int N = 2e5+10; 5 char s[N]; 6 int res[N]; 7 int main() 8 { 9 int T, len, pos, num, flag; 10 scanf("%d", &T); 11 while(T--) 12 { 13 scanf("%s", s+1); 14 len = strlen(s+1); 15 num = pos = 0; 16 s[len+1] = ‘*‘; 17 for(int i = 1; i <= len;) 18 { 19 if(s[i]==‘d‘&&s[i+1]==‘a‘) 20 { 21 flag = 0; 22 i = i + 2; 23 for(int j = 1; j <= 3 && i <= len; i++, j++) 24 if(s[i]<=‘9‘&&s[i]>=‘0‘) 25 { 26 res[++pos] = s[i] - ‘0‘; 27 flag = 1; 28 } 29 if(flag) num++; 30 }else if(s[i]==‘d‘&&s[i+1]==‘i‘) 31 { 32 flag = 0; 33 i = i + 2; 34 for(int j = 1; j <= 1 && i <= len; i++, j++) 35 if(s[i]<=‘9‘&&s[i]>=‘0‘) 36 { 37 res[++pos] = s[i] - ‘0‘; 38 flag = 1; 39 } 40 if(flag) num++; 41 }else i++; 42 } 43 res[pos] += num; 44 for(int i = pos; i >= 1; i--) 45 { 46 res[i-1] += res[i] / 10; 47 res[i] %= 10; 48 } 49 flag = 0; 50 for(int i = 0; i <= pos; i++) 51 { 52 if(res[i]) flag = 1; 53 if(flag) printf("%d", res[i]); 54 } 55 if(flag) printf("\n"); 56 else printf("0\n"); 57 } 58 }
取石子游戏
这是一个大三学长出的防AK题,只要了解SG函数,那么恭喜你,你离AC只有半步之遥了,由于SG函数的时间复杂度是N^2 , 所以肯定要优化,其实我们观察SG函数可以直接得出一个规律,然后这题就AC了。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 int cal(int x) 3 { 4 for(int i = 0; ; i++) 5 if((1<<i) > x) return i % 3; 6 7 } 8 int main() 9 { 10 int T, n, x, res; 11 scanf("%d", &T); 12 while(T--) 13 { 14 scanf("%d", &n); res = 0; 15 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 16 { 17 scanf("%d", &x); 18 res ^= cal(x); 19 } 20 if(res) printf("first\n"); 21 else printf("second\n"); 22 } 23 }
题目够简单吗
签到题,读入然后判断数组里面有没有1就可以了
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 int main() 3 { 4 int T, n, flag; 5 while(scanf("%d", &T) != EOF) 6 { 7 while(T--) 8 { 9 scanf("%d", &n); 10 flag = 0; 11 int x; 12 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 13 { 14 scanf("%d", &x); 15 if(x) flag = 1; 16 } 17 if(flag) printf("hard\n"); 18 else printf("easy\n"); 19 } 20 21 } 22 }
推恩令
又是来自大三学长的防Ak题,总的思想是二分。
首先我们对题目分析后,我们可以将题目转化为有一个全为0的数列,第i我们可以把数列连续颜色的地方变成i然后问我们有多少种方法可以让原始数列变成输入的数列。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 typedef long long ll; 3 ll ans[509][509]; 4 const ll MOD = 292929; 5 int a[509]; 6 void init(int n) 7 { 8 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 9 for(int j = i; j <= n; j++) 10 ans[i][j] = -1; 11 } 12 ll dfs(int l, int r) 13 { 14 if(l>r) return 1; 15 if(ans[l][r]!=-1) return ans[l][r]; 16 ll lans = 0, rans = 0; 17 int pos = l, minn = a[l]; 18 for(int i = l+1; i <= r; i++) 19 if(a[i] < minn) 20 { 21 minn = a[i]; pos = i; 22 } 23 for(int i = l; i <= pos; i++) 24 lans = (lans + dfs(l,i-1) * dfs(i, pos-1) % MOD) % MOD; 25 26 for(int i = pos+1; i <= r+1; i++) 27 rans = (rans + dfs(pos+1, i-1) * dfs(i, r) % MOD) % MOD; 28 29 // printf("%d %d --- %lld %lld\n", l, r, lans * rans + 1); 30 return ans[l][r] = lans * rans % MOD; 31 } 32 int main() 33 { 34 int T, n; 35 scanf("%d", &T); 36 while(T--) 37 { 38 scanf("%d", &n); 39 init(n); 40 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", a+i); 41 printf("%lld\n", dfs(1, n)); 42 } 43 }
五等分的ACM
题意模拟就可以了
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 int cal(int n) 3 { 4 int res = 0; 5 while(n) 6 { 7 int tmp = n % 10; 8 res += tmp * tmp * tmp * tmp * tmp; 9 n /= 10; 10 } 11 return res; 12 } 13 int main() 14 { 15 int T, n; 16 scanf("%d", &T); 17 while(T--) 18 { 19 scanf("%d", &n); 20 if(n==cal(n)) printf("YES\n"); 21 else printf("NO\n"); 22 } 23 }
找找zyh
分析几个样例
我们定义numz , numy , numh 为以z y h结尾的前缀的当前出现次数
那么最终的答案就是numh
转移方程也很好理解, 分别是
当当前字符为 z 时 Numz++;
当当前字符为 y 时 numy += numz
当当前字符为 h 时 numh += numy
字符判断
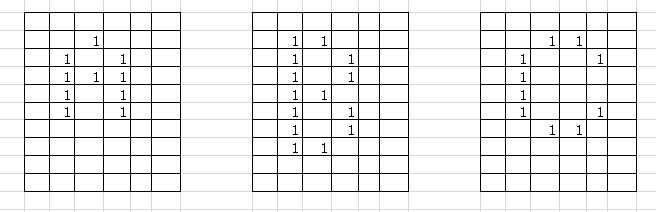
对于这三个样例 我们可以观察到如果用涂色法去涂这几个字母,A需要两次, B需要三次, C需要一次 (需要全部涂满)。
涂色法可以用dfs处理
需要特殊处理的是,在读入后要在周围添一圈留白,不然可能出现留白需要涂多次的情况,这个我们可以在读入的时候就预留出空间。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <cstring> 3 char s[50][50] = {0}; 4 int move[4][2] = {0, 1, 0, -1, 1, 0, -1, 0}; 5 void dfs(int x, int y) 6 { 7 s[x][y] = ‘*‘; 8 int tx, ty; 9 for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) 10 { 11 tx = x + move[i][0]; 12 ty = y + move[i][1]; 13 if(tx<0 || tx>49 || ty<0 || ty>49) continue; 14 if(s[tx][ty]==‘*‘) continue; 15 // printf("goto %d %d\n", tx, ty); 16 dfs(tx, ty); 17 } 18 } 19 int main() 20 { 21 22 int time = 0, n; 23 while(gets(s[1]) != NULL) 24 { 25 time = 0; 26 if(strlen(s[1]) == 0) continue; 27 n = 1; 28 for(int i = 2; ; i++) 29 { 30 gets(s[i]); 31 if(strlen(s[i])==0) break; 32 n++; 33 } 34 35 // for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 36 // puts(s[i]); 37 38 for(int i = 0; i <= 49; i++) 39 for(int j = 0; j <= 49; j++) 40 { 41 if(s[i][j]!=‘*‘) 42 { 43 dfs(i, j); 44 time++; 45 } 46 } 47 48 // printf("%d\n", time); 49 50 if(time==1) printf("C\n"); 51 else if(time==2) printf("A\n"); 52 else printf("B\n"); 53 54 memset(s, 0, sizeof(s)); 55 } 56 return 0; 57 }
足球经理
利用二维数组读入后,我们对于每一个队暴力模拟,计算分数就可以了
计算完分数判断最大值,然后看有没有两个队分数一样就可以
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 int res[120][120]; 6 struct node 7 { 8 int score, id; 9 bool operator < (struct node a) 10 { 11 return score > a.score; 12 } 13 }a[120]; 14 15 int main() 16 { 17 int T, n; 18 while(scanf("%d", &T) != EOF) 19 { 20 while(T--) 21 { 22 scanf("%d", &n); 23 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 24 for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) 25 scanf("%d", &res[i][j]); 26 27 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 28 { 29 a[i].id = i; 30 a[i].score = 0; 31 for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) 32 { 33 if(i==j) continue; 34 if(res[i][j] > res[j][i]) a[i].score += 3; 35 else if(res[i][j]==res[j][i]) a[i].score += 1; 36 } 37 } 38 a[n+1].score = -1; 39 sort(a+1, a+1+n); 40 if(a[1].score != a[2].score) printf("%d\n", a[1].id); 41 else printf("yep!\n"); 42 } 43 } 44 45 }
标签:nod cstring 分解 发放 数字 ini als 数学 scanf
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/loenvom/p/12036606.html