标签:contexts must ide describe primary keyword img startup configure
In XML based Spring MVC configuration, you must have seen two declarations in web.xml file i.e. ContextLoaderListener and DispatcherServlet. Let’s try to understand their purpose in framework and their differences.
Before reading further, please understand that –
DispatcherServlet is essentially a Servlet (it extends HttpServlet) whose primary purpose is to handle incoming web requests matching the configured URL pattern. It take an incoming URI and find the right combination of controller and view. So it is the front controller.
When you define a DispatcherServlet in spring configuration, you provide an XML file with entries of controller classes, views mappings etc. using contextConfigLocationattribute.
<servlet> <servlet-name>employee-services</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:employee-services-servlet.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet> |
If you do not provide configuration file then it will load its own configuration file using [servlet_name]-servlet.xml. Web applications can define any number of DispatcherServlet entries. Each servlet will operate in its own namespace, loading its own application context with mappings, handlers, etc.
It means that each DispatcherServlet has access to web application context. Until specified, each DispatcherServlet creates own internal web application context.
DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext) create a new DispatcherServlet with the given web application context. It is possible only in Servlet 3.x environment through the ServletContext.addServlet(java.lang.String, java.lang.String) API support.ContextLoaderListener creates the root application context and will be shared with child contexts created by all DispatcherServlet contexts. You can have only one entry of this in web.xml.
<listener> <listener-class> org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener </listener-class></listener> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/applicationContext.xml</param-value></context-param> |
The context of ContextLoaderListener contains beans that globally visible, like services, repositories, infrastructure beans, etc. After the root application context is created, it’s stored in ServletContext as an attribute, the name is:
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);//Where attibute is defined in /org/springframework/web/context/WebApplicationContext.java asWebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT"; |
To get root application context in Spring controller, you can use WebApplicationContextUtils class.
@AutowiredServletContext context; ApplicationContext ac = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(context);if(ac == null){ return "root application context is null";} |
Below image describe the whole relation in single view.
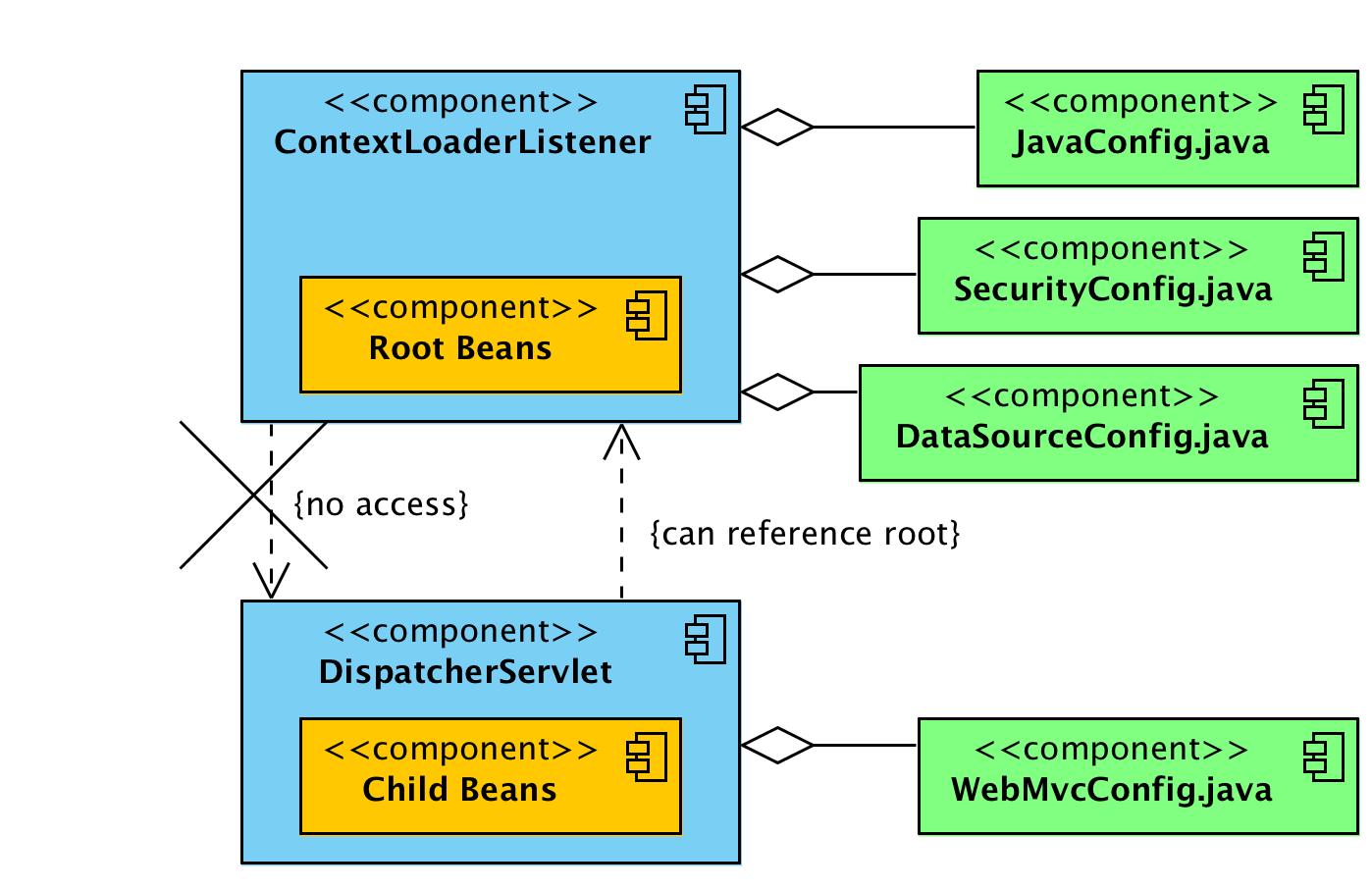 ContextLoaderListener vs DispatcherServlet
ContextLoaderListener vs DispatcherServlet
ContextLoaderListener creates root application context.DispatcherServlet entries create one child application context per servlet entry.ServletContext.WebApplicationContextUtils class.Generally, you will define all MVC related beans (controller and views etc) in DispatcherServlet context, and all cross-cutting beans such as security, transaction, services etc. at root context by ContextLoaderListener.
Generally, this setup works fine because rarely you will need to access any MVC bean (from child context) into security related class (from root context). Mostly we use security beans on MVC classes, and they can access it with above setup.
Happy Learning !!
https://howtodoinjava.com/spring-mvc/contextloaderlistener-vs-dispatcherservlet/
ContextLoaderListener vs DispatcherServlet
标签:contexts must ide describe primary keyword img startup configure
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/feng9exe/p/12092709.html