标签:details https with 直接 为什么 tps begin ace ESS
签到。
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2019/12/21 19:07:29
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << '\n'; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
void pt() {std::cout << '\n'; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void pt(T a, Args...args) {std::cout << a << ' '; pt(args...); }
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int n;
bool ok(ll x) {
for(int i = 2; 1ll * i * i <= x; i++) {
if(x % i == 0) return true;
}
return false;
}
void run(){
for(ll i = 4;; i++) {
if(ok(i) && ok(i + n)) {
cout << i + n << ' ' << i << '\n';
return;
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
while(cin >> n) run();
return 0;
}因为\(n\)比较小,直接枚举循环排列然后check即可。
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2019/12/21 20:39:59
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << '\n'; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
void pt() {std::cout << '\n'; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void pt(T a, Args...args) {std::cout << a << ' '; pt(args...); }
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 2000 + 5;
int n, m;
int a[N], b[N];
void run(){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> b[i];
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
sort(b + 1, b + n + 1);
int ans = INF;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x = -1, ok = 1;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
int p = j, q = (j + i - 1) % n + 1;
int d = (b[p] - a[q] + m) % m;
if(x == -1) x = d;
else if(x != d) ok = 0;
}
if(ok) ans = min(ans, x);
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
while(cin >> n >> m) run();
return 0;
}题意:
给出一个长度为\(n,n\leq 2e5\)的十进制数\(x\)。
然后要找到一个最小的数\(y\),满足\(y\geq x\)且\(y_i=y_{i+k},i\leq n-k\)。
思路:
对于\(x\)来说,若第一次出现\(x_i\not ={x_{i+k}}\)的位置满足\(x_i>x_{i+k}\),那么直接显然\(x_{i+k}=x_i\)。
然后有这样一个性质:
这个较为显然。所以在上面说的情况,因为\(x_{i+k}\)增大了,那么后面直接等于前面相应位置即可。
如果第一次出现的为\(x_i<x_{i+k}\),我们就需要另外考虑。
显然我们只需要在\(1\)~\(k\)的位置找一个值进行增大,因为对应位置必须相等,若在后面增大的话,前面的也会跟着增大。并且因为要求\(y\)最小,所以我们从\(k\)往前来进行增大,若某个位置增加,那么后面的都可以等于前面的。
为什么说是从后往前呢?不是只选一个位置增大就行了么?
因为要考虑\(8999\cdots\)这种需要进位的情况。
细节见代码:
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2019/12/22 10:13:49
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << '\n'; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
void pt() {std::cout << '\n'; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void pt(T a, Args...args) {std::cout << a << ' '; pt(args...); }
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
int n, k;
string s;
void run(){
cin >> s;
cout << n << '\n';
string p = s;
s = s.substr(0, k);
string t = s;
int len = k;
for(;len < n;) s += t, len += k;
s = s.substr(0, n);
if(s >= p) {
cout << s << '\n';
return;
}
for(int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if(s[i] == '9') s[i] = '0';
else {
s[i] += 1;
break;
}
}
for(int i = k; i < n; i++) s[i] = s[i - k];
cout << s << '\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
while(cin >> n >> k) run();
return 0;
}题意:
给出\(n\)列高度为\(a_i\)的格子,类似于下面:
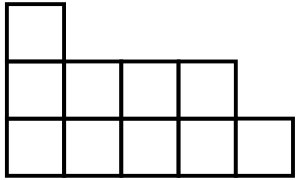
现在要用\(1\times 2\)的多米诺骨牌来填充。问最多可以放置多少个这样的多米诺骨牌。
思路:
我们直接将给出的图黑白染色,那么答案就是
\[
min(黑色格子数量,白色格子数量)
\]
至于为啥,我也不清楚= =
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2019/12/22 10:32:59
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << '\n'; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
void pt() {std::cout << '\n'; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void pt(T a, Args...args) {std::cout << a << ' '; pt(args...); }
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 3e5 + 5;
int n;
int a[N];
ll cnt[2];
void run(){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cnt[i & 1] += (a[i] + 1) / 2;
cnt[!(i & 1)] += a[i] / 2;
}
ll ans = min(cnt[0], cnt[1]);
cout << ans << '\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
while(cin >> n) run();
return 0;
}Codeforces Round #609 (Div. 2)
标签:details https with 直接 为什么 tps begin ace ESS
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/heyuhhh/p/12080358.html