标签:rcp 成绩 没有 打开 getc http 结合 sum define
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { FILE *fin, *fout; // 定义文件类型指针 int ch; fin = fopen("file1.txt", "r"); // 以只读文本方式打开文件file1.txt if (fin == NULL) { printf("fail to open file1.txt\n"); exit(0); } fout = fopen("file2.txt", "w"); // 以写文本方式打开文件file2.txt, 如果文件不存在,就创建一个 if (fout == NULL) { printf("fail to open or create file2.txt\n"); exit(0); } while( !feof(fin) ) { ch = fgetc(fin); // 从fin指向的文件file1.txt中读取单个字符,暂存在字符变量ch中 if(ch >= ‘a‘ && ch <= ‘z‘) // 如果是小写字母,则转换成大写 ch -= 32; fputc(ch, fout); // 将字符变量ch中的字符写入fout指向的文件file2.txt中 } fclose(fin); fclose(fout); return 0; }
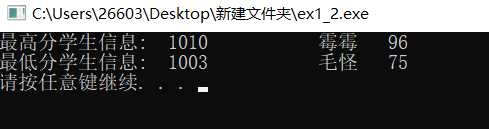
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 10 // 定义一个结构体类型STU typedef struct student { int num; char name[20]; int score; }STU; int main() { STU st, stmax, stmin; int i; FILE *fp; // 以只读文本方式打开文件file1.dat fp = fopen("file1.dat", "r"); if( !fp ) { // 如果打开失败,则输出错误提示信息,然后退出程序 printf("fail to open file1.dat\n"); exit(0); } stmax.score = 0; // 先假定最高分是0,后面如发现比当前最高分还高的分数,就更新最高分 stmin.score = 100; // 先假定最低分是100分,后面如发现比当前最低分更低的分数,就更新最低分 while( !feof(fp) ) { fscanf(fp, "%d %s %d", &st.num, st.name, &st.score); // 从fp指定的文件中格式化读取一个学生信息 if(st.score > stmax.score) stmax = st; else if(st.score < stmin.score) stmin = st; } fclose(fp); printf("最高分学生信息: %5d%15s%5d\n", stmax.num, stmax.name, stmax.score); printf("最低分学生信息: %5d%15s%5d\n", stmin.num, stmin.name, stmin.score); system("pause"); return 0; } // 这是《C语言程序设计教程学习指导》「2.10 文件」中的实验,细微处做了微调 // 这个源代码没有考虑多个高分或多个低分的情形。
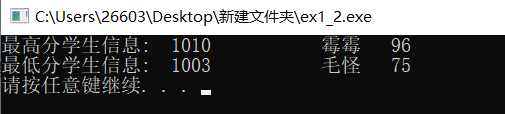
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 10 // 定义一个结构体类型STU typedef struct student { int num; char name[20]; int score; }STU; int main() { STU st, stmax, stmin; int i; FILE *fp; // 以只读文本方式打开文件file1.dat fp = fopen("file1.dat", "r"); if( !fp ) { // 如果打开失败,则输出错误提示信息,然后退出程序 printf("fail to open file1.dat\n"); exit(0); } stmax.score = 0; // 先假定最高分是0,后面如发现比当前最高分还高的分数,就更新最高分 stmin.score = 100; // 先假定最低分是100分,后面如发现比当前最低分更低的分数,就更新最低分 for(i=0; i<N; i++) { fscanf(fp, "%d %s %d", &st.num, st.name, &st.score); // 从fp指定的文件中格式化读取一个学生信息 if(st.score > stmax.score) stmax = st; else if(st.score < stmin.score) stmin = st; } fclose(fp);
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 10 // 定义一个结构体类型STU typedef struct student { int num; char name[20]; int score; }STU; void sort(STU *pst, int n); // 函数声明 int main() { FILE *fin, *fout; STU st[N]; int i; // 以只读文本方式打开文件file1.dat fin = fopen("file1.dat", "r"); if( !fin ) { // 如果打开失败,则输出错误提示信息,然后退出程序 printf("fail to open file1.dat\n"); exit(0); } // 从fin指向的数据文件file1.dat中读取数据到结构体数组st for(i=0; i<N; i++) fscanf(fin, "%d %s %d", &st[i].num, st[i].name, &st[i].score); fclose(fin); // 关闭fin指向的文件file1.dat // 调用函数sort()对数组st中数据,按分数又高到低排序 sort(st, N); // 以写方式打开/创建文本文件file3.dat fout = fopen("file3.dat", "w"); if( !fout ) { // 如果打开失败,则输出错误提示信息,然后退出程序 printf("fail to open file1.dat\n"); exit(0); } // 将排序后的数组st中数据输出到屏幕,同时,也写入文件file3.dat for(i=0; i<N; i++) { printf("%-6d%-10s%3d\n", st[i].num, st[i].name, st[i].score); fprintf(fout, "%-6d%-10s%3d\n", st[i].num, st[i].name, st[i].score); } fclose(fout); // 关闭fout指向的文件file3.dat system("pause"); return 0; } // 函数功能描述:对pst指向的n个STU结构体数据进行排序,按成绩数据项由高到底排序 // 排序算法:冒泡法 void sort(STU *pst, int n) { STU *pi, *pj, t; for(pi = pst; pi < pst+n-1; pi++) for(pj = pi+1; pj < pst+n; pj++) if(pi->score < pj->score) { t = *pi; *pi = *pj; *pj = t; } } // 说明:冒泡排序算法是确定的,但其具体实现方式和细节却是灵活多样的 // 本例中,冒泡排序算法的函数体中,都是通过指针变量操作的。 // 而在前面章节的实例中,冒泡排序的函数体,有些是通过数组实现的,有些是指针和数组的混合 // 请结合代码体会和理解,做到理解算法本质,才能应对和理解灵活多样的实现形式
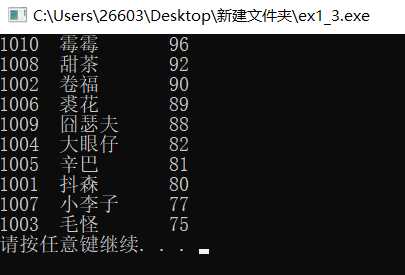
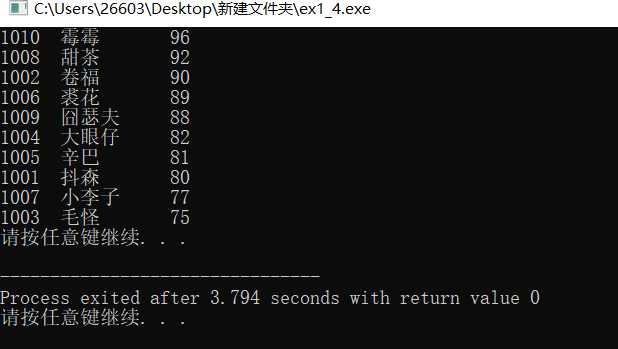
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 10 // 定义一个结构体类型STU typedef struct student { int num; char name[20]; int score; }STU; void sort(STU *pst, int n); // 函数声明 int main() { FILE *fin, *fout; STU st[N]; int i; // 以只读文本方式打开文件file1.dat fin = fopen("file1.dat", "r"); if( !fin ) { // 如果打开失败,则输出错误提示信息,然后退出程序 printf("fail to open file1.dat\n"); exit(0); } // 从fin指向的数据文件file1.dat中读取数据到结构体数组st for(i=0; i<N; i++) fscanf(fin, "%d %s %d", &st[i].num, st[i].name, &st[i].score); fclose(fin); // 关闭fin指向的文件file1.dat // 调用函数sort()对数组st中数据,按分数由高到低排序 sort(st, N); // 以写方式打开/创建二进制文件file4.dat fout = fopen("file4.dat", "wb"); if( !fout ) { // 如果打开失败,则输出错误提示信息,然后退出程序 printf("fail to open file1.dat\n"); exit(0); } // 将排序后的数组st中数据输出到屏幕 for(i=0; i<N; i++) printf("%-6d%-10s%3d\n", st[i].num, st[i].name, st[i].score); // 将排序后的数组st中数据写到二进制文件file4.dat fwrite(st, sizeof(STU), N, fout); // 将从地址st开始的sizeof(STU)×N个字节信息写入fout指向的文件file4.dat中 fclose(fout); // 关闭fout指向的文件file4.dat system("pause"); return 0; } // 函数功能描述:对pst指向的n个STU结构体数据进行排序,按成绩数据项由高到底排序 // 排序算法:冒泡法 void sort(STU *pst, int n) { STU *pi, *pj, t; for(pi = pst; pi < pst+n-1; pi++) for(pj = pi+1; pj < pst+n; pj++) if(pi->score < pj->score) { t = *pi; *pi = *pj; *pj = t; } } // 说明:冒泡排序算法是确定的,但其具体实现方式和细节却是灵活多样的 // 本例中,冒泡排序算法的函数体中,都是通过指针变量操作的。 // 而在前面章节的实例中,冒泡排序的函数体,有些是通过数组实现的,有些是指针和数组的混合 // 请结合代码体会和理解,做到理解算法本质,才能应对和理解灵活多样的实现形式
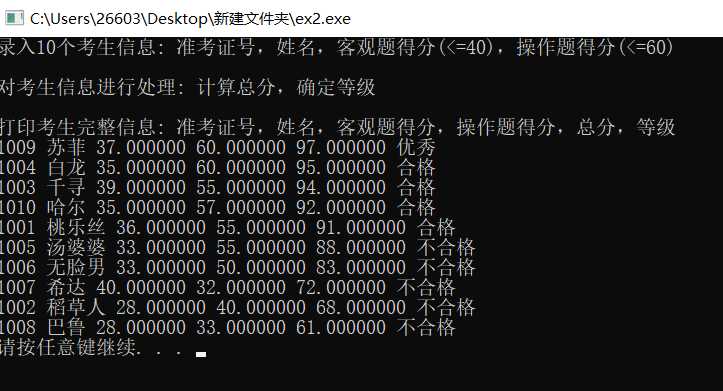
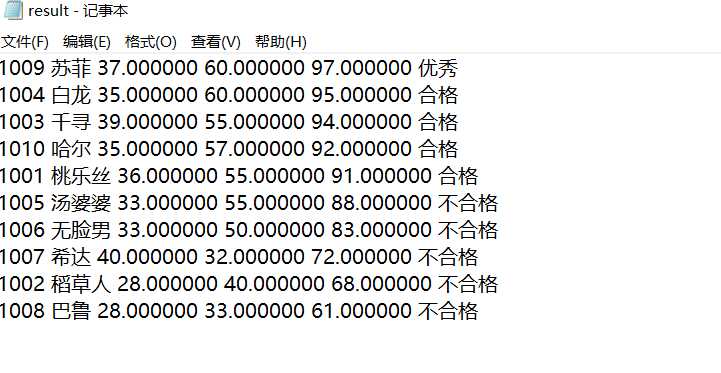
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> const int N = 10; // 定义结构体类型struct student,并定义其别名为STU typedef struct student { long int id; char name[20]; float objective; /*客观题得分*/ float subjective; /*操作题得分*/ float sum; char level[10]; }STU; // 函数声明 void input(STU s[], int n); void output(STU s[], int n); void process(STU s[], int n); int main() { STU stu[N]; printf("录入%d个考生信息: 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分(<=40),操作题得分(<=60)\n", N); input(stu, N); printf("\n对考生信息进行处理: 计算总分,确定等级\n"); process(stu, N); printf("\n打印考生完整信息: 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分,总分,等级\n"); output(stu, N); system("pause"); return 0; } // 从文本文件examinee.txt读入考生信息:准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分 void input(STU s[], int n) { // 补足代码 // ××× int i; FILE *fin; fin=fopen("examinee.txt","r"); if(fin==NULL) { printf("fail to open file"); exit(0); } for(i=0;i<n;i++) { fscanf(fin,"%ld %s %f %f",&s[i].id,s[i].name,&s[i].objective,&s[i].subjective); } fclose(fin); } // 输出考生完整信息: 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分,总分,等级 // 不仅输出到屏幕上,还写到文本文件result.txt中 void output(STU s[], int n) { // 补足代码 // ××× FILE *fout; int i; if((fout=fopen("result.txt","w"))==NULL) { printf("fail to open file"); exit(0); } for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("%ld %s %f %f %f %s\n",s[i].id,s[i].name,s[i].objective,s[i].subjective,s[i].sum,s[i].level); fprintf(fout,"%ld %s %f %f %f %s\n",s[i].id,s[i].name,s[i].objective,s[i].subjective,s[i].sum,s[i].level); } fclose(fout); } // 对考生信息进行处理:计算总分,排序,确定等级 void process(STU s[], int n) { // 补足代码 // ××× int i,j; STU temp; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) s[i].sum = s[i].objective + s[i].subjective; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) for (j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++) if(s[j].sum < s[j+1].sum){ temp = s[j]; s[j] = s[j+1]; s[j+1] = temp; } for (i = 0; i < n; i++){ if((i+1) <= n*0.1) strcpy(s[i].level, "优秀"); else if((i+1) > n*0.1 && (i+1) <= n*0.5) strcpy(s[i].level, "合格"); else strcpy(s[i].level, "不合格"); } }
标签:rcp 成绩 没有 打开 getc http 结合 sum define
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/rsndm/p/12114742.html