标签:return type tin 递归 颜色 大于 重复 ict 否则


"""
学到的新知识:
from collections import defaultditc可以帮我们初始化字典,不至于取到某个不存在的值的时候报错。例如列表类型就会默认初始值为[],str对应的是空字符串,set对应set( ),int对应0
思路:
通过本层构建上一层(DFS,类似于全排列),看是否能构建成功(递归)
"""
from collections import defaultdict
class Solution:
def pyramidTransition(self, bottom: str, allowed) -> bool:
# 先将所有能建成的放在一起,这样就节省找的时间
mat = defaultdict(list)
for i in allowed:
mat[i[:2]].append(i[-1])
return self.DFS(bottom, mat)
def DFS(self, bottom, mat):
# 如果最后只剩下一个,那肯定就是根了
if len(bottom) <= 1:
return True
candidate = []
# 通过这一层构建上一层的每一种解决方案,也是一个DFS的过程,类似于全排列
def generateUpper(bottom, tmp, ind, mat):
if ind == len(bottom) - 1:
candidate.append(tmp.copy())
return
if mat.get(bottom[ind] + bottom[ind + 1]):
for j in mat.get(bottom[ind] + bottom[ind + 1]):
tmp.append(j)
generateUpper(bottom, tmp, ind + 1, mat)
tmp.remove(j)
generateUpper(bottom, [], 0, mat)
# 判断解决方案中是否有成立的
for i in candidate:
if self.DFS(i, mat):
return True
return False
"""
思路:
首先弄清楚边界的概念:
①是整个矩阵的第一列or最后一列or第一行or最后一行
②其四周有其他的颜色(表示和其他连通分量相邻)
即如果该块的四周有不同颜色块或者位于边界才染色,否则只是经过,并不染色。对第一个要特殊判断一下。
"""
import copy
class Solution:
def colorBorder(self, grid, r0: int, c0: int, color: int):
# 用一个新grid的来染色
newgrid = copy.deepcopy(grid)
self.DFS(r0, c0, [], grid, color, newgrid)
# 对第一个特殊判断一下
if not self.judge(r0, c0, grid):
newgrid[r0][c0] = grid[r0][c0]
else:
newgrid[r0][c0] = color
return newgrid
def DFS(self, x, y, vis, grid, color, newgrid):
directx = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
directy = [0, 0, -1, 1]
# 遍历其附近的结点
for i in range(4):
newx, newy = x + directx[i], y + directy[i]
if -1 < newx < len(grid) and -1 < newy < len(grid[0]):
if (newx, newy) not in vis and grid[newx][newy] == grid[x][y]:
# 只有是边界才染色,否则只是走过去,而不染色
if self.judge(newx, newy, grid):
newgrid[newx][newy] = color
self.DFS(newx, newy, vis + [(newx, newy)], grid, color, newgrid)
def judge(self, x, y, grid):
# 判断是否为边界
if x == 0 or x == len(grid)-1 or y == 0 or y == len(grid[0])-1:
return True
directx = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
directy = [0, 0, -1, 1]
# 判断是否与其他连通分量相邻
for i in range(4):
newx, newy = x + directx[i], y + directy[i]
if -1 < newx < len(grid) and -1 < newy < len(grid[0]):
if grid[newx][newy] != grid[x][y]:
return True
return False
"""
思路:
本题重点就是后序遍历
本题卡住的点:
① 删除结点间有前后关系 -> 所以选择后序遍历从后往前删除
② 需要删除根节点的 -> 判断一下根节点是否在需要删除的列表中
"""
class Solution:
def delNodes(self, root: TreeNode, to_delete: List[int]) -> List[TreeNode]:
res = []
# 后序遍历(lastNode为现在结点的前一个结点,check表示这个是前一个结点的左子树or右子树),从子节点往父节点删除
def DFS(root, lastNode, check):
if root:
DFS(root.left, root, 'l')
DFS(root.right, root, 'r')
# 如果找到了需要删除的元素,就把它的左右儿子加到结果列表中
if root.val in to_delete:
if root.left:
res.append(root.left)
if root.right:
res.append(root.right)
# 根据check和lastNode,在原始树中将这个结点置为None
if check == 'l':
lastNode.left = None
elif check == 'r':
lastNode.right = None
DFS(root, None, '-')
# 如果根节点没有被删除,就把修改过的整棵树添加到结果集中
if root.val not in to_delete:
res.append(root)
return res
"""
思路:
题目就是DFS,但是一直超时,还以为是方法有问题,最后竟然只是去重的问题(我屮艸芔茻
好在这道题目没有考虑内部顺序的问题or运气好?直接用set对二维数组去重竟然过了测试用例emmm
"""
class Solution:
def findSubsequences(self, nums):
res = []
vis = set()
def DFS(ind, tmp):
if len(tmp) > 1:
# 如果在这里用not in去重,一定会超时。
res.append(tmp)
# 对于每个数字都有两种选择:选or不选
for i in range(ind, len(nums)):
if len(tmp) == 0 or nums[i] >= tmp[-1]:
if i not in vis:
vis.add(i)
DFS(i + 1, tmp+[nums[i]])
vis.remove(i)
DFS(0, [])
# 对二维数组去重,先将每个列表都转换为元组再去重再转换为列表
res = list(set([tuple(t) for t in res]))
res = [list(v) for v in res]
return res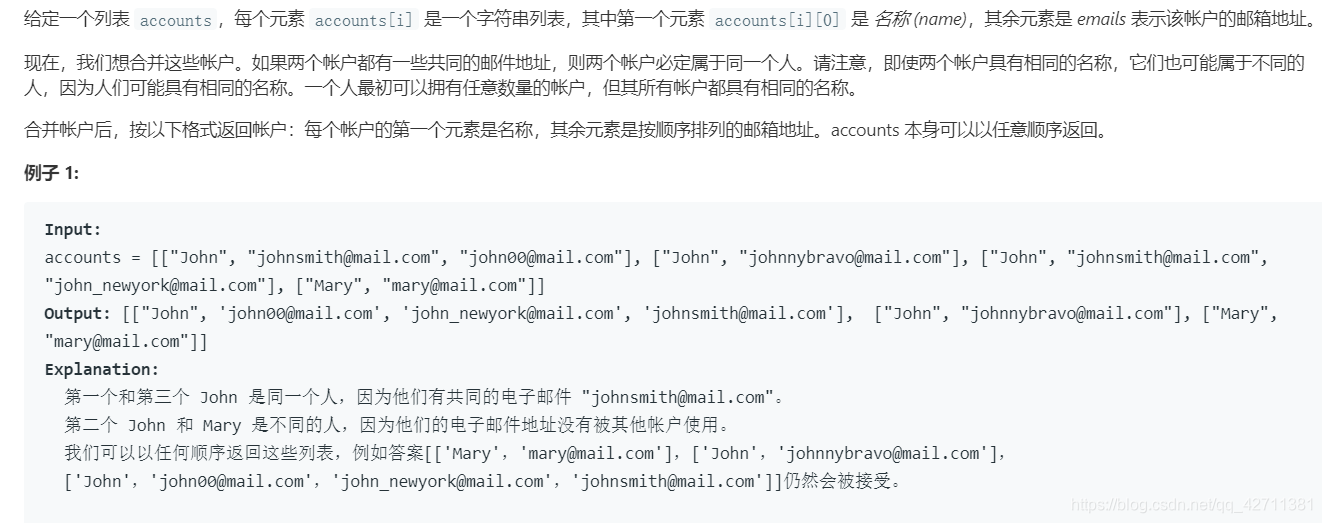
"""
思路:
需要注意一下的是这里返回的时候需要对结果排序
"""
from collections import defaultdict
class Solution:
def accountsMerge(self, accounts):
# 建图
mat = defaultdict(list)
for i in range(len(accounts)):
for j in range(1, len(accounts[i])-1):
mat[accounts[i][j]].append(accounts[i][j+1])
mat[accounts[i][j+1]].append(accounts[i][j])
def DFS(email):
if not mat.get(email):
return
for i in mat[email]:
if i not in vis:
vis.add(i)
res.append(i)
DFS(i)
vis = set()
newAcc = []
"""
每次对某个人的第一个邮箱开始进行遍历,res存储邮箱走过的路径。
如果res为空说明这个人只有一个邮箱,如果res等于这个人的原始邮箱(这两种情况都说明没有和其他人关联),
否则res长度一定大于原始邮箱长度,这说明加入了其他邮箱,将这个新邮箱赋值过去
"""
for i in range(len(accounts)):
# 如果这个人的第一个邮箱已经被访问过了,说明这个人是重复的。
if accounts[i][1] in vis:
continue
res = []
DFS(accounts[i][1])
# 要么是自己本身的邮箱,要么就是拓展后的所有邮箱
if len(res) != 0:
newAcc.append([accounts[i][0]] + sorted(res))
# 只有一个邮箱
else:
newAcc.append(accounts[i])
return newAcc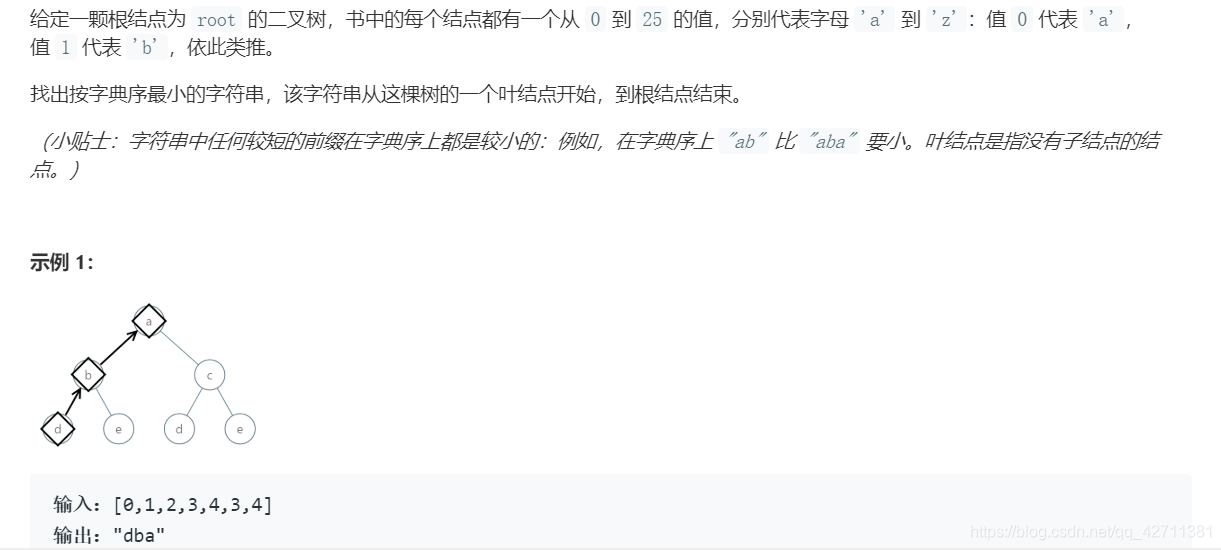
"""
本题 = 记录根到叶子结点的所有路径,然后再找到最小的即可。
"""
class Solution:
def smallestFromLeaf(self, root: TreeNode) -> str:
res = []
# 找到所有路径
def DFS(root, tmp):
if not root:
return
if not root.left and not root.right:
res.append((tmp+[root.val]).copy()[::-1])
return
DFS(root.left, tmp + [root.val])
DFS(root.right, tmp + [root.val])
# 返回最小的
DFS(root, [])
s = ""
for i in min(res):
s += ord(i + 97)
return sLeetcode题解 - DFS部分题目代码+思路(756、1034、1110、491、721、988)
标签:return type tin 递归 颜色 大于 重复 ict 否则
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/NFii/p/12001447.html