标签:参考资料 reac numpy web 误差 title 函数 连接 may
Deep Q-learning Network
参考资料:
Q值的定义及估计方法
1 评价critic的概念
用于评价一个策略π的好坏,而不直接决定动作。
两种critic:状态价值函数,状态-动作价值函数。
2 状态价值函数state-value function Vπ(s)
2.1 定义:
策略π遇到状态s时的累积奖励期望(cumulated reward expect),本身是一个函数或者网络。

注:采取π,处于state时的价值函数(与actor有关)
2.2 Vπ(s)的估计方法:
一个状态对应value可以通过玩到游戏结束计算出相应的累积状态期望,无法穷举所有的state,所以这是一个回归问题。可以通过训练网络估计Vπ。
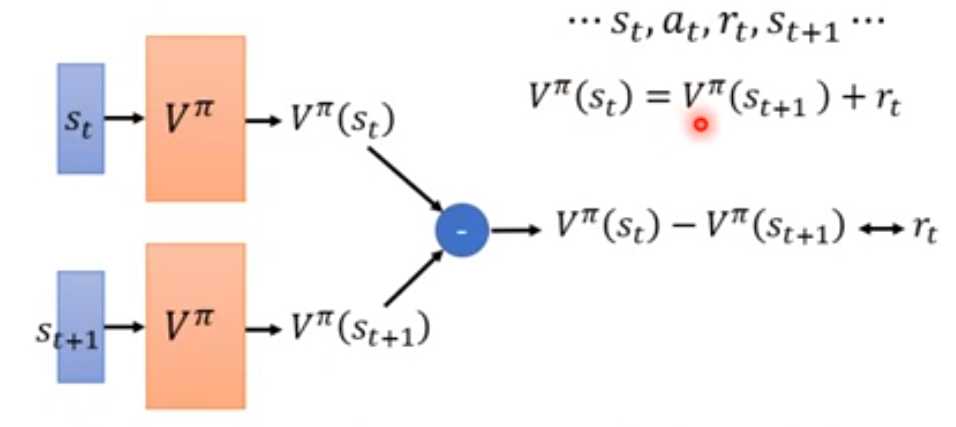
训练的时候不是直接逼近累积奖励,而是训练两步value的差为当前的reward。
MC方差大,每一个action都是随机的,方差累积。
TD估计可能不准确。更常用。
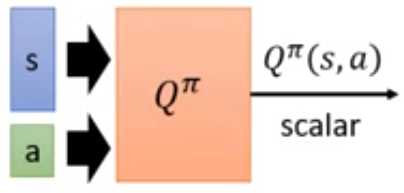
3 状态-动作价值函数state-action value function Qπ(s,a)
3.1 定义
状态s时,采用动作a,接下来用策略π到回合结束的累积奖励期望。
离散动作,输出每一个动作的Q值
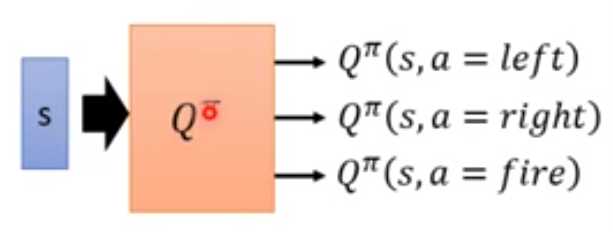
4 QLearning Q值用于reinforcement learning
价值函数是用来评估actor的好坏,但有了这个价值函数就可以决定做的action,也就做RL。
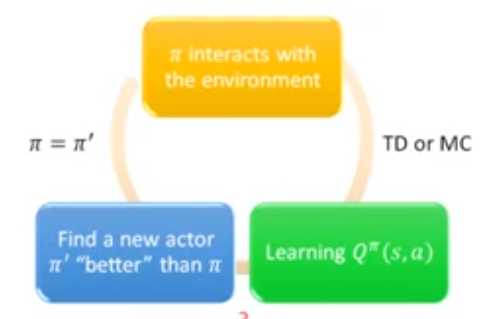
过程:
初始化策略π;
π与环境互动得到数据;
值函数估计MC/TD;
找到一个更好的策略π‘(Value-function更大):
![]()
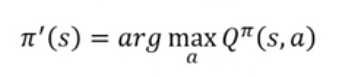
π是状态s时动作随机。计算出Qπ(s, a),选择最大的Q对应的action,更新π’(由Q决定,π‘的state下的action是固定的吗?)
5 Q-learning 实现会用到的tips
5.1 target network
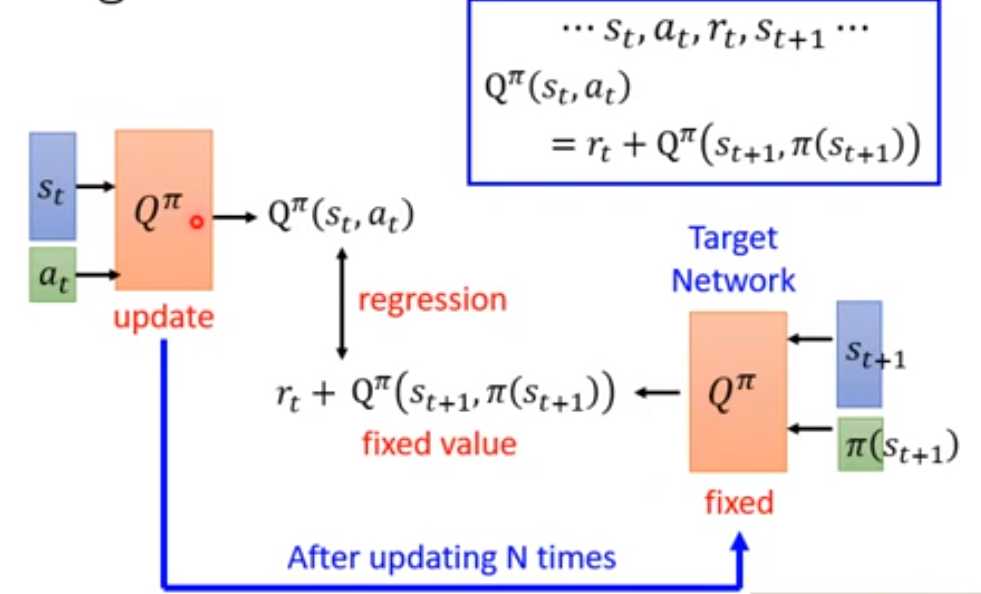
问题:根据TD方式来学习Q时,需要用到target network。左右两边输入网络,输出的差值固定。当把左边作为输入,其期望输出是在变的,这样的regression问题是不好训练的。
方法:把右边作为target network(网络参数固定,输出固定),去训练左边的固定输出期望的回归问题,然后N次之后更新右边的参数,重复训练。
5.2 Epsilon greedy

问题:不是一个好的收集数据的方式。因为选取Q最大的action,容易一直选取同一个action而不做其他的尝试,导致其他更好的动作没有被sample到。
方法:
以很小的概率epsilon会随机动作,并且这个概率会随着学习的次数减小。
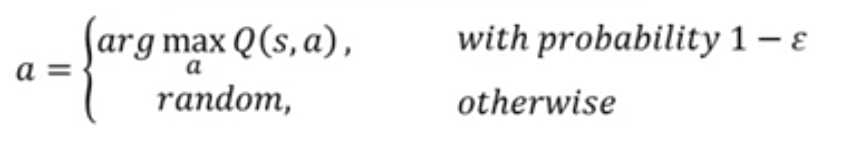
另外一种方法Boltzmann exploration:按照Q的大小来决定action的概率,因为Q有正负,所以先取指数函数。
5.3 replay buffer
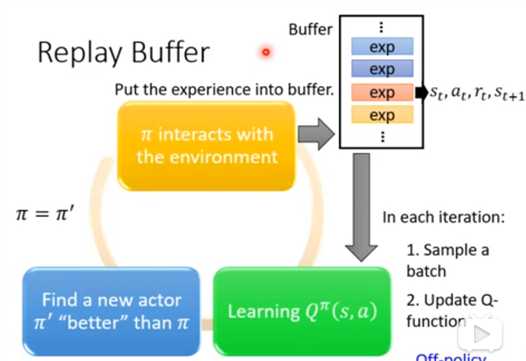
Buffer中存储了很多不同的policy的数据,不只有π。所以是用类似于off-policy的方式,累积很多数据进行学习。
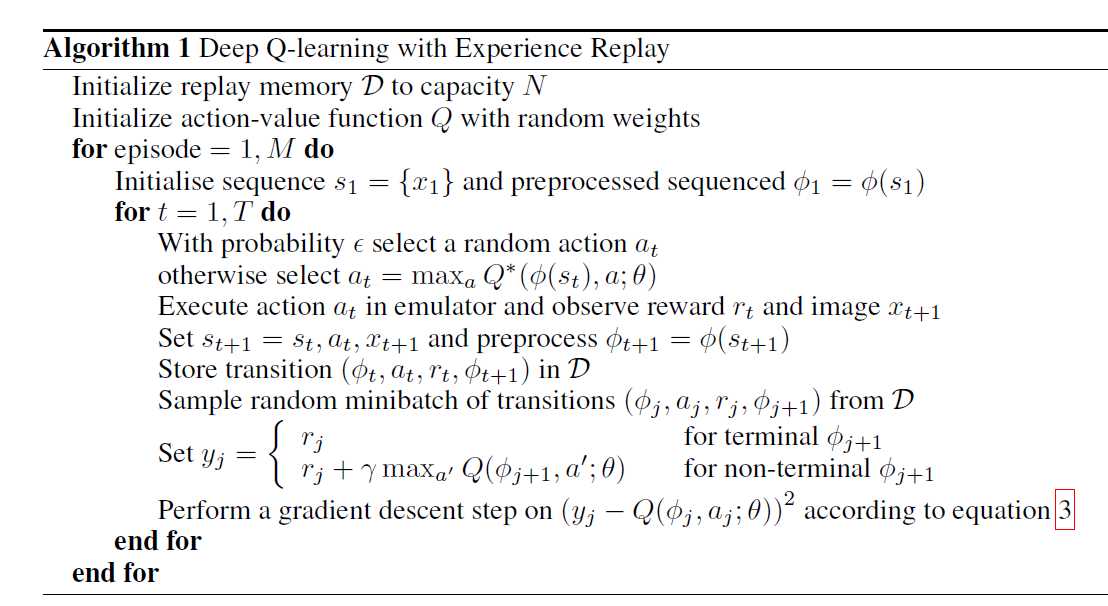
6 算法框架(李宏毅&paper)

Target network固定,输入si+1,输出Q最大值,加上ri,作为Q(si , ai)的期望输出值y,然后将Q的训练作为回归问题,使Q(si , ai)接近于y,隔一段时间将Q的参数更新给target network。
7 代码
"""
Q-learning
"""
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
class QLearningTable:
#初始化QTable,纵轴为state,横轴为action
def __init__(self, actions, learning_rate=0.01, reward_decay=0.9, e_greedy=0.9):
self.actions = actions
self.lr = learning_rate
self.gamma = reward_decay
self.epsilon = e_greedy
self.q_table = pd.DataFrame(columns=self.actions, dtype=np.floa# 用q_target*gamma加上r作为实际值,去修改q_evaluate,但是不能直接做减法t64)#添加状态
#根据Q表进行动作选择,输入observation,输出action
def choose_action(self, observation):
self.check_state_exist(observation)#检测是新的状态则添加
# epsilon greedy,这里应该按照李宏毅的理解,epsilon是一个很小的概率,
# 当大于这个概率则选取最优的动作,否则选择随机的动作
if np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon:
# choose best action
state_action = self.q_table.loc[observation, :]
# some actions may have the same value, randomly choose on in these actions
action = np.random.choice(state_action[state_action == np.max(state_action)].index)
else:
action = np.random.choice(self.actions)
return action
#Q表的更新 输入前一个状态,动作,奖励和后一个状态,进行Q表的更新
def learn(self, s, a, r, s_):
self.check_state_exist(s_)
q_predict = self.q_table.loc[s, a]#原来的Q
if s_ != ‘terminal‘:
q_target = r + self.gamma * self.q_table.loc[s_, :].max()#计算采取最优动作的Q作为q_target
else:
q_target = r #如果已经到了回合结束,则累积奖励期望就是本次的奖励
self.q_table.loc[s, a] += self.lr * (q_target - q_predict)#更新Q表
def check_state_exist(self, state):
if state not in self.q_table.index:
self.q_table = self.q_table.append(
pd.Series(
[0]*len(self.actions),
index=self.q_table.columns,
name=state,
)
)"""
Deep Q-learning Network
"""
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
#import tensorflow as tf
np.random.seed(1)
tf.set_random_seed(1)
# Deep Q Network off-policy
class DeepQNetwork:
def __init__(
self,
n_actions,
n_features,
learning_rate=0.01,
reward_decay=0.9,
e_greedy=0.9,
replace_target_iter=300,
memory_size=500,
batch_size=32,
e_greedy_increment=None,
output_graph=False,
):
self.n_actions = n_actions
self.n_features = n_features
self.lr = learning_rate
self.gamma = reward_decay
self.epsilon_max = e_greedy
self.replace_target_iter = replace_target_iter
self.memory_size = memory_size
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.epsilon_increment = e_greedy_increment
self.epsilon = 0 if e_greedy_increment is not None else self.epsilon_max
# total learning step
self.learn_step_counter = 0
# initialize zero memory [s, a, r, s_]
# buffer长度:两个obsevation(内容为feature,长度为n_features),action和reward长度各为1
self.memory = np.zeros((self.memory_size, n_features * 2 + 2))
# consist of [target_net, evaluate_net]
self._build_net()
t_params = tf.get_collection(‘target_net_params‘)
e_params = tf.get_collection(‘eval_net_params‘)
self.replace_target_op = [tf.assign(t, e) for t, e in zip(t_params, e_params)]
self.sess = tf.Session()
if output_graph:
# $ tensorboard --logdir=logs
# tf.train.SummaryWriter soon be deprecated, use following
tf.summary.FileWriter("logs/", self.sess.graph)
self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
self.cost_his = [] #记录误差用于最后的误差输出
def _build_net(self):
#此处省略神经网络的代码部分,两层全连接层
#store (s, a, r, s_) into buffer
def store_transition(self, s, a, r, s_):
if not hasattr(self, ‘memory_counter‘):
self.memory_counter = 0
transition = np.hstack((s, [a, r], s_))
# replace the old memory with new memory
index = self.memory_counter % self.memory_size
self.memory[index, :] = transition
self.memory_counter += 1
def choose_action(self, observation):
# to have batch dimension when feed into tf placeholder
# 一维数据变成二维
observation = observation[np.newaxis, :]
if np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon:
# forward feed the observation and get q value for every actions
actions_value = self.sess.run(self.q_eval, feed_dict={self.s: observation})
action = np.argmax(actions_value)
else:
action = np.random.randint(0, self.n_actions)
return action
#学习Q值的估计
def learn(self):
# check to replace target parameters
# 检测是不是要把target参数更新为新的参数
if self.learn_step_counter % self.replace_target_iter == 0:
self.sess.run(self.replace_target_op)
print(‘\ntarget_params_replaced\n‘)
# sample batch memory from all memory
if self.memory_counter > self.memory_size:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_size, size=self.batch_size)
else:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_counter, size=self.batch_size)
batch_memory = self.memory[sample_index, :]
#运行两个神经网络,target网络输出的q_next,evaluate网络输出的q_eval
q_next, q_eval = self.sess.run(
[self.q_next, self.q_eval],
feed_dict={
self.s_: batch_memory[:, -self.n_features:], # fixed params, target network 的输入,对应后面的state,s(t+1)
self.s: batch_memory[:, :self.n_features], # newest params, evaluate network的输入,对应前面的state,s(t)
})
# change q_target w.r.t q_eval‘s action
q_target = q_eval.copy()
batch_index = np.arange(self.batch_size, dtype=np.int32)
eval_act_index = batch_memory[:, self.n_features].astype(int)
reward = batch_memory[:, self.n_features + 1]
#计算q_target
# 用q_target*gamma加上r作为实际值,去修改q_evaluate,但是不能直接做减法
q_target[batch_index, eval_act_index] = reward + self.gamma * np.max(q_next, axis=1)
# train eval network, 训练evaluate网络
_, self.cost = self.sess.run([self._train_op, self.loss],
feed_dict={self.s: batch_memory[:, :self.n_features],
self.q_target: q_target})
self.cost_his.append(self.cost)
# increasing epsilon
self.epsilon = self.epsilon + self.epsilon_increment if self.epsilon < self.epsilon_max else self.epsilon_max
self.learn_step_counter += 1标签:参考资料 reac numpy web 误差 title 函数 连接 may
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ceciliaxu/p/12102499.html