标签:连接池 文件下载 aec 认证 小文件 因此 for byte imp
安装
pip install requests
pip install -i https://pypi.doubanio.com/simple/ requests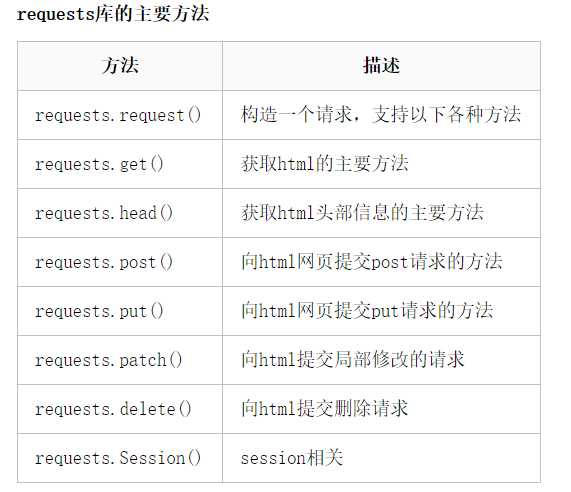
requests.request(method, url,** kwargs)类能够构造一个请求,支持不同的请求方式
import requests
response = requests.request(method='get', url='https://www.baidu.com')
print(response.status_code)request类中几个参数:
k1=v1&k2=v2的模式增加到url中,get请求中用的较多。stream=True,requests无法将连接释放回连接池,除非下载完了所有数据,或者调用了response.close。import requests
response = requests.request(method='get', url='http://www.httpbin.org/get')当一个请求被发送后,会有一个response响应。requests同样为这个response赋予了相关方法:
ValueError。stream=True的情况下,当遍历生成器时,以块的形式返回,也就是一块一块的遍历要下载的内容。避免了遇到大文件一次性的将内容读取到内存中的弊端,如果stream=False,全部数据作为一个块返回。chunk_size参数指定块大小。stream=True时,迭代响应数据,每次一行,也就是一行一行的遍历要下载的内容。同样避免了大文件一次性写入到内存中的问题。当然,该方法不安全。至于为啥不安全,咱也不知道,主要是官网上没说!经查,如果多次调用该方法,iter_lines不保证重新进入时的安全性,因此可能会导致部分收到的数据丢失。response.headers.get(‘Content-Type‘, ‘哎呀,没取到!‘)response.encoding = “gbk”指定为gbk。requests.get(url, params=None, **kwargs)发送GET请求。相关参数:
get请求难免会带一些额外的参数K1=V1&K2=V2。
我们可以手动的拼接:
import requests
response = requests.get(url='http://www.httpbin.org/get?k1=v1&k2=v2')
print(response.url) # http://www.httpbin.org/get?k1=v1&k2=v2
print(response.json().get('args')) # {'k1': 'v1', 'k2': 'v2'}现在,我们可以使用params参数来解决这个问题。
import requests
xxx = {"user": "xxx", "pwd": "666"}
response = requests.get(url='http://www.httpbin.org/get', params=xxx)
print(response.url) # http://www.httpbin.org/get?user=%E5%BC%A0%E5%BC%80&pwd=666
print(response.json().get('args')) # {'pwd': '666', 'user': 'xxx'}GET请求中如何携带headers。
import requests
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
headers = {"user-agent": UserAgent().random}#(随机一个请求头,fake_useragent模块)
response = requests.get(url='http://www.httpbin.org/get', headers=headers)
print(response.json()['headers']['User-Agent']) # Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; zh-TW) AppleWebKit/533.19.4 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Safari/533.18.5GET请求中如何携带cookies。
import requests
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
cookies = {
"user": "xxx",
"pwd": "666"
}
response = requests.get(url='http://www.httpbin.org/cookies', cookies=cookies)
print(response.json()) # {'cookies': {'pwd': '666', 'user': 'xxx'}}因为url的返回值是json形式cookies也在里面,所以我们要去json中取,而不是从response.cookies取。
再来看响应中的cookies:
import requests
url = 'http://www.baidu.com'
response = requests.get(url=url)
print(response.cookies) # <RequestsCookieJar[<Cookie BDORZ=27315 for .baidu.com/>]>
print(response.cookies.get_dict()) # {'BDORZ': '27315'}
print(response.cookies.items()) # [('BDORZ', '27315')]如果你访问的是一个小文件,或者图片之类的,我们可以直接写入到本地就完了,也就是不用管stream,让它默认为False即可。
import requests
import webbrowser
url = 'https://timgsa.baidu.com/timg?image&quality=80&size=b9999_10000&sec=1568638318957&di=1d7f37e7caece1c39af05b624f42f0a7&imgtype=0&src=http%3A%2F%2Fimg3.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201501%2F17%2F20150117224236_vYFmL.jpeg'
response = requests.get(url=url)
f = open('a.jpeg', 'wb')
f.write(response.content)
f.close()
webbrowser.open('a.jpeg')那要是下载大文件,可就不能这么干了:
import requests
import webbrowser
url = 'https://timgsa.baidu.com/timg?image&quality=80&size=b9999_10000&sec=1568638318957&di=1d7f37e7caece1c39af05b624f42f0a7&imgtype=0&src=http%3A%2F%2Fimg3.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201501%2F17%2F20150117224236_vYFmL.jpeg'
response = requests.get(url=url, stream=True)
with open('a.jpeg', 'wb') as f:
for chunk in response.iter_content(chunk_size=256):
f.write(chunk)
webbrowser.open('a.jpeg')使用response.iter_content(chunk_size=256)一块一块下载,并且可以指定chunk_size大小。
当然,也可以使用response.iter_lines一行一行遍历下载,但是官网说不安全
requests.post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs)发送POST请求,相关参数:
在post请求中,data与json既可以是str类型,也可以是dict类型。
区别:
1、不管json是str还是dict,如果不指定headers中的content-type,默认为application/json
2、data为dict时,如果不指定content-type,默认为application/x-www-form-urlencoded,相当于普通form表单提交的形式
3、data为str时,如果不指定content-type,默认为application/json
4、用data参数提交数据时,request.body的内容则为a=1&b=2的这种形式,用json参数提交数据时,request.body的内容则为‘{"a": 1, "b": 2}‘的这种形式
import requests
url = 'http://www.httpbin.org/post'
# data为字典
data_dict = {"k1": "v1"}
response = requests.post(url=url, data=data_dict)
print(response.json())
# data为字符串
data_str = "abc"
response = requests.post(url=url, data=data_str)
print(response.json(), type(response.json()['data']))
# data为文件对象
file = open('a.jpg', 'rb')
response = requests.post(url=url, data=file)
print(response.json())基于POST请求的文件上传,使用files参数。
import requests
file = {"file": open('a.jpg', 'rb')}
response = requests.post('http://www.httpbin.org/post', files=file)
print(response.json())import requests
url = 'http://www.httpbin.org/post'
response = requests.post(url=url, json={"user": "zhangkai"})
print(response.json())requests.head(url, **kwargs)发送HEAD请求,相关参数:
import requests
url = 'http://httpbin.org/get'
response = requests.head(url=url)
print(response.headers)
'''
{
'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials': 'true',
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*',
'Content-Encoding': 'gzip',
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Date': 'Mon, 16 Sep 2019 10:58:07 GMT',
'Referrer-Policy': 'no-referrer-when-downgrade',
'Server': 'nginx',
'X-Content-Type-Options': 'nosniff',
'X-Frame-Options': 'DENY',
'X-XSS-Protection': '1; mode=block',
'Connection': 'keep-alive'
}
'''使用requests.head(url, **kwargs)的优点就是以较少的流量获得响应头信息,也可以用在分页中。
超时,在规定的时间无响应。
import requests
respone=requests.get('https://www.12306.cn', timeout=0.0001)标签:连接池 文件下载 aec 认证 小文件 因此 for byte imp
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zzsy/p/12243759.html