标签:object 简单 技术 art 胜利 try 核心 步骤 判断
前言
写程序已经丢掉很长一段时间了,最近觉得完全把技术丢掉可能是个死路,还是应该捡起来,所以打算借CSDN来记录学习过程, 由于以前没事的时候断断续续学习过python和用flask框架写过点web,所以第一步想捡起python,但是,单纯学习python有点枯燥,正好看到pygame,感觉还挺简单,所以想先写个小游戏练练手。
准备
python基础相关准备:
准备完成五子棋单机人机游戏,目前已完成界面以及判定输赢等功能,还未加入电脑AI,以后有时间再加(不知是否会坑),目前实现主要功能如下:
游戏界面是下面这个样子:
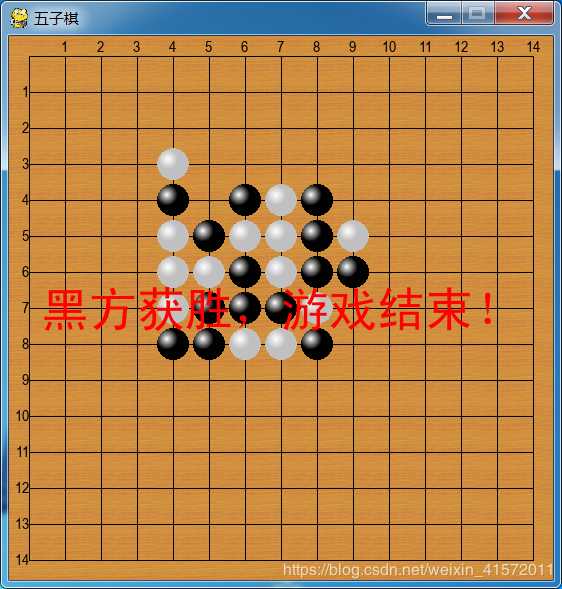
整个游戏的核心是将棋盘分成两个层面,第一个层面是物理层面上的,代表在物理像素的位置,主要用于绘图等操作,另外一个层面是将棋盘抽象成15*15的一个矩阵,黑子和白子是落在这个矩阵上的某个位置,具体位置用坐标(i,j)(0<=i,j<15)来表示,主要用于判断输赢和落子等。
def main(): pygame.init() #pygame初始化 size = width,height = 544,544 screen = pygame.display.set_mode(size, 0, 32) pygame.display.set_caption(‘五子棋‘) font = pygame.font.Font(‘simhei.ttf‘, 48) clock = pygame.time.Clock() #设置时钟 game_over = False renju = Renju() # Renju是核心类,实现落子及输赢判断等 renju.init() # 初始化 while True: clock.tick(20) # 设置帧率 for event in pygame.event.get(): if event.type == pygame.QUIT: sys.exit() if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN and (not game_over): if event.button == 1: # 按下的是鼠标左键 i,j = renju.get_coord(event.pos) # 将物理坐标转换成矩阵的逻辑坐标 if renju.check_at(i, j): # 检查(i,j)位置能否被占用,如未被占用返回True renju.drop_at(i, j) # 在(i,j)位置落子,该函数将黑子或者白子画在棋盘上 if renju.check_over(): # 检查是否存在五子连线,如存在则返回True text = ‘‘ if renju.black_turn: #check_at会切换落子的顺序,所以轮到黑方落子,意味着最后落子方是白方,所以白方顺利 text = ‘白方获胜,游戏结束!‘ else: text = ‘黑方获胜,游戏结束!‘ gameover_text = font.render(text, True, (255,0,0)) renju.chessboard().blit(gameover_text, (round(width/2-gameover_text.get_width()/2), round(height/2-gameover_text.get_height()/2))) game_over = True else: print(‘此位置已占用,不能在此落子‘) screen.blit(renju.chessboard(),(0,0)) pygame.display.update() pygame.quit()
Position = namedtuple(‘Position‘, [‘x‘, ‘y‘]) class Renju(object): background_filename = ‘chessboard.png‘ white_chessball_filename = ‘white_chessball.png‘ black_chessball_filename = ‘black_chessball.png‘ top, left, space, lines = (20, 20, 36, 15) # 棋盘格子位置相关??? color = (0, 0, 0) # 棋盘格子线颜色 black_turn = True # 黑子先手 ball_coord = [] # 记录黑子和白子逻辑位置 def init(self): try: self._chessboard = pygame.image.load(self.background_filename) self._white_chessball = pygame.image.load(self.white_chessball_filename).convert_alpha() self._black_chessball = pygame.image.load(self.black_chessball_filename).convert_alpha() self.font = pygame.font.SysFont(‘arial‘, 16) self.ball_rect = self._white_chessball.get_rect() self.points = [[] for i in range(self.lines)] for i in range(self.lines): for j in range(self.lines): self.points[i].append(Position(self.left + i*self.space, self.top + j*self.space)) self._draw_board() except pygame.error as e: print(e) sys.exit() def chessboard(self): return self._chessboard # 在(i,j)位置落子 def drop_at(self, i, j): pos_x = self.points[i][j].x - int(self.ball_rect.width/2) pos_y = self.points[i][j].y - int(self.ball_rect.height/2) ball_pos = {‘type‘:0 if self.black_turn else 1, ‘coord‘:Position(i,j)} if self.black_turn: # 轮到黑子下 self._chessboard.blit(self._black_chessball, (pos_x, pos_y)) else: self._chessboard.blit(self._white_chessball, (pos_x, pos_y)) self.ball_coord.append(ball_pos) # 记录已落子信息 self.black_turn = not self.black_turn # 切换黑白子顺序 # 画棋盘上的格子线,如果棋盘背景图做的足够精确,可省略此步骤 def _draw_board(self): # 画坐标数字 for i in range(1, self.lines): coord_text = self.font.render(str(i), True, self.color) self._chessboard.blit(coord_text, (self.points[i][0].x-round(coord_text.get_width()/2), self.points[i][0].y-coord_text.get_height())) self._chessboard.blit(coord_text, (self.points[0][i].x-coord_text.get_width(), self.points[0][i].y-round(coord_text.get_height()/2))) for x in range(self.lines): # 画横线 pygame.draw.line(self._chessboard, self.color, self.points[0][x], self.points[self.lines-1][x]) # 画竖线 pygame.draw.line(self._chessboard, self.color, self.points[x][0], self.points[x][self.lines-1]) # 判断是否已产生胜方 def check_over(self): if len(self.ball_coord)>8: # 只有黑白子已下4枚以上才判断 direct = [(1,0),(0,1),(1,1),(1,-1)] #横、竖、斜、反斜 四个方向检查 for d in direct: if self._check_direct(d): return True return False # 判断最后一个棋子某个方向是否连成5子,direct:(1,0),(0,1),(1,1),(1,-1) def _check_direct(self, direct): dt_x, dt_y = direct last = self.ball_coord[-1] line_ball = [] # 存放在一条线上的棋子 for ball in self.ball_coord: if ball[‘type‘] == last[‘type‘]: x = ball[‘coord‘].x - last[‘coord‘].x y = ball[‘coord‘].y - last[‘coord‘].y if dt_x == 0: if x == 0: line_ball.append(ball[‘coord‘]) continue if dt_y == 0: if y == 0: line_ball.append(ball[‘coord‘]) continue if x*dt_y == y*dt_x: line_ball.append(ball[‘coord‘]) if len(line_ball) >= 5: # 只有5子及以上才继续判断 sorted_line = sorted(line_ball) for i,item in enumerate(sorted_line): index = i+4 if index < len(sorted_line): if dt_x == 0: y1 = item.y y2 = sorted_line[index].y if abs(y1-y2) == 4: # 此点和第5个点比较y值,如相差为4则连成5子 return True else: x1 = item.x x2 = sorted_line[index].x if abs(x1-x2) == 4: # 此点和第5个点比较x值,如相差为4则连成5子 return True else: break return False # 检查(i,j)位置是否已占用 def check_at(self, i, j): for item in self.ball_coord: if (i,j) == item[‘coord‘]: return False return True # 通过物理坐标获取逻辑坐标 def get_coord(self, pos): x, y = pos i, j = (0, 0) oppo_x = x - self.left if oppo_x > 0: i = round(oppo_x / self.space) # 四舍五入取整 oppo_y = y - self.top if oppo_y > 0: j = round(oppo_y / self.space) return (i, j)
Renju类有几个函数说明:
标签:object 简单 技术 art 胜利 try 核心 步骤 判断
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/pypypy/p/12116585.html