标签:关系 eth time 三级 tar Matter prope 效果 要求
地区数据往往是存在强上下级关系的一种数据结构,在电商系统中是比较常应用到的,比如北京的下级地区只有海淀区、通州区……,而不会是太原市,而且在开发人员传递地区值的时候往往要传递很多的值,比如省、市、区、镇、省Id,市id、区id、镇id,这样影响了代码的美观性及校验强上下级关系代码的复杂性。基于这样的问题要求我们必须要实现一种可以简洁传递参数并且可以实现地区格式化的一种格式化器。这样衍生出了我们基于Spring Formatter地区自动化格式的一种格式化器。
常规做法的地区参数传递:
?province_id=1&county_id=2&city_id=3&town_id=4
在controller接收参数时:
@PostMapping
public Result someMethod(Integer provinceId,Integer countyId,Integer cityId,Integer townId){ //街道id不为空找到级联的父 if(townId!=null){ //找到区 countyId=findCounty(townId) //找到市 cityId=findCity(countyId); //找到省 provinceId=findProvince(cityId); } //如果是只保存到区的需求,也要依次寻找级联父 if(countyId!=null){ //找到市 cityId=findCity(countyId); //找到省 provinceId=findCity(cityId); } //如果是保存到市也是同样,不在赘述 }
使用注解后效果:
参数传递:
xxx?region=3
在controller接收参数时
public result someMethod(@RegionFormat Region region) {
//这里的region对象中的省市区街道已经按相应的级别对应好,直接使用即可
if(region.getProvinceProId!=null){ // 保存省id}
if(region.getCityId!=null){ // 保存市id}
if(region.getCountyId=!=null{//保存区id}
if(region.getTwonId=!=null{//保存街道id}
}
根据上述需求,如下是基于javashop电商系统中,地区参数接收注解的架构和实现:
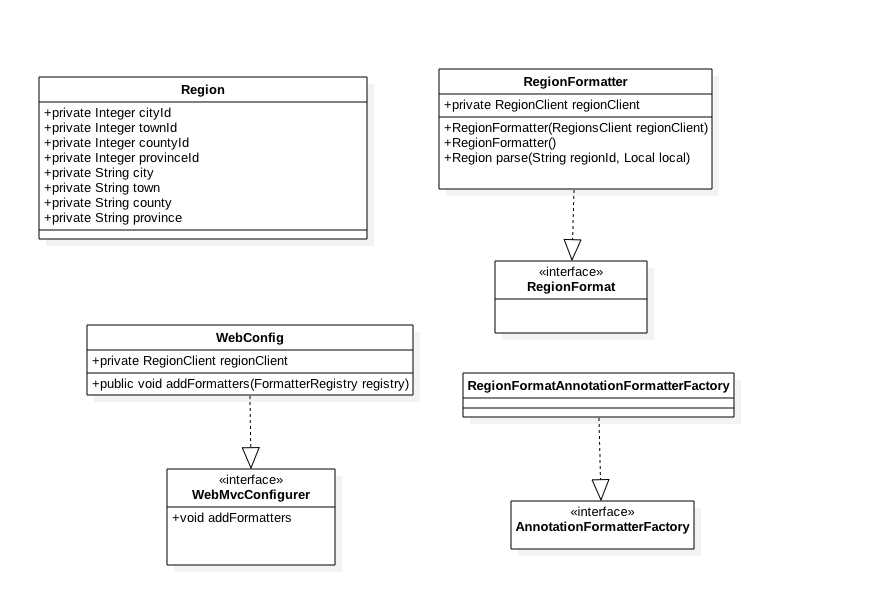
1、 RegionFormatter地区格式化器实现RegionFomat注解接口,实现地区转换器方法pase方法,传入地区id和地区语言,最后将转换后的数据输出。如下代码
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
public @interface RegionFormat {
}
public class RegionFormatter implements Formatter<Region> {
private RegionsClient regionsClient;
public RegionFormatter(RegionsClient regionsClient) {
this.regionsClient = regionsClient;
}
public RegionFormatter() {
}
/**
* 地区转换器
*
* @param regionId 地区id(只允许第三级或者第四级地区id)
* @param locale 国际化US
* @return 地区对象
* @throws ParseException
*/
@Override
public Region parse(String regionId, Locale locale) throws ParseException {
Regions regions = regionsClient.getModel(Integer.valueOf(regionId));
if (regions == null || regions.getRegionGrade() < 3) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("地区不合法,请联系管理员");
}
//根据底层地区id反推出上级id
String regionPath = regions.getRegionPath();
regionPath = regionPath.substring(1, regionPath.length());
String[] regionPathArray = regionPath.split(",");
//给地区赋值
List rList = new ArrayList();
for (String path : regionPathArray) {
Regions region = regionsClient.getModel(Integer.valueOf(path));
if (regions == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("地区不合法,请联系管理员");
}
rList.add(region);
}
return this.createRegion(rList);
}
/**
* 组织地区数据
*
* @param list 地区集合
* @return 地区
*/
private Region createRegion(List<Regions> list) {
//将地区数据组织好存入Region对象
Region region = new Region();
region.setProvinceId(list.get(0).getId());
region.setProvince(list.get(0).getLocalName());
region.setCityId(list.get(1).getId());
region.setCity(list.get(1).getLocalName());
region.setCountyId(list.get(2).getId());
region.setCounty(list.get(2).getLocalName());
//如果地区数据为四级,为第四级地区赋值
if (list.size() == 4) {
region.setTown(list.get(3).getLocalName());
region.setTownId(list.get(3).getId());
} else {
region.setTown("");
region.setTownId(0);
}
return region;
}
/**
* 将格式化的地区toString输出
*
* @param object 地区对象
* @param locale 国际化US
* @return
*/
@Override
public String print(Region object, Locale locale) {
return object.toString();
}
}
2、 RegionFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory地区格式化工厂实现AnnotationFormatterFactory自定义格式工厂接口,将要实现的自动注解RegionFomat传入。如下代码:
public class RegionFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory implements AnnotationFormatterFactory<RegionFormat> {
/**
* 获取被注解对象的类型
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public Set<Class<?>> getFieldTypes() {
return new HashSet<Class<?>>(asList(Region.class));
}
/**
* 获取输出对象
*
* @param annotation 注解实例
* @param fieldType 被注解字段的类型
* @return 地区格式化后输出的对象
*/
@Override
public Printer<?> getPrinter(RegionFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {
return new RegionFormatter();
}
/**
* 获取解析器
*
* @param annotation 注解实例
* @param fieldType 被注解字段的类型
* @return 地区格式化后对象
*/
@Override
public Parser<?> getParser(RegionFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {
return new RegionFormatter();
}
}
3、 WebConfig实现WebMvcConfigurer,注册自定义的地区格式化器。如下代码:
public class RegionFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory implements AnnotationFormatterFactory<RegionFormat> {
/**
* 获取被注解对象的类型
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public Set<Class<?>> getFieldTypes() {
return new HashSet<Class<?>>(asList(Region.class));
}
/**
* 获取输出对象
*
* @param annotation 注解实例
* @param fieldType 被注解字段的类型
* @return 地区格式化后输出的对象
*/
@Override
public Printer<?> getPrinter(RegionFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {
return new RegionFormatter();
}
/**
* 获取解析器
*
* @param annotation 注解实例
* @param fieldType 被注解字段的类型
* @return 地区格式化后对象
*/
@Override
public Parser<?> getParser(RegionFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {
return new RegionFormatter();
}
}
1、支持对象属性注解
@RegionFormat
@ApiModelProperty(name = "region", value = "地区")
private Region region;
2、值Controller入参注解
@ApiOperation(value = "平台添加店铺", response = ShopVO.class)
@PostMapping()
public ShopVO save(@Valid ShopVO shop,
@RegionFormat @RequestParam("license_region") Region licenseRegion,
@RegionFormat @RequestParam("bank_region") Region bankRegion,
@RegionFormat @RequestParam("shop_region") Region shopRegion) {
}
使用上述地区格式化器方法,假设如下请求
xxx?region=3
则会将id为1的地区及父的信息读取并且形成Region对象。
例如region=3的地区为长安街,父级为东城区->北京,形成的Region对象如下。
{
"cityId": 2,
"townId": 0,
"countyId": 3,
"provinceId": 1,
"province": "长安街",
"county": "东城区",
"city": "北京市",
"town": ""
}
如果传递的是townId,则会自动填充county、city及province。
如果传递的是countyId,则会自动填充city、province,此时townId为0。
同时支持对象属性级别注解:
对象:
public Person{
//所属区域
@RegionFormat
private Region region;
//geter and seter
}
controller:
@PostMapping()
public Result save(Person person) {
//这里的地区已经按上述规则赋值
person.getRegion()
}
标签:关系 eth time 三级 tar Matter prope 效果 要求
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/javashop-docs/p/12299556.html