标签:exception ken 发送 其它 app 解码 gis tco thrown
目录
在看 Sharding-Proxy 源码之前,强烈建议先阅读一直官网的两篇文章:
sharding-proxy
├── sharding-proxy-backend 负责与底层mysql通信
├── sharding-proxy-bootstrap 启动sharding-proxy
├── sharding-proxy-common yaml配置文件加载...
├── sharding-proxy-frontend 启动socket,代理mysql/pg
│ ├── sharding-proxy-frontend-core 启动sokcet
│ ├── sharding-proxy-frontend-mysql 实现类MySQLProtocolFrontendEngine
│ ├── sharding-proxy-frontend-postgresql 实现类PostgreSQLProtocolFrontendEngine
│ └── sharding-proxy-frontend-spi 核心spi,DatabaseProtocolFrontendEngine
└── sharding-proxy-transport 代理数据库对应的编解码
├── sharding-proxy-transport-core 核心api,DatabasePacket和PacketPayload
├── sharding-proxy-transport-mysql MySQL协议编解码
└── sharding-proxy-transport-postgresql pg协议编解码总结: Sharding-Proxy 包功能说明
sharding-proxy-bootstrap:启动入口,调用 LogicSchemas 加载配置,ShardingProxy 启动程序,绑定 socket。
sharding-proxy-frontend-core:启动netty,hander 的初始化类为 ServerHandlerInitializer,编解码对应的 Handler 为 PacketCodec,业务处理对应的 Handler 为 FrontendChannelInboundHandler。这两个 Handler 实际的工作都委托给了 DatabaseProtocolFrontendEngine。
sharding-proxy-frontend-spi:核心 spi,DatabaseProtocolFrontendEngine 包含编解码,执行器。 DatabaseProtocolFrontendEngine 目前有 MySQL 和 PG 两个实现。
sharding-proxy-frontend-mysql:实现类 MySQLProtocolFrontendEngine
sharding-proxy-transport-mysql:mysql 报文解析,主要接口为 MySQLPacket。
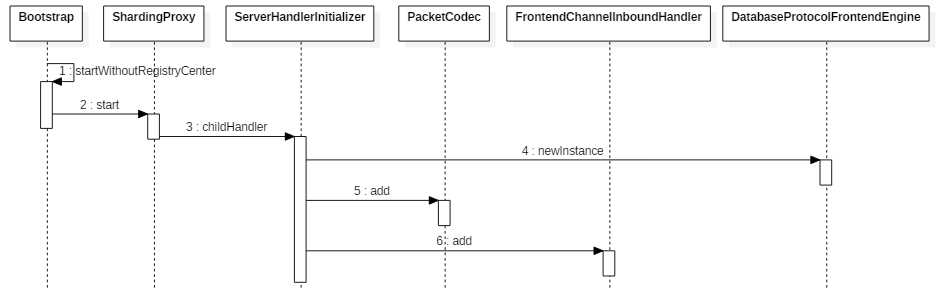
总结: Sharding-Proxy 启动流程最核心的是通过 ServerHandlerInitializer 加载了 PacketCodec(编解码) 和 FrontendChannelInboundHandler(业务处理器) 两个处理器。这两个处理的具体工作都委托给了 DatabaseProtocolFrontendEngine 完成,有 MySQL 和 PostgreSQL 两个实现。
Bootstrap
启动入口位于 sharding-proxy-bootstrap 工程中。Bootstrap 提供了有注册中心和无注册中心两种启动方式,以无注册中心的启动方式为例:
private static void startWithoutRegistryCenter(
final Map<String, YamlProxyRuleConfiguration> ruleConfigs,
final YamlAuthenticationConfiguration authentication,
final Properties prop, final int port) throws SQLException {
Authentication authenticationConfiguration = getAuthentication(authentication);
ShardingProxyContext.getInstance().init(authenticationConfiguration, prop);
// 加载配置规则
LogicSchemas.getInstance().init(
getDataSourceParameterMap(ruleConfigs),
getRuleConfiguration(ruleConfigs));
initOpenTracing();
// 启动 sharding-proxy
ShardingProxy.getInstance().start(port);
}Bootstrap 启动最核心的步骤是 ShardingProxy 启动代理。Sharding-Proxy 会启动一个 Netty 服务器,默认端口为 3307。
ShardingProxy
程序启动入口位于 sharding-proxy-frontend-core 工程中。Netty 服务器通过 ServerHandlerInitializer 加载对应的 Handler,包括 PacketCodec(编解码) 和 FrontendChannelInboundHandler(业务处理器) 两个处理器。
DatabaseProtocolFrontendEngine databaseProtocolFrontendEngine =
DatabaseProtocolFrontendEngineFactory.newInstance(
LogicSchemas.getInstance().getDatabaseType());
pipeline.addLast(new PacketCodec(databaseProtocolFrontendEngine.getCodecEngine()));
pipeline.addLast(new FrontendChannelInboundHandler(databaseProtocolFrontendEngine));总结: 这两个 Handler 的实际工作都是委托给 DatabaseProtocolFrontendEngine 完成,目前有 MySQL 和 PG 两个实现。
DatabaseProtocolFrontendEngine
位于 sharding-proxy-frontend-spi工程中。DatabaseProtocolFrontendEngine 是一个 SPI 接口,目前提供了 MySQL 和 PostgreSQL 两种实现,分别位于 sharding-proxy-frontend-mysql 和 sharding-proxy-frontend-postgresql 工程中。
public interface DatabaseProtocolFrontendEngine extends DatabaseTypeAwareSPI {
FrontendContext getFrontendContext();
AuthenticationEngine getAuthEngine();
void release(BackendConnection backendConnection);
// 编解码器
DatabasePacketCodecEngine getCodecEngine();
// SQL执行引擎
CommandExecuteEngine getCommandExecuteEngine();
}总结: DatabaseProtocolFrontendEngine 方法最重要的两个属性是 DatabasePacketCodecEngine 解码器和 CommandExecuteEngine SQL执行引擎。
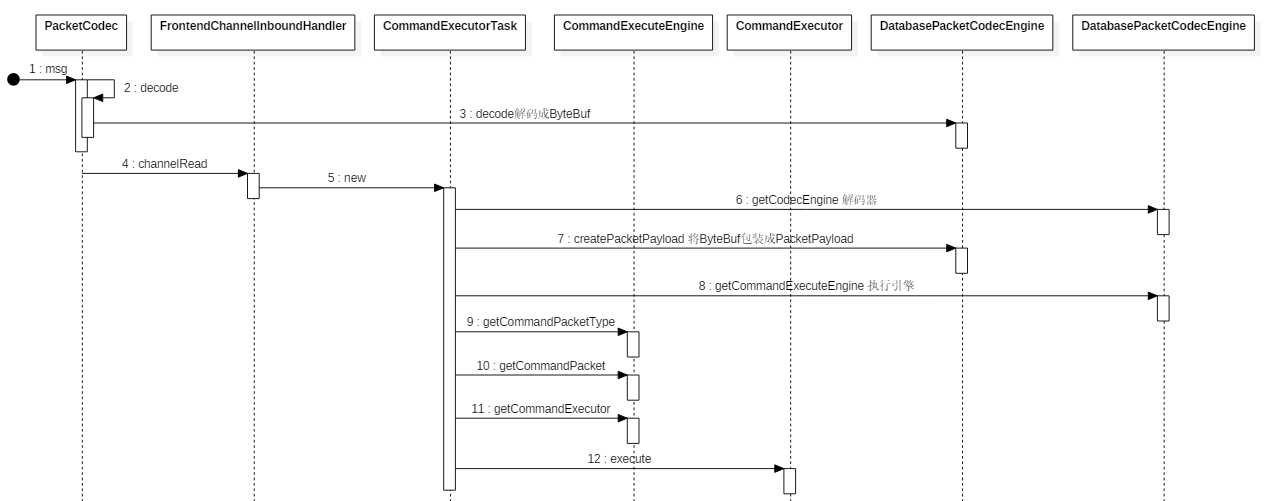
总结: Sharding-Proxy 接收到消息后处理过程有如下几步:
FrontendChannelInboundHandler
消息处理的入口 FrontendChannelInboundHandler 位于 sharding-proxy-frontend-core 工程中。Sharding-Proxy 接收到请求后,先由 PacketCodec 按长度解码,然后由 FrontendChannelInboundHandler 进行处理,代码如下:
@Override
public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext context, final Object message) {
if (!authorized) {
authorized = auth(context, (ByteBuf) message);
return;
}
// CommandExecutorSelector 返回 ExecutorService,任务执行 CommandExecutorTask
CommandExecutorSelector.getExecutor(
databaseProtocolFrontendEngine.getFrontendContext()
.isOccupyThreadForPerConnection(),
backendConnection.isSupportHint(),
backendConnection.getTransactionType(),
context.channel().id())
.execute(new CommandExecutorTask(databaseProtocolFrontendEngine, backendConnection, context, message));
}CommandExecutorTask
// 核心api,处理编解码,sql执行
private final DatabaseProtocolFrontendEngine databaseProtocolFrontendEngine;
// 管理后台 MySQL 连接
private final BackendConnection backendConnection;
// 按长度解码后的client请求信息,ByteBuf
private final Object message;
@Override
public void run() {
// 按包长度解码成 ByteBuf,client
PacketPayload payload = databaseProtocolFrontendEngine.getCodecEngine()
.createPacketPayload((ByteBuf) message));
// 将 ByteBuf 解析成具体的命令,并转发到 backendConnection,响应 client
isNeedFlush = executeCommand(context, payload, backendConnection);
}
private boolean executeCommand(final ChannelHandlerContext context,
final PacketPayload payload, final BackendConnection backendConnection)
throws SQLException {
// 执行引擎
CommandExecuteEngine commandExecuteEngine = databaseProtocolFrontendEngine
.getCommandExecuteEngine();
// mysql命令类型
CommandPacketType type = commandExecuteEngine.getCommandPacketType(payload);
// 解码
CommandPacket commandPacket = commandExecuteEngine.getCommandPacket(
payload, type, backendConnection);
// 执行器
CommandExecutor commandExecutor = commandExecuteEngine.getCommandExecutor(
type, commandPacket, backendConnection);
// 向真实 mysql 服务器发送 sql,并返回结果 responsePackets
Collection<DatabasePacket> responsePackets = commandExecutor.execute();
if (responsePackets.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
// 将返回结果伪装成 mysql 协议,返回给客户端 client
for (DatabasePacket each : responsePackets) {
context.write(each);
}
if (commandExecutor instanceof QueryCommandExecutor) {
commandExecuteEngine.writeQueryData(context, backendConnection,
(QueryCommandExecutor) commandExecutor, responsePackets.size());
return true;
}
return databaseProtocolFrontendEngine.getFrontendContext()
.isFlushForPerCommandPacket();
}总结: CommandExecutorTask 内部很多工作都委托给了 CommandExecuteEngine 完成,CommandExecuteEngine 也有 MySQL 和 PostgreSQL 两个实现。CommandExecuteEngine 主要是对具体的协议解码 CommandPacket,并获取具体的执行器 CommandExecutor。
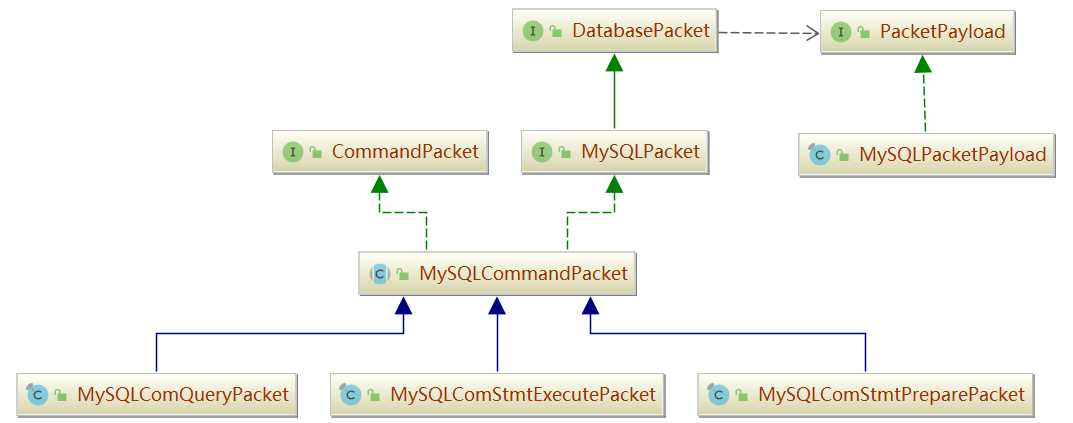
位于 sharding-proxy-transport-mysql 工程中。
MySQLPacketCodecEngine:实现 DatabasePacketCodecEngine 接口,根据包长度解析报文,并将解析的 ByteBuf 包装成 MySQLPacketPayload。
MySQLPacketPayload:实现 PacketPayload 接口,本质是对 ByteBuf 的包装,提供对 ByteBuf 的 read/write 字段。
MySQLCommandPacketFactory:将 MySQLPacketPayload 解析成具体协议的报文 MySQLPacket。
MySQLPacket:实现了 DatabasePacket 接口。将 ByteBuf 解析成具体的命令,主要分两大类:
位于 sharding-proxy-frontend-mysql 工程中。Sharding-Sphere 将客户端发送的 SQL 命令解析后,转发给底层的 MySQL 服务器,核心的接口类如下:
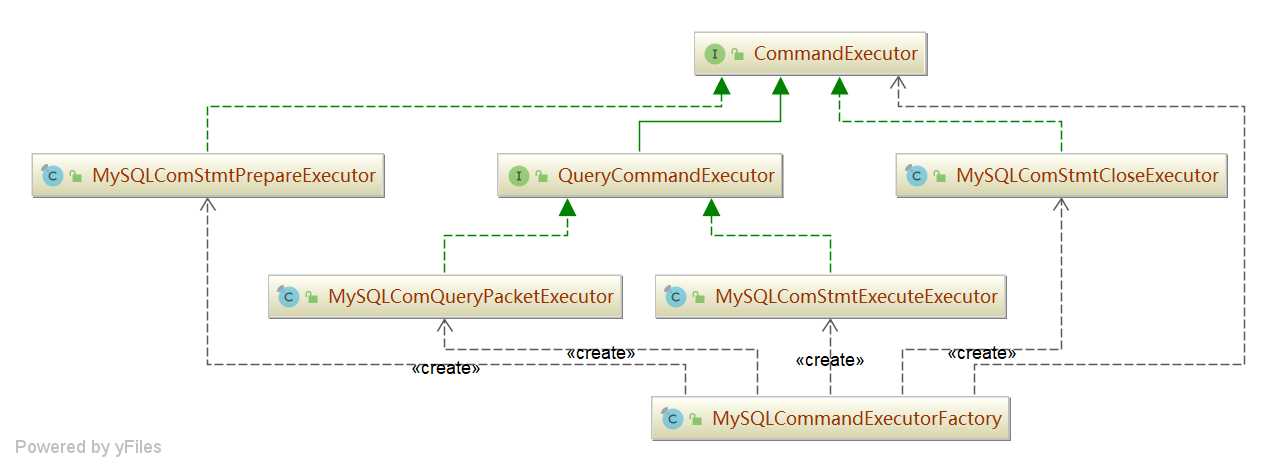
CommandExecutor:核心接口,SQL 执行器。Sharding-Proxy 解析 client 的命令,转发给 MySQL 服务器,并将 MySQL 服务器返回的结果按 MySQL 协议包伪装后响应给 client。
注意: 并不是所有的 client 请求都转发到 mysql 服务器上了。如 MySQL 预解析操作分为 prepare、execute、close、reset 四步,分别对应 MySQLComStmtPrepareExecutor、MySQLComStmtExecuteExecutor、MySQLComStmtCloseExecutor、MySQLComStmtResetExecutor 四个类。除了 execute 会将请求转发给底层 mysql 服务器外,其它的解析是在代理层(sharding-proxy)完成的,将 SQLParseEngine 解析后结果缓存在 MySQLBinaryStatementRegistry 实例中,这样能避免重复解析 SQL 提高性能。
public MySQLComQueryPacketExecutor(final MySQLComQueryPacket comQueryPacket,
final BackendConnection backendConnection) {
// 包含 SQL 和 connection,textProtocolBackendHandler 可以执行 SQL
textProtocolBackendHandler = TextProtocolBackendHandlerFactory.newInstance(
DatabaseTypes.getActualDatabaseType("MySQL"),
comQueryPacket.getSql(), backendConnection);
}
@Override
public Collection<DatabasePacket> execute() {
...
// 委托给 textProtocolBackendHandler 执行
BackendResponse backendResponse = textProtocolBackendHandler.execute();
// 包装返回的结果
// error
if (backendResponse instanceof ErrorResponse) {
return Collections.<DatabasePacket>singletonList(createErrorPacket(
((ErrorResponse) backendResponse).getCause()));
}
// update
if (backendResponse instanceof UpdateResponse) {
return Collections.<DatabasePacket>singletonList(createUpdatePacket(
(UpdateResponse) backendResponse));
}
// query
isQuery = true;
return createQueryPackets((QueryResponse) backendResponse);
}总结: MySQLComQueryPacketExecutor 总体过程非常清晰,解析、转发、响应。
public MySQLComStmtExecuteExecutor(
final MySQLComStmtExecutePacket comStmtExecutePacket,
final BackendConnection backendConnection) {
databaseCommunicationEngine = DatabaseCommunicationEngineFactory.getInstance()
.newBinaryProtocolInstance(backendConnection.getLogicSchema(),
comStmtExecutePacket.getSql(), comStmtExecutePacket.getParameters(),
backendConnection);
}
@Override
public Collection<DatabasePacket> execute() {
// 委托给 databaseCommunicationEngine 执行
BackendResponse backendResponse = databaseCommunicationEngine.execute();
// 包装返回的结果,同 MySQLComQueryPacketExecutor
...
}总结: 可以看到,和 MySQLComQueryPacketExecutor 基本类似,唯一不同的在于MySQLComQueryPacketExecutor 真正调用 TextProtocolBackendHandler 执行,而 MySQLComStmtExecuteExecutor 调用 DatabaseCommunicationEngine 执行。
那问题就来了,为什么会有 TextProtocolBackendHandler 和 DatabaseCommunicationEngine 两个执行器?它们到底是什么关系呢?TextProtocolBackendHandler 的实现类其实就是调用 DatabaseCommunicationEngine。
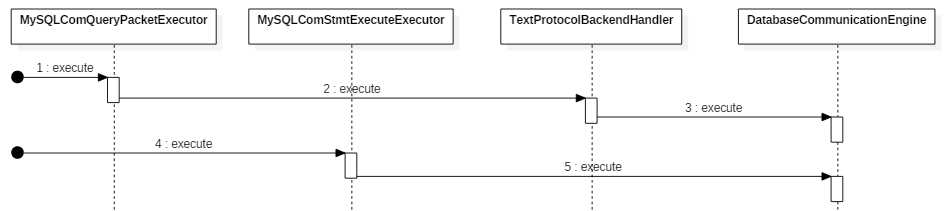
总结: 无论是 MySQLComQueryPacketExecutor 还是 MySQLComStmtExecuteExecutor 最终都是调用 DatabaseCommunicationEngine 执行。
位于 sharding-proxy-backend 工程中。
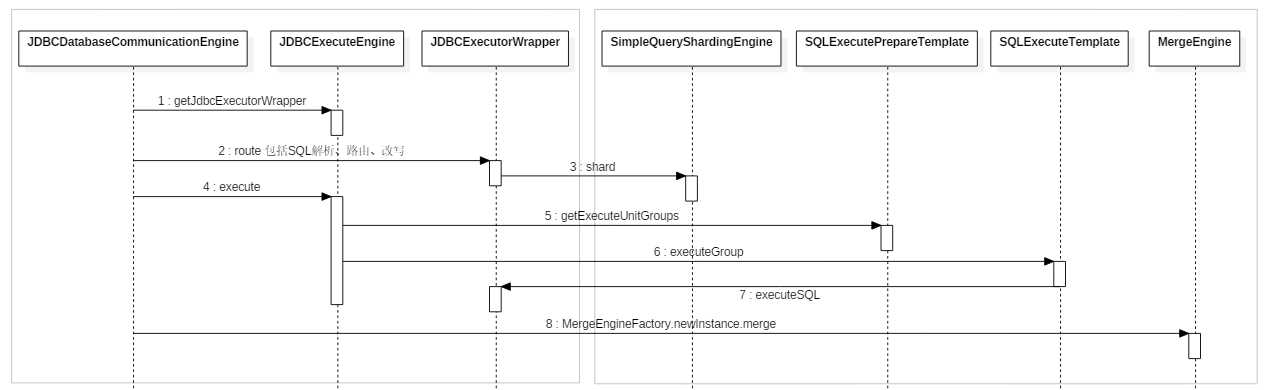
总结: Sharding-Proxy 消息处理过程和 Sharding-Jdbc 处理过程差不多,也要经过 SQL 解析、路由、改写、合并这四个核心过程。前面三个类是 Sharding-Proxy 中的,后面四个类则是 Sharding-Jdbc 的,两套逻辑共用一套核心代码。
DatabaseCommunicationEngine
DatabaseCommunicationEngine 是 Sharding-Proxy 内部转发执行器,负责将请求转发给底层 MySQL 服务器。
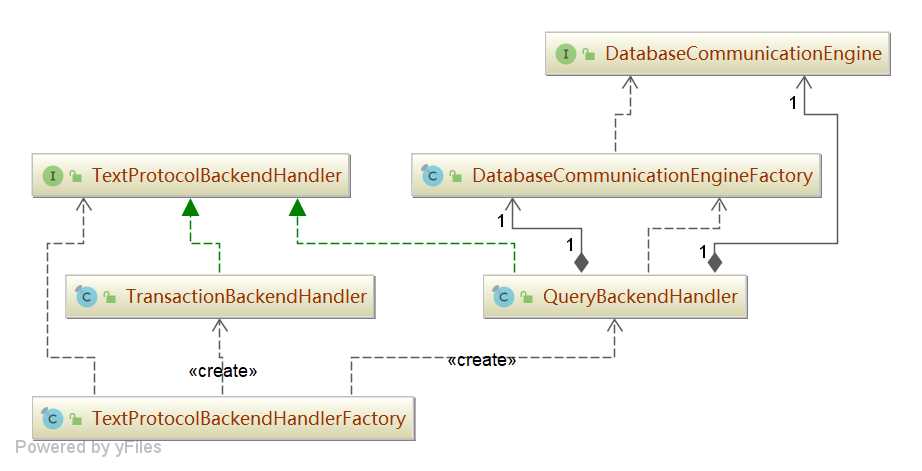
我们看一下 QueryBackendHandler 的实现类。
public final class QueryBackendHandler implements TextProtocolBackendHandler {
@Override
public BackendResponse execute() {
...
databaseCommunicationEngine = databaseCommunicationEngineFactory
.newTextProtocolInstance(backendConnection.getLogicSchema(),
sql, backendConnection);
return databaseCommunicationEngine.execute();
}
}
说明: TextProtocolBackendHandler 是不使用预解析的执行器,调用 databaseCommunicationEngineFactoy.newTextProtocolInstance,而使用预解析的 MySQLComStmtExecuteExecutor 内部调用 DatabaseCommunicationEngineFactory.newBinaryProtocolInstance。我们看一下这两个方法的内部实现。
public DatabaseCommunicationEngine newTextProtocolInstance(final LogicSchema logicSchema,
final String sql, final BackendConnection backendConnection) {
return new JDBCDatabaseCommunicationEngine(logicSchema, sql,
new JDBCExecuteEngine(backendConnection,
new StatementExecutorWrapper(logicSchema)));
}
public DatabaseCommunicationEngine newBinaryProtocolInstance(
final LogicSchema logicSchema, final String sql,
final List<Object> parameters,
final BackendConnection backendConnection) {
return new JDBCDatabaseCommunicationEngine(logicSchema, sql,
new JDBCExecuteEngine(backendConnection,
new PreparedStatementExecutorWrapper(logicSchema, parameters)));
}
说明: 在 Sharding-Proxy 中 TextProtocol 代表的是不使用预解析,而 BinaryProtocol 代表使用预解析。JDBCDatabaseCommunicationEngine 内部直接委托给 JDBCExecuteEngine 完成。
JDBCDatabaseCommunicationEngine
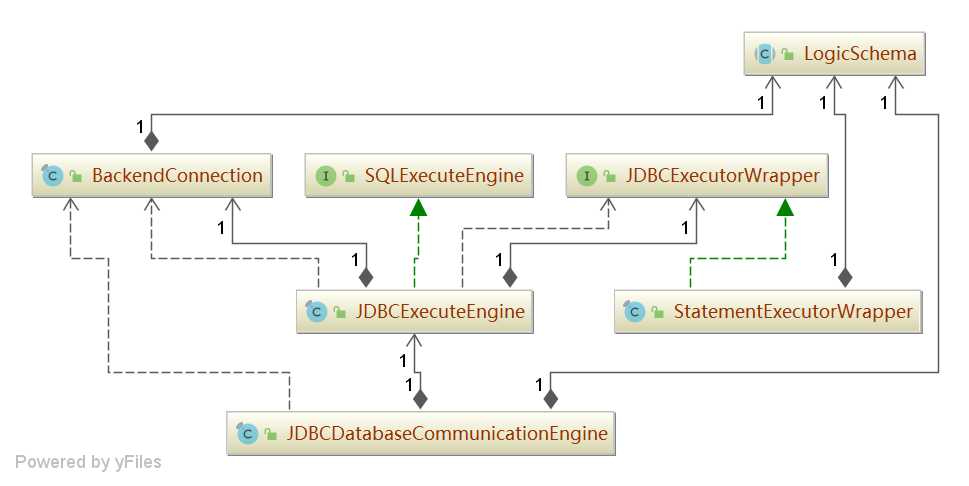
JDBCDatabaseCommunicationEngine 执行过程的代码如下:
private final String sql;
private final JDBCExecuteEngine executeEngine;
@Override
public BackendResponse execute() {
try {
// 1. SQL 路由、改写
SQLRouteResult routeResult = executeEngine.getJdbcExecutorWrapper().route(sql);
return execute(routeResult);
} catch (final SQLException ex) {
return new ErrorResponse(ex);
}
}
private BackendResponse execute(final SQLRouteResult routeResult) throws SQLException {
...
// 2. SQL 执行
response = executeEngine.execute(routeResult);
if (logicSchema instanceof ShardingSchema) {
logicSchema.refreshTableMetaData(routeResult.getSqlStatementContext());
}
// 4. 结果合并
return merge(routeResult);
}
总结: JDBCDatabaseCommunicationEngine 执行 SQL 过程包括:SQL 路由、改写、执行、结果合并,其中前三步都是委托 JDBCExecuteEngine 完成的。
JDBCExecuteEngine
// 管理底层 MySQL 连接
private final BackendConnection backendConnection;
// ①根据SQL生成执行计划(包括SQL解析、路由、改写);②生成Statement;③执行SQL
private final JDBCExecutorWrapper jdbcExecutorWrapper;
// 生成执行计划 RouteUnit -> StatementExecuteUnit
private final SQLExecutePrepareTemplate sqlExecutePrepareTemplate;
// 执行 StatementExecuteUnit
private final SQLExecuteTemplate sqlExecuteTemplate;
@Override
public BackendResponse execute(final SQLRouteResult routeResult) throws SQLException {
final SQLStatementContext sqlStatementContext = routeResult.getSqlStatementContext();
boolean isReturnGeneratedKeys = sqlStatementContext.getSqlStatement()
instanceof InsertStatement;
boolean isExceptionThrown = ExecutorExceptionHandler.isExceptionThrown();
// 执行计划,ProxyJDBCExecutePrepareCallback用于创建执行计划
Collection<ShardingExecuteGroup<StatementExecuteUnit>> sqlExecuteGroups =
sqlExecutePrepareTemplate.getExecuteUnitGroups(
routeResult.getRouteUnits(),
new ProxyJDBCExecutePrepareCallback(
backendConnection, jdbcExecutorWrapper, isReturnGeneratedKeys));
// 执行SQL,ProxySQLExecuteCallback用于执行SQL
Collection<ExecuteResponse> executeResponses = sqlExecuteTemplate.executeGroup(
(Collection) sqlExecuteGroups,
new ProxySQLExecuteCallback(backendConnection, jdbcExecutorWrapper,
isExceptionThrown, isReturnGeneratedKeys, true),
new ProxySQLExecuteCallback(backendConnection, jdbcExecutorWrapper,
isExceptionThrown, isReturnGeneratedKeys, false));
ExecuteResponse executeResponse = executeResponses.iterator().next();
// 组装结果
return executeResponse instanceof ExecuteQueryResponse
? getExecuteQueryResponse(((ExecuteQueryResponse) executeResponse)
.getQueryHeaders(), executeResponses)
: new UpdateResponse(executeResponses);
}每天用心记录一点点。内容也许不重要,但习惯很重要!
标签:exception ken 发送 其它 app 解码 gis tco thrown
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/12233756.html