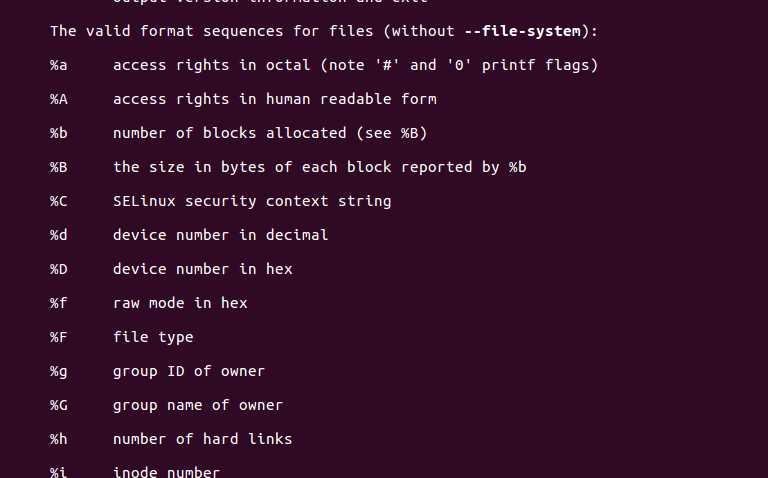
标签:设备文件 man ast octal success 程序 功能 printf 编号
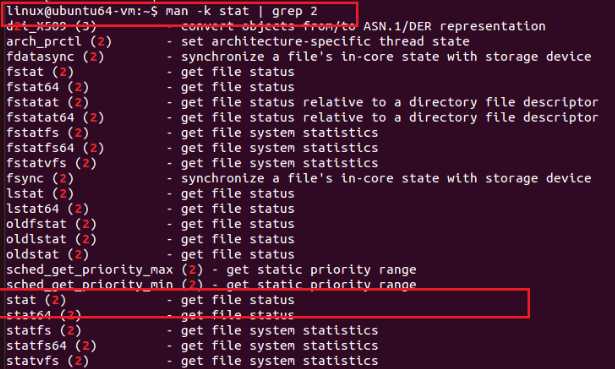
使用命令 man 1 stat 查看,截图如下:
用户运行 mystat.c 程序,输入文件名
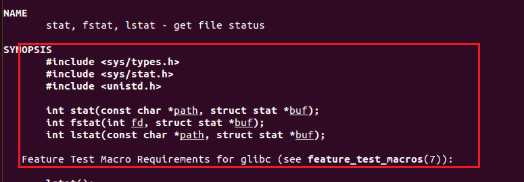
由man 2 stat函数学习后可知调用stat函数实现功能
结构体struct stat:
struct stat { dev_t st_dev; //文件的设备编号 ino_t st_ino; //节点 mode_t st_mode; //文件的类型和存取的权限 nlink_t st_nlink; //连到该文件的硬连接数目,刚建立的文件值为1 uid_t st_uid; //用户ID gid_t st_gid; //组ID dev_t st_rdev; //(设备类型)若此文件为设备文件,则为其设备编号 off_t st_size; //文件字节数(文件大小) unsigned long st_blksize; //块大小(文件系统的I/O 缓冲区大小) unsigned long st_blocks; //块数 time_t st_atime; //最后一次访问时间 time_t st_mtime; //最后一次修改时间 time_t st_ctime; //最后一次改变时间(指属性) };
### 产品代码 mystate.c,提交码云链接
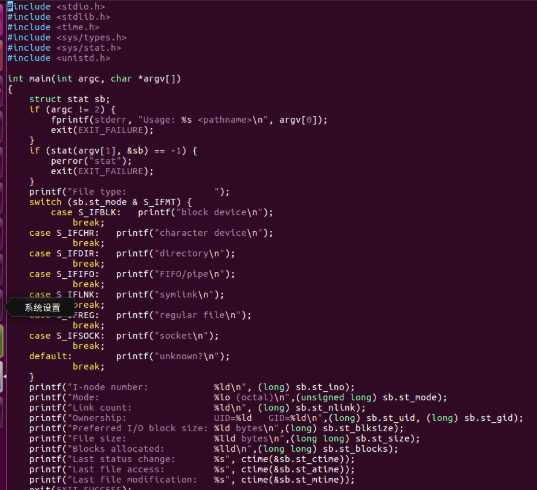
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <time.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { struct stat sb; if (argc != 2) { fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <pathname>\n", argv[0]); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } if (stat(argv[1], &sb) == -1) { perror("stat"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } printf("File type: "); switch (sb.st_mode & S_IFMT) { case S_IFBLK: printf("block device\n"); break; case S_IFCHR: printf("character device\n"); break; case S_IFDIR: printf("directory\n"); break; case S_IFIFO: printf("FIFO/pipe\n"); break; case S_IFLNK: printf("symlink\n"); break; case S_IFREG: printf("regular file\n"); break; case S_IFSOCK: printf("socket\n"); break; default: printf("unknown?\n"); break; } printf("I-node number: %ld\n", (long) sb.st_ino); printf("Mode: %lo (octal)\n",(unsigned long) sb.st_mode); printf("Link count: %ld\n", (long) sb.st_nlink); printf("Ownership: UID=%ld GID=%ld\n",(long) sb.st_uid, (long) sb.st_gid); printf("Preferred I/O block size: %ld bytes\n",(long) sb.st_blksize); printf("File size: %lld bytes\n",(long long) sb.st_size); printf("Blocks allocated: %lld\n",(long long) sb.st_blocks); printf("Last status change: %s", ctime(&sb.st_ctime)); printf("Last file access: %s", ctime(&sb.st_atime)); printf("Last file modification: %s", ctime(&sb.st_mtime)); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); }
标签:设备文件 man ast octal success 程序 功能 printf 编号
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/fakerli/p/12105401.html