标签:tps init 而不是 cep 阶段 out 存储 tree lse
https://medium.com/@itsromiljain/curious-case-of-concurrenthashmap-90249632d335 这个讲的就是1.7的概念性
https://crossoverjie.top/2018/07/23/java-senior/ConcurrentHashMap/ 分析对比写的不错
具体代码去看jdk
1.7
/** * Segment 数组,存放数据时首先需要定位到具体的 Segment 中。 */ final Segment<K,V>[] segments; transient Set<K> keySet; transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
Segment是一个内部类
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L; // 和 HashMap 中的 HashEntry 作用一样,真正存放数据的桶 transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table; transient int count; transient int modCount; transient int threshold; final float loadFactor; }
HashEnrty
static final class HashEnrty<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; volatile V value; volatile HashEnrty<K,V> next; }
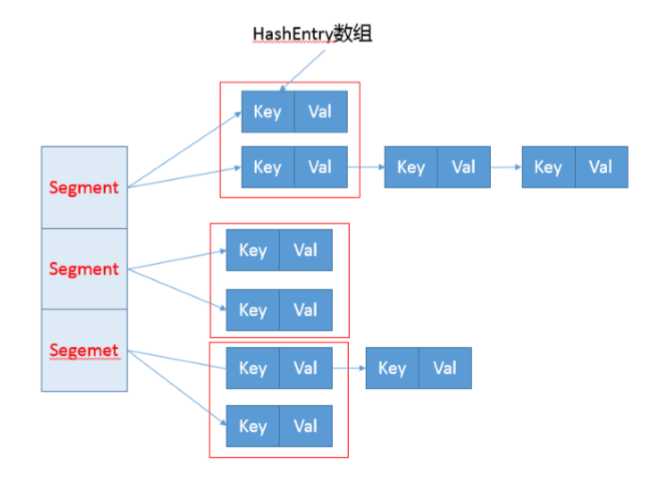
1.ConcurrentHashMap会获取再入锁,以保证数据一致性,Segment本身就是基于ReentrantLock的扩展实现,所以,在并发修改期间,相应Segment是被锁定的。
2.在最初阶段,进行重复性的扫描,以确定相应key值是否已经在数组里面,进而决定是更新还是放置操作,你可以在代码里看到相应的注释。重复扫描、检测冲突 是ConcurrentHashMap的常见技巧。
3.它进行的不是整体的扩容,而是单独 对Segment进行扩容
1.8
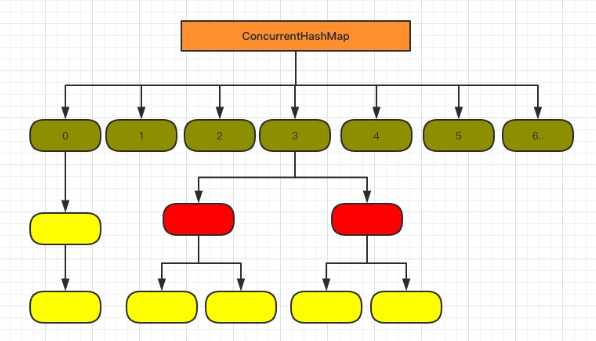
抛弃了原有的 Segment 分段锁,而采用了 CAS + synchronized 来保证并发安全性。
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); int binCount = 0; for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; K fk; V fv; if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) // 判断是否需要初始化 tab = initTable(); else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { // 进行写数据 if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value))) break; // no lock when adding to empty bin } else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) // 扩容 tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); else if (onlyIfAbsent // check first node without acquiring lock && fh == hash && ((fk = f.key) == key || (fk != null && key.equals(fk))) && (fv = f.val) != null) return fv; else { V oldVal = null; synchronized (f) { // 为了确保能写入,锁 if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { if (fh >= 0) { binCount = 1; for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) { K ek; if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { oldVal = e.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) e.val = value; break; } Node<K,V> pred = e; if ((e = e.next) == null) { pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value); break; } } } else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { Node<K,V> p; binCount = 2; if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value)) != null) { oldVal = p.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) p.val = value; } } else if (f instanceof ReservationNode) throw new IllegalStateException("Recursive update"); } } if (binCount != 0) { if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) treeifyBin(tab, i); // 转换红黑树 if (oldVal != null) return oldVal; break; } } } addCount(1L, binCount); return null; }
1.它进行的不是整体的扩容,而是单独 对Segment进行扩容
2.因为不再使用Segment,初始化操作大大简化,修改为lazy-load形式,这样可以有效避免初始开销,解决了老版本很多人抱怨的这一点。
3.数据存储利用volatile来保证可见性。
4.使用CAS等操作,在特定场景进行无锁并发操作。
5.使用Unsafe、LongAdder之类底层手段,进行极端情况的优化。
它使用的是synchronized,而不是通常建议的ReentrantLock之类,这是为什么呢?现代JDK中,synchronized已经被不断优化,可以不再过分担心性能差异,另外,相比于ReentrantLock,它可以减少内存消耗,这是个非常大的优势。
标签:tps init 而不是 cep 阶段 out 存储 tree lse
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/CherryTab/p/12169045.html