标签:sqrt with open get open dir png inter 原理 开始
测绘行业基础计算的代码,废话不多说,先介绍下基本原理。
一 高斯正反算基本原理
1 高斯投影坐标正算
(1)高斯投影正算:已知椭球面上某点的大地坐标(B,L),求该点在高斯投影平面上的直
角坐标(X,Y),即(B,L)-->(X,Y)的坐标变换。
(2)投影变换必须满足的条件:
中央子午线投影后为直线;
中央子午线投影后长度不变;
投影具有正形性质,即正形投影条件。
(3)公式如下:
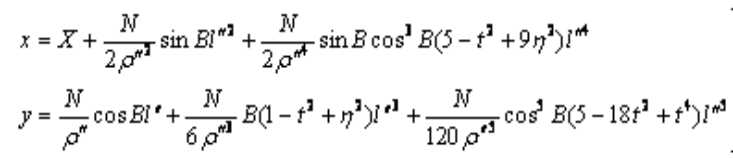
1 高斯投影坐标反算
(1)高斯投影反算:已知在高斯投影平面上的直
角坐标(X,Y),反求该点在椭球面上的大地坐标(B,L),即(X,Y)-->(B,L)的坐标变换。
(2)同正算一样,对投影函数提出三个条件:
x坐标轴投影成中央子午线,是投影的对称轴;
x轴上长度投影保持不变;
正形投影条件。
(3)反算公式
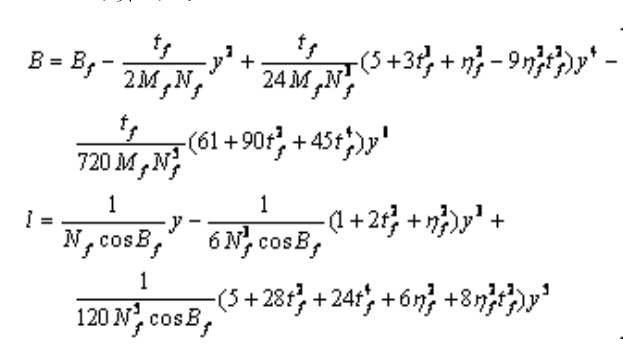
公式随手截的图,所以分辨率....
具体公式,学测绘的书上都有的
二 实现代码
其实这个小程序真要动手写起来难度不大,难的是算法原理的理解和公式中每个字母所代表的含义,以下是具体代码:
1 import tkinter 2 import tkinter.filedialog as fdg 3 import re 4 import math 5 6 7 8 """ 9 =================> 用户UI界面相关 <================== 10 """ 11 root = tkinter.Tk() 12 root.title(‘杨宇航-高斯正反算‘) 13 root.resizable(width=False, height=False) 14 root.geometry(‘500x700‘) 15 16 17 18 19 # # =============== 高斯正算UI界面 ============== 20 # # 文本坐标文件导入 21 label_wel_zheng = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘<高斯正算>‘,font=(‘黑体‘,16),fg=‘black‘) 22 label_wel_zheng.place(x=185, y=10) 23 label_open = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘1.请选择转化文件:‘,font=(‘黑体‘,10),fg=‘black‘) 24 label_open.place(x=5, y=40) 25 open_pth_Z = tkinter.Variable() 26 entry_open = tkinter.Entry(root,width=59,textvariable=open_pth_Z).place(x=70, y=70) 27 bot_open = tkinter.Button(root,width=8,height=1,text=‘导入文件‘,font=(‘黑体‘,9),fg=‘black‘,bg=‘orange‘,command=lambda :File_Open_Z()) 28 bot_open.place(x=5,y=70) 29 # # 椭球选择 30 label_glo = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘2.请选择椭球(填入相应椭球代号):‘,font=(‘黑体‘,10),fg=‘black‘) 31 label_glo.place(x=5, y=100) 32 glo_Z = tkinter.Variable() 33 entry_glo = tkinter.Entry(root,textvariable=glo_Z).place(x=227,y=100) 34 label_gloa = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘A:克拉索夫斯基椭球‘,font=(‘黑体‘,12),fg=‘black‘) 35 label_gloa.place(x=5, y=125) 36 label_glob = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘B:WGS-84椭球‘,font=(‘黑体‘,12),fg=‘black‘) 37 label_glob.place(x=255, y=125) 38 label_gloc = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘C:CGCS-2000椭球‘,font=(‘黑体‘,12),fg=‘black‘) 39 label_gloc.place(x=5, y=155) 40 label_glod = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘D:IUGG-75椭球‘,font=(‘黑体‘,12),fg=‘black‘) 41 label_glod.place(x=255, y=155) 42 # # 投影带选择 43 label_num = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘3.请选择投影带(填入相应投影带代号):‘,font=(‘黑体‘,10),fg=‘black‘) 44 label_num.place(x=5, y=190) 45 num = tkinter.Variable() 46 entry_num = tkinter.Entry(root,textvariable=num).place(x=255,y=190) 47 label_num3 = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘A:三度带投影‘,font=(‘黑体‘,12),fg=‘black‘) 48 label_num3.place(x=5, y=220) 49 label_num6 = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘B:六度带投影‘,font=(‘黑体‘,12),fg=‘black‘) 50 label_num6.place(x=255, y=220) 51 # # 最终坐标文件保存 52 label_save = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘4.请选择转化结果输出路径:‘,font=(‘黑体‘,10),fg=‘black‘) 53 label_save.place(x=5,y=250) 54 save_pth_Z = tkinter.Variable() 55 entry_save = tkinter.Entry(root,width=59,textvariable=save_pth_Z).place(x=70, y=275) 56 bot_save = tkinter.Button(root,width=8,height=1,text=‘保存文件‘,font=(‘黑体‘,9),fg=‘black‘,bg=‘orange‘,command=lambda :File_Save_Z()) 57 bot_save.place(x=5,y=275) 58 # # 定义开始转换按钮及其他内容 59 bot_start_Z = tkinter.Button(root,text=‘开始转化‘,font=(‘黑体‘,10),fg=‘white‘,bg=‘blue‘,command=lambda :Gaosi_Zheng()) 60 bot_start_Z.place(x=210, y=310) 61 show1 = tkinter.Variable() 62 label_show = tkinter.Label(root,textvariable=show1).place(width=480,height=42,x=5,y=333) 63 64 65 66 67 # # =============== 高斯反算UI界面 ============== 68 # # 文本坐标文件导入 69 label_open = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘<高斯反算>‘,font=(‘黑体‘,16),fg=‘black‘) 70 label_open.place(x=185, y=380) 71 label_open = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘1.请选择转化文件:‘,font=(‘黑体‘,10),fg=‘black‘) 72 label_open.place(x=5, y=410) 73 open_pth_F = tkinter.Variable() 74 entry_open = tkinter.Entry(root,width=50,textvariable=open_pth_F).place(x=70, y=440) 75 bot_open = tkinter.Button(root,width=8,height=1,text=‘导入文件‘,font=(‘黑体‘,9),fg=‘black‘,bg=‘orange‘,command=lambda :File_Open_F()) 76 bot_open.place(x=5,y=440) 77 # # 椭球选择 78 label_glo = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘2.请选择椭球(填入相应椭球代号):‘,font=(‘黑体‘,10),fg=‘black‘) 79 label_glo.place(x=5, y=470) 80 glo_F = tkinter.Variable() 81 entry_glo = tkinter.Entry(root,textvariable=glo_F).place(x=227,y=470) 82 label_gloa = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘A:克拉索夫斯基椭球‘,font=(‘黑体‘,12),fg=‘black‘) 83 label_gloa.place(x=5, y=495) 84 label_glob = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘B:WGS-84椭球‘,font=(‘黑体‘,12),fg=‘black‘) 85 label_glob.place(x=255, y=495) 86 label_gloc = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘C:CGCS-2000椭球‘,font=(‘黑体‘,12),fg=‘black‘) 87 label_gloc.place(x=5, y=525) 88 label_glod = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘D:1975国际椭球‘,font=(‘黑体‘,12),fg=‘black‘) 89 label_glod.place(x=255, y=525) 90 # # 最终坐标文件保存 91 label_num = tkinter.Label(root,text=‘3.请选择文件输出路径:‘,font=(‘黑体‘,10),fg=‘black‘) 92 label_num.place(x=5, y=560) 93 save_pth_F = tkinter.Variable() 94 entry_save = tkinter.Entry(root,width=59,textvariable=save_pth_F).place(x=70,y=590) 95 bot_save = tkinter.Button(root,width=8,height=1,text=‘保存文件‘,font=(‘黑体‘,9),fg=‘black‘,bg=‘orange‘,command=lambda :File_Save_F()) 96 bot_save.place(x=5,y=590) 97 # # 定义开始转换按钮及其他内容 98 bot_start = tkinter.Button(root,text=‘开始转换‘,font=(‘黑体‘,10),fg=‘white‘,bg=‘blue‘,command=lambda :Gaosi_Fan()) 99 bot_start.place(x=210, y=620) 100 show2 = tkinter.Variable() 101 label_show = tkinter.Label(root,textvariable=show2).place(width=480,height=42,x=5,y=665) 102 103 104 105 106 """ 107 =====================> 操作函数相关 <====================== 108 """ 109 110 # # 坐标文件显示函数 111 def File_Open_Z(): 112 file_open_name = fdg.askopenfilename() 113 open_pth_Z.set(file_open_name) 114 def File_Open_F(): 115 file_open_name = fdg.askopenfilename() 116 open_pth_F.set(file_open_name) 117 118 # # 椭球选择函数 119 def Ch_Glob_Z(): 120 s = glo_Z.get() 121 if s == ‘A‘: 122 a = 6378245 123 e2 = 0.006693421622966 124 e_2 = 0.006738525414683 125 elif s == ‘B‘: 126 a = 6378137 127 e2 = 0.00669437999013 128 e_2 = 0.00673949674227 129 elif s == ‘C‘: 130 a = 6378137 131 e2 = 0.00669438002290 132 e_2 = 0.00673949677548 133 elif s == ‘D‘: 134 a = 6378140 135 e2 = 0.006694384999588 136 e_2 = 0.006739501219473 137 return [a, e2, e_2] 138 139 def Ch_Glob_F(): 140 s = glo_F.get() 141 if s == ‘A‘: 142 a = 6378245 143 e2 = 0.006693421622966 144 e_2 = 0.006738525414683 145 elif s == ‘B‘: 146 a = 6378137 147 e2 = 0.00669437999013 148 e_2 = 0.00673949674227 149 elif s == ‘C‘: 150 a = 6378137 151 e2 = 0.00669438002290 152 e_2 = 0.00673949677548 153 elif s == ‘D‘: 154 a = 6378140 155 e2 = 0.006694384999588 156 e_2 = 0.006739501219473 157 return [a, e2, e_2] 158 159 160 # # 高斯正算主函数 161 def Gaosi_Zheng(): 162 with open(open_pth_Z.get(), ‘r‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘) as f_open: 163 STR_LI = f_open.readlines() # 最初数据读入列表 164 for i in STR_LI: 165 INT_list = list(eval(i)) 166 L1 = INT_list[0] 167 B1 = INT_list[1] 168 # 投影带选择get 169 nnn = num.get() 170 if nnn == ‘A‘: 171 n = int(L1 / 3) 172 l = math.radians(L1 - n * 3) 173 L, B = math.radians(L1), math.radians(B1) 174 TUP = Ch_Glob_Z() 175 a = TUP[0] 176 e2 = TUP[1] 177 e_2 = TUP[2] 178 elif nnn == ‘B‘: 179 n = int(L1 / 6) + 1 180 l0 = 6 * n - 3 181 l = math.radians(L1 - l0) 182 L, B = math.radians(L1), math.radians(B1) 183 TUP = Ch_Glob_Z() 184 a = TUP[0] 185 e2 = TUP[1] 186 e_2 = TUP[2] 187 t = math.tan(B) 188 q = e_2 * (math.cos(B) ** 2) 189 # 高斯正算函数主体 190 # 计算X 191 m0 = a * (1 - e2) 192 m2 = (3 / 2) * e2 * m0 193 m4 = (5 / 4) * e2 * m2 194 m6 = (7 / 6) * e2 * m4 195 m8 = (9 / 8) * e2 * m6 196 a0 = m0 + (1 / 2) * m2 + (3 / 8) * m4 + (5 / 16) * m6 + (35 / 128) * m8 197 a2 = (1 / 2) * m2 + (1 / 2) * m4 + (15 / 32) * m6 + (7 / 16) * m8 198 a4 = (1 / 8) * m4 + (3 / 16) * m6 + (7 / 32) * m8 199 a6 = (1 / 32) * m6 + (1 / 16) * m8 200 a8 = (1 / 128) * m8 201 X1 = a0 * B - (1 / 2) * a2 * (math.sin(2 * B)) + (1 / 4) * a4 * (math.sin(4 * B)) - (1 / 6) * a6 * ( 202 math.sin(6 * B)) + (1 / 8) * a8 * (math.sin(8 * B)) 203 204 N = a / (math.sqrt(1 - e2*(math.sin(B)**2))) 205 X2 = (1 / 2) * N * math.sin(B) * math.cos(B) * (l ** 2) 206 X3 = (1 / 24) * N * (math.sin(B)) * (math.cos(B) ** 3) * (5 - t ** 2 + 9 * q + 4 * (q ** 2)) * (l ** 4) 207 X4 = (1 / 720) * N * (math.sin(B)) * (math.cos(B) ** 5) * (61 - 58 * t ** 2 + t ** 4) * (l ** 6) 208 X = (X1 + X2 + X3 + X4) # X坐标通用值 209 X = round(X, 5) 210 Y1 = N * (math.cos(B)) * l 211 Y2 = (1 / 6) * N * (math.cos(B) ** 3) * (1 - t ** 2 + q) * (l ** 3) 212 Y3 = (1 / 120) * N * (math.cos(B) ** 5) * (5 - 18 * t ** 2 + t ** 4 + 14 * q - 58 * q * t ** 2) * (l ** 5) 213 Y = (Y1 + Y2 + Y3) + 500000 + (n * 1000000) # Y坐标通用值 214 Y = round(Y, 5) 215 Q = str((X, Y)) 216 with open(save_pth_Z.get(),‘a‘,encoding=‘utf-8‘) as f_save: # 将转换成功的坐标文件存入用户所选路径 217 f_save.write(Q + ‘,‘) 218 show1.set(‘坐标转化成功!‘) 219 220 # # 高斯反算主函数 221 def Gaosi_Fan(): 222 with open(open_pth_F.get(), ‘r‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘) as f: 223 ff = f.readlines() 224 a = eval(ff[0]) 225 for i in a: 226 X = i[0] # X 为 float 类型 227 st = str(i[1]) 228 n = eval(re.findall(‘^..‘, st)[0]) 229 Y = i[1] - n*1000000 - 500000 230 # 根据椭球选择相应的 a,e2,e_2 231 TUP = Ch_Glob_F() 232 a = TUP[0] 233 e2 = TUP[1] 234 e_2 = TUP[2] 235 m0 = a * (1 - e2) 236 m2 = (3 / 2) * e2 * m0 237 m4 = (5 / 4) * e2 * m2 238 m6 = (7 / 6) * e2 * m4 239 m8 = (9 / 8) * e2 * m6 240 a0 = m0 + (1 / 2) * m2 + (3 / 8) * m4 + (5 / 16) * m6 + (35 / 128) * m8 241 a2 = (1 / 2) * m2 + (1 / 2) * m4 + (15 / 32) * m6 + (7 / 16) * m8 242 a4 = (1 / 8) * m4 + (3 / 16) * m6 + (7 / 32) * m8 243 a6 = (1 / 32) * m6 + (1 / 16) * m8 244 a8 = (1 / 128) * m8 245 # 计算底点纬度 Bf 246 Bfi1 = X / a0 247 for i in range(100): 248 Bfi = Bfi1 249 FBi = -(a2 / 2) * math.sin(2 * Bfi) + (a4 / 4) * math.sin(4 * Bfi) - (a6 / 6) * math.sin(6 * Bfi) 250 Bfi1 = (X - FBi) / a0 251 if Bfi1 - Bfi < 0.00000000001: 252 Bf = Bfi1 253 # 定义其他量 Nf, Mf, qf, tf 254 Nf = a / (math.sqrt(1 - e2*(math.sin(Bf)**2))) 255 Mf = (a*(1-e2)) / math.sqrt((1-e2*(math.sin(Bf)**2))**3) 256 tf = math.tan(Bf) 257 qf = e_2 * (math.cos(Bf))**2 258 # 纬度值 B 259 B1 = tf * (Y**2) / (2*Mf*Nf) 260 B2 = tf * (5+3*(tf**2)+(qf**2)-9*(qf**2)*(tf**2)) * (Y**4) / (24*Mf*(Nf**3)) 261 B3 = tf * (61+90*(tf**2)+45*(tf**4)) * (Y**6) / (720*Mf*(Nf**5)) 262 BB = Bf - B1 + B2 - B3 263 BB = math.degrees(BB) + 0.000001 264 B = round(BB,5) 265 # 经度值 L 266 L0 = 0 267 L1 = Y / (Nf*math.cos(Bf)) 268 L2 = ((1+2*(tf**2)+qf**2)*(Y**3)) / (6*(Nf**3)*math.cos(Bf)) 269 L3 = (5+28*(tf**2)+24*(tf**4)*(Y**5)) / (120*(Nf**5)*math.cos(Bf)) 270 if n >= 12 and n <= 23: 271 L0 = math.radians(6)*n - math.radians(3) 272 if n >= 24 and n <= 45: 273 L0 = math.radians(3)*n 274 LL = L0 + L1 - L2 + L3 275 LL = math.degrees(LL) + 0.000001 276 L = round(LL,5) 277 A = (L, B) 278 END = str(A) 279 with open(save_pth_F.get(), ‘a‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘) as f_save: 280 f_save.write(END + ‘,‘) 281 show2.set(‘坐标转化成功!‘) 282 283 284 # 最终计算结果输出函数 285 def File_Save_Z(): 286 file_save_name = fdg.asksaveasfilename( 287 defaultextension = ‘.txt‘, # 默认后缀名 288 filetypes = [(‘文本文件类型‘,‘*.txt‘), # 下拉文件类型 289 (‘其他类型‘,‘*.*‘)], 290 initialdir = ‘C:\\Users\\Desktop‘, # 默认打开路径 291 initialfile = ‘text‘, # 默认文件保存名 292 title = ‘文件另存为‘ 293 ) 294 save_pth_Z.set(file_save_name) 295 296 def File_Save_F(): 297 file_save_name = fdg.asksaveasfilename( 298 defaultextension = ‘.txt‘, # 默认后缀名 299 filetypes = [(‘文本文件类型‘,‘*.txt‘), # 下拉文件类型 300 (‘其他类型‘,‘*.*‘)], 301 initialdir = ‘C:\\Users\\Desktop‘, # 默认打开路径 302 initialfile = ‘text‘, # 默认文件保存名 303 title = ‘文件另存为‘ 304 ) 305 save_pth_F.set(file_save_name) 306 307 308 309 root.mainloop()
标签:sqrt with open get open dir png inter 原理 开始
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/skygrass0531/p/12298307.html