标签:connect oca 添加 locate 信息 turn throw 输出 简单的
BIO称为阻塞IO,主要应用与文件IO和网络IO,在JDK1.4之前我们建立网络连接的时候只能采用BIO,需要先在服务端建立一个ServerSocket,然后在客户端启动Socket来对服务端进行通信,默认情况下服务端需要对每个请求建立一堆线程等待请求,而客户端发送请求后,先咨询服务端是否有线程响应,如果没有则会一直等待或者遭到拒绝请求,如果有的话,客户端线程会等待请求结束后才继续执行,这就是阻塞式IO。
由客户端通过Socket s = new Socket(“127.0.0.1”,8888);连接服务端;
服务端通过ServerSocket ss = new Socket(9999);和Socket s = ss.accept();监听客户端的请求;
客户端先通过输出流向服务端发送消息,服务端先通过输入流读取消息,读取消息后通过输出流向客户端输出返回消息,客户端再通过输入流读取服务端返回的消息。
双发等待消息的过程中都是阻塞的。
服务端代码如下:
package bio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/*
* BIO阻塞式IO服务端程序
* */
public class TCPServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建ServerSocket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
while(true){
System.out.println("测试阻塞1");
//2.监听是否有客户端连接
Socket s = ss.accept();//阻塞
System.out.println("测试阻塞2");
//3.从连接中取输入流并接收消息
InputStream inputStream =
s.getInputStream();//此步不阻塞
System.out.println("测试阻塞3");
byte[] b = new byte[32];
inputStream.read(b);//阻塞
System.out.println("测试阻塞4");
String hostAddress =
ss.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
String hostName =
ss.getInetAddress().getHostName();
System.out.println(hostAddress+":"+hostName+"说:"+new String(b).trim());
//4.从连接中取输出流并会话
OutputStream outputStream =
s.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("收到".getBytes());
//5.关闭连接
s.close();
}
}
}
客户端代码如下:
package bio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* BIO阻塞式IO客户端程序
* */
public class TCPClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
while (true){
//1.创建Socket对象
Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1",8888);
//2.从连接中取出输出流并发送消息
OutputStream outputStream = s.getOutputStream();
System.out.println("请输入:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String msg = scanner.nextLine();
outputStream.write(msg.getBytes());
//3.从连接中取出输入流并接收会话
InputStream inputStream = s.getInputStream();//此步不阻塞
byte[] b = new byte[32];
inputStream.read(b);//阻塞
System.out.println("服务端返回:" + new String(b).trim());
//关闭连接
s.close();
}
}
}
NIO:全称 non-blocking IO,即非阻塞式IO,从JDK1.4开始提供
BIO与NIO区别:
BIO: 流 数组 阻塞式
NIO: 通道Channel Buffer 非阻塞式
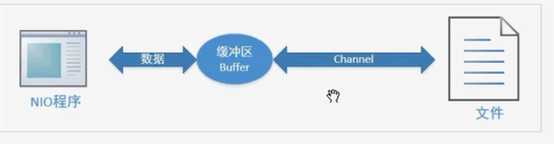
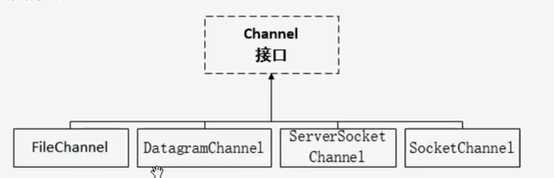
使用NIO完成本地文件编程,代码如下:
package nio;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOAboutFile {
//向本地文件中写数据
public void writeToFile() throws IOException {
//1.获取连接到文件的输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("nio.txt");
//2.通过输出流获取通道
FileChannel channel = fos.getChannel();
//3.创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//4.向缓冲区中添加数据
byteBuffer.put("helloNIO".getBytes());
//由于管道从缓存中读取数据时是从当前位置开始读取,会导致读出的数据为空
//所以此处调用byteBuffer.flip()方法,使当前位置指向缓冲区的开头
byteBuffer.flip();
//管道向文件中写数据,数据来源于缓冲区
channel.write(byteBuffer);
//关闭资源
//channel.close();
fos.close();
}
//从本地文件读取数据
public void readFromFile() throws IOException {
File file = new File("nio.txt");
//1.获取连接到文件的输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//2.通过输入流获取通道
FileChannel fileChannel = fis.getChannel();
//3.创建缓冲区,初始大小和文件长度相同
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int)file.length());
//4.从文件读取数据放到缓冲区中
fileChannel.read(byteBuffer);
//5.从缓冲区中读取数据
byte[] array = byteBuffer.array();
System.out.println("文件中的内容为:" + new String(array).trim());
//6.关闭资源
fileChannel.close();
fis.close();
}
//实现文件复制
public void copyFile(String from,String to) throws IOException {
//1.创建两个流:输入流和输出流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(from);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(to);
//2.创建对应的两个管道
FileChannel fromChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel toChannel = fos.getChannel();
//3.将一个管道中的内容拷贝到另一个管道中,从而输出到指定文件中
/*fromChannel.transferTo(0,fromChannel.size(),toChannel);*/
toChannel.transferFrom(fromChannel,0,fromChannel.size());
//4.关闭资源
fromChannel.close();
toChannel.close();
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
NIOAboutFile nf = new NIOAboutFile();
//写入文件
nf.writeToFile();
//从文件中读取
nf.readFromFile();
//拷贝文件
nf.copyFile("nio.txt","copy2.txt");
}
}
使用NIO完成简单的客户端和服务器端通信代码:
1、服务器端代码如下:
package nio.socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
/*
* NIO处理网络数据
* */
public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.建立服务器端的通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//2.创建一个Selector选择器对象
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//3.设置服务器端通道监听的端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
//4.设置非阻塞式的方式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//5.将服务器端通道注册给selector选择器对象,监听的方式是监听连接:即是否有客户端连接服务器端
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//6.处理客户端连接
while(true){
//6.1监听是否有客户端连接
if(selector.select(2000)==0){//NIO非阻塞式的优势,即没有客户端连接时可以做其他事
System.out.println("Server端:没有客户端连接,可以做其他事情!");
continue;
}
//6.2得到SelectionKey,判断通道里的事件
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(keyIterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
if(key.isAcceptable()){//客户端连接事件
System.out.println("OP_ACCEPT");
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//将客户端通道也注册给selector选择器
//客户端发送过来数据,我服务器端需要从该通道中读取数据,所以参数用OP_READ
//缓冲区应该对应客户端发送的附件,只不过在我们的例子中客户端没有发送附件
//有此行代码,下边的key.isReadable()判断才会成功
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
}
if(key.isReadable()){//读取客户端数据事件
System.out.println("客户端连接之后,但是没有发送数据之前,该行代码是否会执行");//不会
//从客户端读取数据,需要先获得客户端通道
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer)key.attachment();
//从通道中读取数据放入到缓冲区中
channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println("客户端发送的数据为:"+new String(buffer.array()).trim());
}
//6.3事件处理完毕后,需要手动从当前集合中移除该key,否则会重复处理
//如果没有该行代码,40行会报空指针异常,即在没有客户端连接的情况下,强行获取客户端通道,会报空指针
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
2、客户端代码如下:
package nio.socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建客户端的网络通道
SocketChannel channel = SocketChannel.open();
//2.设置非阻塞式的方式
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//3.提供服务器端的IP地址和多口号
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9999);
//4.客户端通道与服务器端地址建立连接
if(!channel.connect(address)){
//如果没有连接上,则换另一种非阻塞式的方式继续尝试连接
while(!channel.finishConnect()){//NIO做为非阻塞式的优势
System.out.println("连接服务器的同时客户端可以处理其他事情");
}
}
//5.创建缓冲区并向缓冲区存入数据
String msg = "hello server,i‘m client!";
//用于测试如果客户端不发送数据给服务器端,服务器端的isReadable()判断是否能够成立
/*Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String msg = scanner.nextLine();*/
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes());
//6.channel通道将buffer缓冲区中的数据发给服务器
channel.write(buffer);
//7.暂时不关闭客户端资源,防止服务器端异常
System.in.read();
}
}
使用NIO完成多人聊天,代码如下:
1、服务器端代码如下:
package nio.socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
/*
* 类似于微信的群聊,也类似与activemq的topic:一人发送消息,其他多人接收消息
* */
public class ChatServer {
private ServerSocketChannel listenerChannel;
private Selector selector;
private static final int PORT = 9999;
public ChatServer(){
try {
//1.建立服务器端的通道
listenerChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//2.创建一个Selector选择器对象
selector = Selector.open();
//3.设置服务器端通道监听的端口
listenerChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
//4.设置非阻塞式的方式
listenerChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//5.将服务器端通道注册给selector选择器对象,监听的方式是监听连接:即是否有客户端连接服务器端
listenerChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
printInfo("ChatServer is ready.....");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//6.处理客户端连接
public void start(){
try {
while(true){
//6.1监听是否有客户端连接
if(selector.select(2000)==0){//NIO非阻塞式的优势,即没有客户端连接时可以做其他事
System.out.println("Server端:没有客户端连接,可以做其他事情!");
continue;
}
//6.2得到SelectionKey,判断通道里的事件
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(keyIterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
if(key.isAcceptable()){//客户端连接事件
System.out.println("OP_ACCEPT");
SocketChannel socketChannel = listenerChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//将客户端通道也注册给selector选择器
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
if(key.isReadable()){//读取客户端数据事件
readMsg(key);
}
//6.3事件处理完毕后,需要手动从当前集合中移除该key,否则会重复处理
//如果没有该行代码,40行会报空指针异常,即在没有客户端连接的情况下,强行获取客户端通道,会报空指针
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//读取客户端发来的数据并广播出去
public void readMsg(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel =(SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int count = channel.read(buffer);
if(count>0){
String msg = new String(buffer.array());
printInfo(msg);
//广播给其他客户端
broadcast(channel,msg);
}
}
//将信息广播给其他客户端
public void broadcast(SocketChannel except,String msg) throws IOException {
System.out.println("服务器发送了广播....");
for(SelectionKey key:selector.keys()){
Channel channel = key.channel();
if(channel instanceof SocketChannel && !channel.equals(except)){
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes());
SocketChannel targetChannel = (SocketChannel)channel;
//将信息发送给其他客户端
targetChannel.write(buffer);
}
}
}
//封装打印方法
public void printInfo(String str){
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("[" + sdf.format(new Date()) +"]->" + str);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ChatServer().start();
}
}
2、客户端代码如下:
package nio.socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class ChatClient {
private final String HOST="127.0.0.1";//服务器地址
private final int PORT=9999;//服务器端口
private SocketChannel socketChannel;//客户端通道
private String username;//客户端姓名
public ChatClient() throws IOException {
//1.创建客户端的网络通道
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
//2.设置非阻塞式的方式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//3.提供服务器端的IP地址和多口号
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(HOST, PORT );
//4.客户端通道与服务器端地址建立连接
if(!socketChannel.connect(address)){
//如果没有连接上,则换另一种非阻塞式的方式继续尝试连接
while(!socketChannel.finishConnect()){//NIO做为非阻塞式的优势
System.out.println("连接服务器的同时客户端可以处理其他事情");
}
}
//5.获取客户端姓名
username = socketChannel.getLocalAddress().toString().substring(1);
System.out.println("--------------Client(" + username +") is ready------------");
}
//发送消息
public void sendMsg(String msg) throws IOException {
if(msg.equalsIgnoreCase("bye")){
socketChannel.close();
return;
}
msg = username +"说:" + msg;
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes());
socketChannel.write(buffer);
}
//接收消息
public void receiveMsg() throws IOException {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int count = socketChannel.read(buffer);
if(count>0){
String msg = new String(buffer.array()).trim();
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
}
3、启动客户端代码如下:
package nio.socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ChatTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ChatClient chatClient = new ChatClient();
//单起一个线程用于接收消息
new Thread(){
public void run(){
try {
while (true){
chatClient.receiveMsg();
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}.start();
//模拟聊天窗口,录入信息后发送
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scanner.hasNext()){
String msg = scanner.nextLine();
chatClient.sendMsg(msg);
}
}
}
小总结:
IO方式通常分为几种:同步阻塞式的BIO,同步非阻塞式的NIO,异步非阻塞式的AIO
标签:connect oca 添加 locate 信息 turn throw 输出 简单的
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiao1572662/p/12149877.html